Solar eclipse of September 13, 2080
| Solar eclipse of September 13, 2080 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.0723 |
| Magnitude | 0.8743 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°06′N 25°48′E / 61.1°N 25.8°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 16:38:09 |
| References | |
| Saros | 126 (51 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9688 |
A partial solar eclipse will occur on September 13, 2080.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2080-2083
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| 121 | March 21, 2080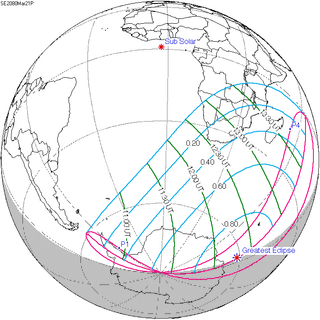 Partial |
126 | September 13, 2080 Partial |
| 131 | March 10, 2081 Annular |
136 | September 3, 2081 Total |
| 141 | February 27, 2082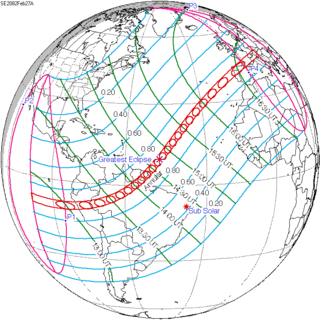 Annular |
146 | August 24, 2082 Total |
| 151 | February 16, 2083 Partial |
156 | August 13, 2083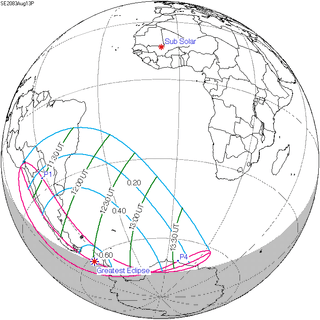 Partial |
Saros 126
It is a part of Saros cycle 126, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 10, 1179. It contains annular eclipses from June 4, 1323 through April 4, 1810 and hybrid eclipses from April 14, 1828 through May 6, 1864. It contains total eclipses from May 17, 1882 through August 23, 2044. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on May 3, 2459. The longest duration of central eclipse (annular or total) was 5 minutes, 46 seconds of annularity on November 22, 1593. The longest duration of totality was 2 minutes, 36 seconds on July 10, 1972.[1]
| Series members 39–49 occur between 1901 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
 June 8, 1918 |
 June 19, 1936 |
 June 30, 1954 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 July 10, 1972 |
 July 22, 1990 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 45 | 46 | 47 |
 August 12, 2026 |
 August 23, 2044 |
 September 3, 2062 |
| 48 | 49 | |
 September 13, 2080 |
 September 25, 2098 | |
References
- ↑ Solar_Saros_series_126, accessed October 2010
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of September 13, 2080. |
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
