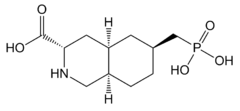
LY-235,959
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number |
137433-06-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 131938 |
| ChemSpider | 116555 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H20NO5P |
| Molar mass | 277.11 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
LY-235,959 is a competitive antagonist at the NMDA receptor.[1] It has analgesic and neuroprotective effects and causes hypothermia in animal models,[2] as well as reducing the development of tolerance to morphine and altering the reinforcing effects of cocaine.[3][4][5][6][7]
References
- ↑ Allen, R. M.; Dykstra, L. A. (2001). "N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists potentiate the antinociceptive effects of morphine in squirrel monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 298 (1): 288–297. PMID 11408554.
- ↑ Rawls, S. M.; Cowan, A.; Tallarida, R. J.; Geller, E. B.; Adler, M. W. (2002). "N-Methyl-D-aspartate Antagonists and WIN 55212-2 \4,5-Dihydro-2-methyl-4(4-morpholinylmethyl)-1-(1-naphthalenyl-carbonyl)-6H-pyrrolo\3,2,1-i,j]quinolin-6-one], a Cannabinoid Agonist, Interact to Produce Synergistic Hypothermia". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 303 (1): 395–402. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.037473. PMID 12235276.
- ↑ Allen, R. M.; Carelli, R. M.; Dykstra, L. A.; Suchey, T. L.; Everett, C. V. (2005). "Effects of the Competitive N-Methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Antagonist, LY235959 \(-)-6-Phosphonomethyl-deca-hydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic Acid], on Responding for Cocaine under Both Fixed and Progressive Ratio Schedules of Reinforcement". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 315 (1): 449–457. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.086355. PMID 16024734.
- ↑ Allen, R. M.; Dykstra, L. A.; Carelli, R. M. (2007). "Continuous exposure to the competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, LY235959, facilitates escalation of cocaine consumption in Sprague–Dawley rats". Psychopharmacology. 191 (2): 341–351. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0661-3. PMID 17225167.
- ↑ Fischer, B. D.; Ward, S. J.; Henry, F. E.; Dykstra, L. A. (2010). "Attenuation of morphine antinociceptive tolerance by a CB1 receptor agonist and an NMDA receptor antagonist: Interactive effects". Neuropharmacology. 58 (2): 544–550. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.08.005. PMC 2813317
 . PMID 19699755.
. PMID 19699755. - ↑ Dykstra, L. A.; Fischer, B. D.; Balter, R. E.; Henry, F. E.; Schmidt, K. T.; Miller, L. L. (2011). "Opioid antinociception, tolerance and dependence". Behavioural Pharmacology. 22 (5 and 6): 540–547. doi:10.1097/FBP.0b013e328348ed08. PMC 3155647
 . PMID 21712708.
. PMID 21712708. - ↑ Bicca, M. A.; Figueiredo, C. P.; Piermartiri, T. C.; Meotti, F. C.; Bouzon, Z. L.; Tasca, C. I.; Medeiros, R.; Calixto, J. B. (2011). "The selective and competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, (−)-6-phosphonomethyl-deca-hydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, prevents synaptic toxicity induced by amyloid-β in mice". Neuroscience. 192: 631–641. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.038. PMID 21756976.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.