Epostane
Epostane
 |
| Names |
| Other names
Win-32729 |
| Identifiers |
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image |
| PubChem |
6917713 |
InChI=1S/C22H31NO3/c1-18-8-6-16-14(15(18)7-9-20(18,3)25)5-10-22-19(16,2)11-13(12-23)17(24)21(22,4)26-22/h14-16,24-25H,5-11H2,1-4H3/t14-,15-,16-,18-,19+,20-,21+,22-/m0/s1 Key: CETKWEWBSMKADK-GSXVSZIWSA-N
|
C[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1CC[C@]2(C)O)CC[C@]45[C@@]3(CC(=C([C@]4(O5)C)O)C#N)C
|
| Properties |
| |
C22H31NO3 |
| Molar mass |
357.49 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
|
| Infobox references |
|
|
Epostane (INN, USAN, BAN) (developmental code name WIN-32729) is an inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) that was developed as an contraceptive, abortifacient, and oxytocic drug but was never marketed.[1][2] By inhibiting 3β-HSD, epostane blocks the biosynthesis of progesterone from pregnenolone (and also the conversion of dehydroepiandrosterone to androstenedione), thereby functioning as an antiprogestogen and terminating pregnancy.[1] The drug was trialed and in a study was found to be slightly more effective at inducing abortion relative to mifepristone.[3]
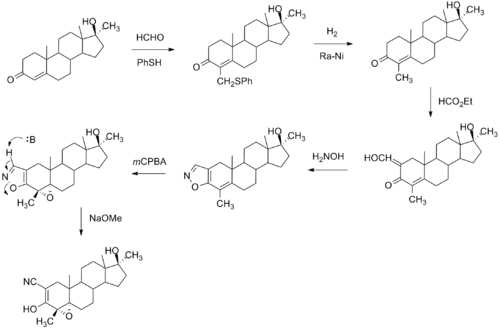
Synthesis
References
|
|---|
|
Progestogens
(and progestins) | |
|---|
|
| SPRMs | |
|---|
|
| Antiprogestogens | |
|---|
|
See also: Androgens and antiandrogens • Estrogens and antiestrogens • Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids • Mineralocorticoids and antimineralocorticoids • Gonadotropins and GnRH |
|
|---|
|
| HMGCR | |
|---|
|
| FPS | |
|---|
|
| 24-DHCR24 | |
|---|
|
20,22-Desmolase
(P450scc) | |
|---|
|
17α-Hydroxylase,
17,20-Lyase | |
|---|
|
| 3α-HSD | |
|---|
|
| 3β-HSD | |
|---|
|
| 11β-HSD | |
|---|
|
| 21-Hydroxylase | |
|---|
|
| 11β-Hydroxylase | |
|---|
|
| 18-Hydroxylase | |
|---|
|
| 17β-HSD | |
|---|
|
| 5α-Reductase | |
|---|
|
| Aromatase |
- Inhibitors: 4-AT
- 4-Cyclohexylaniline
- 4-Hydroxytestosterone
- 5α-DHNET
- 20α-Dihydroprogesterone
- Abyssinone II
- Aminoglutethimide
- Anastrozole
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Atamestane
- ATD
- Bifonazole
- CGP-45,688
- CGS-47,645
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin)
- Clotrimazole
- Corynesidone A
- Coumestrol
- DHT
- Difeconazole
- Econazole
- Ellagitannins
- Endosulfan
- Exemestane
- Fadrozole
- Fatty acids (e.g., conjugated linoleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, palmitic acid)
- Fenarimol
- Finrozole
- Flavonoids (e.g., 7-hydroxyflavone, 7-hydroxyflavanone, 7,8-DHF, acacetin, apigenin, baicalein, biochanin A, chrysin, EGCG, gossypetin, hesperetin, liquiritigenin, myricetin, naringenin, pinocembrin, rotenone, quercetin, sakuranetin, tectochrysin)
- Formestane
- Imazalil
- Isoconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Letrozole
- Liarozole
- Melatonin
- MEN-11066
- Miconazole
- Minamestane
- Nimorazole
- NKS01
- Norendoxifen
- ORG-33,201
- Penconazole
- Phenytoin
- Prochloraz
- PGE2 (dinoprostone)
- Plomestane
- Prochloraz
- Propioconazole
- Pyridoglutethimide
- Quinolinoids (e.g., berberine, casimiroin, triptoquinone A, XHN22, XHN26, XHN27)
- Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalenone)
- Rogletimide
- Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol)
- Talarozole
- Terpenoids (e.g., dehydroabietic acid, (–)-dehydrololiolide, retinol (vitamin A), Δ9-THC, tretinoin)
- Testolactone
- Tioconazole
- Triadimefon
- Triadimenol
- Troglitazone
- Valproic acid
- Vorozole
- Xanthones (e.g., garcinone D, garcinone E, α-mangostin, γ-mangostin, monodictyochrome A, monodictyochrome B)
- YM-511
- Zinc
|
|---|
|
| SST/EST | |
|---|
|
| STS |
- AHBS
- Danazol
- Estrone-3-O-sulfamate (EMATE)
- Irosustat (STX64, 667 Coumate, BN-83495)
- KW-2581
- Progestogens
- SR-16157
- STX213
- STX681
- STX1938
|
|---|
|
| 27-Hydroxylase | |
|---|
|
| Others |
- Inhibitors: Inhibit estradiol degradation: Cimetidine
|
|---|
|
See also: Androgenics • Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics |