Daniel Sickles
| Daniel Edgar Sickles | |
|---|---|
|
Major General Sickles circa 1862 | |
| Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from New York's 10th district | |
|
In office March 4, 1893 – March 3, 1895 | |
| Preceded by | William Bourke Cockran |
| Succeeded by | Amos J. Cummings |
| Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from New York's 3rd district | |
|
In office March 4, 1857 – March 3, 1861 | |
| Preceded by | Guy R. Pelton |
| Succeeded by | Benjamin Wood |
| United States Minister to Spain | |
|
In office May 15, 1869 – January 31, 1874 | |
| Preceded by | John P. Hale |
| Succeeded by | Caleb Cushing |
| Member of the New York Senate from the district | |
|
In office January 1, 1856 – March 3, 1857 | |
| Preceded by | Thomas J. Barr |
| Succeeded by | Francis B. Spinola |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
October 20, 1819 New York City, New York |
| Died |
May 3, 1914 (aged 94) New York City, New York |
| Resting place | Arlington National Cemetery |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse(s) |
Teresa Bagioli Sickles (m. 1852–67) Carmina Creagh (m. 1871–1914)\ |
| Awards | Medal of Honor |
| Military service | |
| Nickname(s) | "Devil Dan"[1] |
| Allegiance |
United States of America Union |
| Service/branch |
United States Army Union Army |
| Years of service | 1861–1869 |
| Rank |
|
| Commands |
Excelsior Brigade III Corps |
| Battles/wars | |
Daniel Edgar Sickles (October 20, 1819 – May 3, 1914) was an American politician, soldier, and diplomat.
Born to a wealthy family in New York City, Sickles was involved in a number of public scandals, most notably the killing of his wife's lover, Philip Barton Key II, son of Francis Scott Key.[2] He was acquitted after using temporary insanity as a legal defense for the first time in United States history. This became a defense associated with 'crimes of passion' (crime passionnel in French).
Upon the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, Sickles became one of the war's most prominent political generals, recruiting the New York regiments that became known as the Excelsior Brigade in the Army of the Potomac. Despite his lack of military experience, he served as a brigade, division, and corps commander in some of the early Eastern campaigns. His military career ended at the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863, after he moved his III Corps (without orders) to an untenable position where it was virtually destroyed. He was wounded by cannon fire and had to have his leg amputated. He was eventually awarded the Medal of Honor for his actions.[3]
Sickles devoted considerable effort to trying to gain credit for helping achieve the Union victory at Gettysburg, writing articles and testifying before Congress in a manner that denigrated the intentions and actions of his superior officer, the army commander, Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. After the war, Sickles was appointed as a commander for military districts in the South during Reconstruction. He also served as U.S. Minister to Spain. Later he was re-elected to Congress, where he helped pass legislation to preserve the Gettysburg Battlefield.
Early life and politics
In 1819, Sickles was born in New York City to Susan Marsh Sickles and George Garrett Sickles, a patent lawyer and politician.[4] (His year of birth is sometimes given as 1825, and Sickles was known to have claimed as such. Historians speculate that Sickles chose to appear younger when he married a woman half his age.) He learned the printer's trade and studied at the University of the City of New York (now New York University).[5] He studied law in the office of Benjamin Butler, was admitted to the bar in 1846, and was elected as a member of the New York State Assembly (New York Co.) in 1847.[4]
On September 27, 1852, Sickles married Teresa Bagioli against the wishes of both families—he was 33, she about 15 or 16.[6] She was reported as sophisticated for her age, speaking five languages.
In 1853 Sickles became corporation counsel of New York City, but resigned soon afterward when appointed as secretary of the U.S. legation in London, under James Buchanan,[5] by appointment of President Franklin Pierce. He returned to the United States in 1855, when he was elected as a member of the New York State Senate (3rd D.) in 1856. He was re-elected to the 1857. In 1856 he was elected as a Democrat to the 35th, and held office from March 4, 1857, to March 3, 1861, a total of two terms.
Murder of Key

Sickles was censured by the New York State Assembly for escorting a known prostitute, Fanny White, into its chambers. He also reportedly took her to England, while leaving his pregnant wife at home. He presented White to Queen Victoria, using as her alias the surname of a New York political opponent.[4]
In 1859, in Lafayette Square, across the street from the White House, Sickles shot and killed Philip Barton Key II, the district attorney of the District of Columbia;[7] he was the son of Francis Scott Key. Sickles had discovered that Philip Key was having an affair with his young wife.[2][8]
Trial
"You are here to fix the price of the marriage bed!", roared Associate Defense Attorney John Graham, in a speech so packed with quotations from Othello, Judaic history and Roman law that it lasted two days and later appeared as a book.
Time magazine article, "Yankee King of Spain", June 18, 1945[9]
Sickles surrendered at Attorney General Jeremiah Black's house, a few blocks away on Franklin Square, and confessed to the murder. After a visit to his home, accompanied by a constable, Sickles was taken to jail. He was able to receive visitors, and so many came that he was granted the use of the head jailer's apartment to receive them.[10] He received numerous perquisites, including being allowed to retain his personal weapon, and receive numerous visitors. They included many congressmen, senators, and other leading members of Washington society. President James Buchanan sent Sickles a personal note.

Harper's Magazine reported that the visits of his wife's mother and her clergyman were painful for Sickles. Both told him that Teresa was distracted with grief, shame, and sorrow, and that the loss of her wedding ring (which Sickles had taken on visiting his home) was more than Teresa could bear.
Sickles was charged with murder. He secured several leading politicians as defense attorneys, among them Edwin M. Stanton, later to become Secretary of War, and Chief Counsel James T. Brady, like Sickles associated with Tammany Hall. Sickles pleaded temporary insanity—the first use of this defense in the United States.[11] Before the jury, Stanton argued that Sickles had been driven insane by his wife's infidelity, and thus was out of his mind when he shot Key. The papers soon trumpeted that Sickles was a hero for "saving all the ladies of Washington from this rogue named Key".[12]
Sickles had obtained a graphic confession from Teresa; it was ruled inadmissible in court, but, was leaked by him to the press and printed in the newspapers in full. The defense strategy ensured that the trial was the main topic of conversations in Washington for weeks, and the extensive coverage of national papers was sympathetic to Sickles.[13] In the courtroom, the strategy brought drama, controversy, and, ultimately, an acquittal for Sickles.
Sickles publicly forgave Teresa, and "withdrew" briefly from public life, although he did not resign from Congress. The public was apparently more outraged by Sickles's forgiveness and reconciliation with his wife, than by the murder and his unorthodox acquittal.[14]
Civil War
In the 1850s, Sickles had received a commission in the 12th Regiment of the New York National Guard, and had attained the rank of major.[15] (He insisted on wearing his militia uniform for ceremonial occasions while serving in London, and caused a minor diplomatic scandal by snubbing Queen Victoria at an Independence Day celebration.[16]) At the outbreak of the Civil War, Sickles worked to repair his public image by raising volunteer units in New York for the Union Army. Because of his previous military experience and political connections, he was appointed colonel of one of the four regiments he organized. He was promoted to brigadier general of volunteers in September 1861, where he was notorious before beginning any fighting.
In March 1862, he was forced to relinquish his command when the U.S. Congress refused to confirm his commission. He lobbied his Washington political contacts and reclaimed both his rank and his command on May 24, 1862, in time to rejoin the Army in the Peninsula Campaign.[4] Because of this interruption, Sickles missed his brigade's significant actions at the Battle of Williamsburg. Despite his lack of previous combat experience, he did a competent job commanding the "Excelsior Brigade" of the Army of the Potomac in the Battle of Seven Pines and the Seven Days Battles. He was absent for the Second Battle of Bull Run,[8] having used his political influences to obtain leave to go to New York City to recruit new troops. He also missed the Battle of Antietam because the III Corps, to which he was assigned as a division commander, was stationed on the lower Potomac, protecting the capital.
Sickles was a close ally of Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker, his original division commander, who eventually commanded the Army of the Potomac. Both men had notorious reputations as political climbers and as hard-drinking ladies' men. Accounts at the time compared their army headquarters to a rowdy bar and bordello.
Sickles' division was in reserve at the Battle of Fredericksburg. On January 16, 1863, President Abraham Lincoln nominated Sickles for promotion to the grade of major general to rank from November 29, 1862.[17] Although the U.S. Senate did not confirm the promotion until March 9, 1863, and the President did not formally appoint Sickles until March 11, 1863,[17] Hooker, now commanding the Army of the Potomac, gave Sickles command of the III Corps in February 1863.
This decision was controversial as Sickles became the only corps commander without a West Point military education. His energy and ability were conspicuous in the Battle of Chancellorsville. He aggressively recommended pursuing troops he saw in his sector on May 2, 1863. Sickles thought the Confederates were retreating, but these turned out to be elements of Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's corps, stealthily marching around the Union flank. He also vigorously opposed Hooker's orders moving him off good defensive terrain in Hazel Grove. In both of these cases, it is easy to imagine the disastrous battle turning out very differently for the Union if Hooker had heeded his advice.
Gettysburg
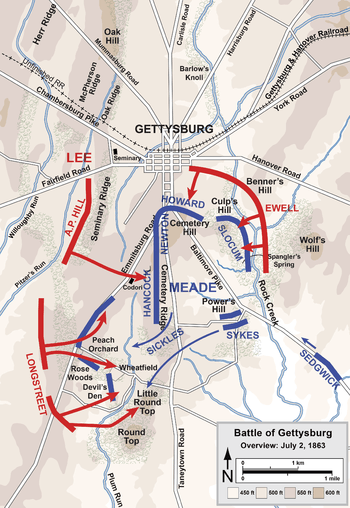
The Battle of Gettysburg was the occasion of the most famous incident, and the effective end, of Sickles' military career. On July 2, 1863, Army of the Potomac commander Maj. Gen. George G. Meade ordered Sickles' corps to take up defensive positions on the southern end of Cemetery Ridge, anchored in the north to the II Corps and to the south, the hill known as Little Round Top. Sickles was unhappy to see the "Peach Orchard," a slightly higher terrain feature, to his front. He violated orders by marching his corps almost a mile in front of Cemetery Ridge. This had two effects: it greatly diluted the concentrated defensive posture of his corps by stretching it too thin, and it created a salient that could be bombarded and attacked from multiple sides. About this time (3 p.m.), Meade called a meeting of his corps commanders.[18] Sickles did not appear.[18] An aide to Brig. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren soon reported the situation.[18] Meade and Warren rode to Sickles' position, where Meade demanded an explanation from the general.[18] Meade refused Sickles' offer to withdraw because he realized it was too late[19] and the Confederates would soon attack, putting a retreating force in even greater peril.[18]
The Confederates attacked at about the time the meeting finished and Meade returned to his headquarters.[18] The Confederate assault by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet's corps, primarily by the division of Maj. Gen. Lafayette McLaws, smashed the III Corps and rendered it useless for further combat. Gettysburg campaign historian Edwin B. Coddington assigns "much of the blame for the near disaster" in the center of the Union line to Sickles.[20] Stephen W. Sears wrote that "Dan Sickles, in not obeying Meade's explicit orders, risked both his Third Corps and the army's defensive plan on July 2.[21] However, Sickles' maneuver has recently been credited by John Keegan with blunting the whole Confederate offensive that was intended to cause the collapse of the Union line.[22] Similarly, James M. McPherson wrote that "Sickles's unwise move may have unwittingly foiled Lee's hopes."[19]
During the height of the Confederate attack, Sickles was wounded by a cannonball that mangled his right leg. He was carried by a detail of soldiers to the shade of the Trostle farmhouse, where a saddle strap was applied as a tourniquet. He ordered his aide, Major Harry Tremain, "Tell General Birney he must take command." As Sickles was carried by stretcher to the III Corps hospital on the Taneytown Road, he attempted to raise his soldiers' spirits by grinning and puffing on a cigar along the way.[23] His leg was amputated that afternoon. He insisted on being transported to Washington, D.C., which he reached on July 4, 1863. He brought some of the first news of the great Union victory, and started a public relations campaign to defend his behavior in the conflict. On the afternoon of July 5, President Lincoln and his son, Tad, visited General Sickles, as he was recovering in Washington.

Sickles had recent knowledge of a new directive from the Army Surgeon General to collect and forward "specimens of morbid anatomy ... together with projectiles and foreign bodies removed" to the newly founded Army Medical Museum in Washington, D.C. He preserved the bones from his leg and donated them to the museum in a small coffin-shaped box, along with a visiting card marked, "With the compliments of Major General D.E.S." For several years thereafter, he reportedly visited the limb on the anniversary of the amputation. The museum, now known as the National Museum of Health and Medicine, still displays this artifact. (Other Civil War-era specimens of note on display include the hip of General Henry Barnum.)
Sickles ran a vicious campaign against General Meade's character after the Civil War. Sickles felt that Meade had wronged him at Gettysburg and that credit for winning the battle belonged to him. In anonymous newspaper articles and in testimony before a congressional committee, Sickles maintained that Meade had secretly planned to retreat from Gettysburg on the first day. While his movement away from Cemetery Ridge may have violated orders, Sickles always asserted that it was the correct move because it disrupted the Confederate attack, redirecting its thrust, and effectively shielding the Union's real objectives, Cemetery Ridge and Cemetery Hill. Sickles's redeployment took Confederate commanders by surprise, and historians have argued about its ramifications ever since.
Sickles eventually received the Congressional Medal of Honor for his actions, although it took him 34 years to get it. The official citation accompanying his medal recorded that Sickles "displayed most conspicuous gallantry on the field, vigorously contesting the advance of the enemy and continuing to encourage his troops after being himself severely wounded."[24]
Postbellum career
Despite his one-legged disability, Sickles remained in the army until the end of the war and was disgusted that Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant would not allow him to return to a combat command. In 1867, he received appointments as brevet brigadier general and major general in the regular army for his services at Fredericksburg and Gettysburg, respectively.[5]
Soon after the close of the Civil War, in 1865, he was sent on a confidential mission to Colombia (the "special mission to the South American Republics") to secure its compliance with a treaty agreement of 1846 permitting the United States to convey troops across the Isthmus of Panama.[5] From 1865 to 1867, he commanded the Department of South Carolina, the Department of the Carolinas, the Department of the South, and the Second Military District. In 1866, he was appointed colonel of the 42nd U.S. Infantry (Veteran Reserve Corps), and in 1869 he was retired with the rank of major general.[5]
Sickles served as U.S. Minister to Spain from 1869 to 1874, after the Senate failed to confirm Henry Shelton Sanford to the post, and took part in the negotiations growing out of the Virginius Affair. His inaccurate and emotional messages to Washington promoted war, until he was overruled by Secretary of State Hamilton Fish and the war scare died out.[25]
Sickles maintained his reputation as a ladies' man in the Spanish royal court and was rumored to have had an affair with the deposed Queen Isabella II. Following the death of Teresa in 1867, in 1871 he married Carmina Creagh, the daughter of Chevalier de Creagh of Madrid, a Spanish Councillor of State. They had two children.
Sickles was appointed as president of the New York State Board of Civil Service Commissioners from 1888 to 1889, Sheriff of New York County in 1890. He was elected again as a representative in the 53rd Congress, serving from 1893 to 1895. For most of his postwar life, he was the chairman of the New York Monuments Commission, but he was forced out when $27,000 was found to have been embezzled.[26]
He had an important part in efforts to preserve the Gettysburg Battlefield, sponsoring legislation to form the Gettysburg National Military Park, buy up private lands, and erect monuments. He procured the original fencing used on East Cemetery Hill to mark the park's borders. This fencing came directly from Lafayette Square in Washington, D.C.[27][28]
Of the principal senior generals who fought at Gettysburg, virtually all, with the conspicuous exception of Sickles, have been memorialized with statues. When asked why there was no memorial to him, Sickles supposedly said, "The entire battlefield is a memorial to Dan Sickles." The monument to the New York Excelsior Brigade was originally commissioned to include a bust of Sickles, but it includes a figure of an eagle instead.
Death
Sickles lived out the remainder of his life in New York City, dying on May 3, 1914 at the age of 94. His funeral was held at St. Patrick's Cathedral in Manhattan on May 8, 1914. He was buried in Arlington National Cemetery.[24][29]
In popular media
- American Scoundrel: The Life of the Notorious Civil War General Dan Sickles is a 2002 biography by the novelist Thomas Keneally.
- Sickles is featured in the alternate history novels, Gettysburg: A Novel of the Civil War (2003) and Grant Comes East (2004), the first two books of the Civil War trilogy by Newt Gingrich and William R. Forstchen.
- In Stephen L. Carter's 2012 alternate history novel, The Impeachment of Abraham Lincoln, Sickles is featured as one of the defense counsel in Lincoln's trial before the United States Senate.
Medal of Honor citation

- Rank and organization: Major General, U.S. Volunteers
- Place and Date: At Gettysburg, Pa., July 2, 1863.
- Entered Service At: New York, N.Y.
- Birth: New York, N.Y.
- Date of Issue: October 30, 1897.
Citation:
- Displayed most conspicuous gallantry on the field vigorously contesting the advance of the enemy and continuing to encourage his troops after being himself severely wounded.[30][31]
Images
 General Sickles (center) with his staff, after the loss of his leg at Gettysburg
General Sickles (center) with his staff, after the loss of his leg at Gettysburg 1888, Generals Carr, Sickles, and Graham stand by the Trostle Barn where Sickles was wounded
1888, Generals Carr, Sickles, and Graham stand by the Trostle Barn where Sickles was wounded Sickles in 1902
Sickles in 1902 Sickles funeral in Manhattan on May 8, 1914
Sickles funeral in Manhattan on May 8, 1914 Sickles funeral in Manhattan on May 8, 1914
Sickles funeral in Manhattan on May 8, 1914
See also
- List of American Civil War generals
- List of American Civil War Medal of Honor recipients: Q–S
- List of U.S. political appointments that crossed party lines
Notes
- ↑ Devil Dan Sickles' Deadly Salients - America's Civil War magazine, November 1998
- 1 2 "Assassination of Philip Barton Key, by Daniel E. Sickles of New York". Hartford Daily Courant. March 1, 1859. Retrieved November 30, 2010.
For more than a year there have been floating rumors of improper intimacy between Mr. Key and Mrs. Sickles. They have from time to time attended parties, the opera, and rode out together. Mr. Sickles has heard of these reports, but would never credit them until Thursday evening last. On that evening, just as a party was about breaking up at his house, Mr Sickles received among his papers...
- ↑ "Daniel Sickles". Congressional Medal of Honor Society. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Beckman, p. 1784.
- 1 2 3 4 5
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sickles, Daniel Edgar". Encyclopædia Britannica. 25 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 36.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sickles, Daniel Edgar". Encyclopædia Britannica. 25 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 36. - ↑ Keneally, p. 21, states 15. W.A. Swanberg, Sickles the Incredible, pp. 77-80 states 16. Relying in part on Swanberg, 77-80 and in part on other sources, Hessler, pp. 4-6 says 16. Teresa's exact birth date in 1836 is unknown.
- ↑ Keneally, p. 66.
- 1 2 Tagg, p. 62.
- ↑ "Yankee King of Spain". Time Magazine June 18, 1945. June 18, 1945. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- ↑ Sickles, Assumption College
- ↑ Stankowski, J. E. (2009). "Temporary Insanity". Wiley Encyclopedia of Forensic Science. Wiley Encyclopedia of Forensic Science. doi:10.1002/9780470061589.fsa272. ISBN 9780470018262.
- ↑ Editorial: "No sympathy needed", Harpers Magazine, 12 March 1859
- ↑ Assumption.edu: "Both Harper's Weekly and Leslie's ran images of Sickles in prison. Harper's was the more bathetic. It showed a haggard sufferer, hands clasped as if in prayer, staring upwards. Light illumines his face and the wall immediately behind, but the rest of the cell is in shadows. Its title was 'Hon. Daniel E. Sickles in prison at Washington,' but it might well have been captioned 'More Sinned Against Than Sinning.' In a later issue, the magazine editorialized against what it described as a publicity campaign to create sympathy for the Congressman. ... The New York Times, the city's other major Democratic daily and the New York Herald's chief rival for the ear of the Buchanan administration, editorialized that the homicide in no way unfitted the Congressman for office." The source gives many more such cites.
- ↑ Harper's editorial on the verdict, May 7, 1859, in which they reject the insanity defense as essentially a sham and note that the prosecution did not try very hard.
- ↑ Sickles, Daniel E.; et al. (1908). The Union Army: States and Regiments, Volume II. Federal Publishing Company. p. 17.
- ↑ Weintraub, Stanley (2011). Victorian Yankees at Queen Victoria's Court: American Encounters with Victoria and Albert. pp. 81–83.
- 1 2 Eicher, p. 705.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Eicher, David J. The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. ISBN 0-684-84944-5. p. 534.
- 1 2 McPherson, p. 657.
- ↑ Coddington, p. 411.
- ↑ Sears, p. 507.
- ↑ Keegan, p. 195.
- ↑ Keneally, pp. 287-88.
- 1 2 Eicher, p. 488.
- ↑ Richard H. Bradford, The Virginius Affair(1980)
- ↑ "Seeks To Wipe Out Sickles Commission. Fine Arts Federation Would Have a State Art Board Named to Take Its Place". New York Times. December 12, 1912. Retrieved November 30, 2010.
- ↑ James Hessler. "Dan Sickles/The Battlefield Preservationist". civilwar.org. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ↑ "Daniel Edgar Sickles, Major General United States Army/From a contemporary news report". arlingtoncemetery.net. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ↑ "Crowds Bare Heads At Sickles Funeral. Military Cortege Marches Up Fifth Avenue to Services in St. Patrick's Cathedral.". New York Times. May 9, 1914. Retrieved November 30, 2010.
Between lines of watchers who bared their heads as the flag-covered coffin passed, a military funeral procession marched up Fifth Avenue from Ninth Street to St. Patrick's Cathedral yesterday morning. On a gun caisson amid a guard of honor, composed of his old comrades in the civil war, was the body of Major Gen. Daniel E. Sickles, commander of the Third Army Corps and one of the last of the heroes of Gettysburg.
- ↑ ""Civil War Medal of Honor citations" (S-Z): Sickles, Daniel E.". AmericanCivilWar.com. Retrieved November 9, 2007.
- ↑ ""Medal of Honor website" (M-Z): Sickles, Daniel E.". United States Army Center of Military History. Retrieved November 9, 2007.
References
- Beckman, W. Robert. "Daniel Edgar Sickles." In Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History, edited by David S. Heidler and Jeanne T. Heidler. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2000. ISBN 0-393-04758-X.
- Coddington, Edwin B. The Gettysburg Campaign; a study in command. New York: Scribner's, 1968. ISBN 0-684-84569-5.
- Eicher, David J. The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. ISBN 0-684-84944-5.
- Eicher, John H., and David J. Eicher. Civil War High Commands. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2001. ISBN 0-8047-3641-3.
- Hessler, James A. Sickles at Gettysburg: The Controversial Civil War General Who Committed Murder, Abandoned Little Round Top, and Declared Himself the Hero of Gettysburg. New York: Savas Beatie LLC, 2009. ISBN 978-1-932714-84-5.
- Keegan, John. The American Civil War: A Military History. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2009. ISBN 978-0-307-26343-8.
- Keneally, Thomas. American Scoundrel: The Life of the Notorious Civil War General Dan Sickles. New York: Nan A. Talese/Doubleday, 2002. ISBN 0-385-50139-0.
- McPherson, James M. Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (Oxford History of the United States). New York: Oxford University Press, 1988. ISBN 0-19-503863-0.
- Roberts, Sam (March 1, 1992). "Sex, Politics and Murder on the Potomac". New York Times. Retrieved August 8, 2008. Review of The Congressman Who Got Away With Murder, By Nat Brandt.
- Sears, Stephen W. Gettysburg. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2003. ISBN 0-395-86761-4.
- Swanberg, W. A. Sickles the Incredible. New York: Scribner's, 1956. OCLC 31029447.
- Tagg, Larry. The Generals of Gettysburg, Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing, 1998. ISBN 1-882810-30-9.
- Warner, Ezra J. Generals in Blue: Lives of the Union Commanders. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1964. ISBN 0-8071-0822-7.
Further reading
- Barram, Rick, "The 72nd New York Infantry in the Civil War, A History and Roster",McFarland and Company, 2014, ISBN 978-0-7864-7644-2
- Bradford, Richard H. The Virginius Affair. Boulder: Colorado Associated University Press, 1980. ISBN 0-87081-080-4.
- Brandt, Nat. The Congressman Who Got Away With Murder. Syracuse, NY: University of Syracuse Press, 1991. ISBN 0-8156-0251-0.
- Hessler, James A. Sickles at Gettysburg: The Controversial Civil War General Who Committed Murder, Abandoned Little Round Top, and Declared Himself the Hero of Gettysburg. New York: Savas Beatie, 2009. ISBN 978-1-932714-64-7.
External links
United States Congress. "SICKLES, Daniel Edgar (id: S000402)". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Retrieved on September 30, 2008
- "Sickles articles at Arlington National Cemetery site". Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- "Mr. Lincoln and New York: Daniel Sickles". Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- "Sickles's amputated leg bones". Retrieved September 29, 2010. preserved at the National Museum of Health and Medicine
- "Daniel Sickles". Claim to Fame: Medal of Honor recipients. Find a Grave. Retrieved February 22, 2010.
- "Daniel Sickles". Claim to Fame: Medal of Honor recipients. Find a Grave. Retrieved July 26, 2010.
- "Photograph of Daniel Edgar Sickles from the Maine Memory Network". Retrieved September 29, 2010.
| New York State Senate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Thomas J. Barr |
New York State Senate 3rd District 1856–1857 |
Succeeded by Francis B. Spinola |
| United States House of Representatives | ||
| Preceded by Guy R. Pelton |
Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from New York's 3rd congressional district 1857–1861 |
Succeeded by Benjamin Wood |
| Preceded by William B. Cockran |
Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from New York's 10th congressional district 1893–1895 |
Succeeded by Andrew J. Campbell (died before taking office) Amos J. Cummings (elected to replace Campbell) |
| Military offices | ||
| Preceded by George Stoneman |
Commander of the III Corps (Army of the Potomac) February 5, 1863 – May 29, 1863 |
Succeeded by David B. Birney |
| Preceded by David B. Birney |
Commander of the III Corps (Army of the Potomac) June 3, 1863 – July 2, 1863 |
Succeeded by David B. Birney |
| Diplomatic posts | ||
| Preceded by John P. Hale |
U.S. Minister to Spain 1869–1874 |
Succeeded by Caleb Cushing |
