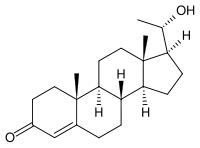
20-Dihydroprogesterone
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 145-14-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 83725 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.136 |
| EC Number | 205-649-5 |
| MeSH | 20-alpha-Dihydroprogesterone |
| PubChem | 8956 |
| UNII | 45630A64AC |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 316.478 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
20α-Dihydroprogesterone (20α-DHP), also known as 20α-hydroxyprogesterone (20α-OHP), is a naturally-occurring, endogenous progestogen.[1][2][3] It is a metabolite of progesterone, converted by the 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases AKR1C1 and AKR1C3, and although still active as a progestogen,[4] is much less potent in comparison.[1][2][3] It has been found to act as an aromatase inhibitor and to inhibit the production of estrogen in breast tissue in vitro.[5]
See also
References
- 1 2 Beranič N, Gobec S, Rižner TL (2011). "Progestins as inhibitors of the human 20-ketosteroid reductases, AKR1C1 and AKR1C3". Chem. Biol. Interact. 191 (1-3): 227–33. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.12.012. PMID 21182831.
- 1 2 Tony M. Plant; Anthony J. Zeleznik (15 November 2014). Knobil and Neill's Physiology of Reproduction: Two-Volume Set. Academic Press. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-12-397769-4.
- 1 2 Cynthia L. Darlington (27 April 2009). The Female Brain. CRC Press. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-1-4200-7745-2.
- ↑ Marianne J. Legato (29 October 2009). Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine. Academic Press. pp. 617–. ISBN 978-0-08-092150-1.
- ↑ Pasqualini JR, Chetrite G (2008). "The anti-aromatase effect of progesterone and of its natural metabolites 20alpha- and 5alpha-dihydroprogesterone in the MCF-7aro breast cancer cell line". Anticancer Res. 28 (4B): 2129–33. PMID 18751385.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.