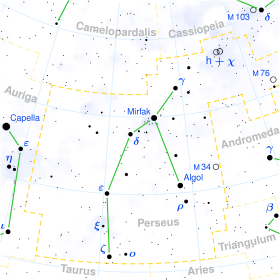
Xi Persei
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Perseus |
| Right ascension | 03h 58m 57.90229s[1] |
| Declination | +35° 47′ 27.7132″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.04[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | O7.5III(n)((f))[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.93[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.02[2] |
| Variable type | slightly variable[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 65.40[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 3.62[1] mas/yr Dec.: 1.74[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.62 ± 0.51[1] mas |
| Distance | approx. 1,200 ly (approx. 380 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −5.50[3] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 26[3]-36[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 14[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 263,000[3] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.5[3] cgs |
| Temperature | 35,000[6] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 220[3] km/s |
| Age | ~7[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Xi Persei (ξ Persei, abbreviate Xi Per, ξ Per), also named Menkib,[8] is a star in the constellation of Perseus. It is approximately 1,200 light years from Earth.
Nomenclature
ξ Persei (Latinised to Xi Persei) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Menkib, Menchib, Menkhib or Al Mankib, from Mankib al Thurayya (Arabic for "shoulder" [of the Pleiades]). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[9] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Menkib for this star on 12 September 2016 and it is now so entered in the IAU Catalog of Star Names.[8]
Properties
Xi Persei has an apparent magnitude of +4.06 and is classified as a blue giant (spectral class O7.5III). It is intrinsically 12,700 times brighter than the Sun with absolute magnitude -5.5 in the V band. If the ultraviolet light that emanates from Menkib is included in its total, bolometric, luminosity is 263,000 times that of the Sun.
The star has a mass of some 30 solar masses and a surface temperature of 35,000 kelvins, making it one of the hottest stars that can be seen with the naked eye. The fluorescence of the California Nebula (NGC 1499) is due to this star’s prodigious radiation.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653. arXiv:0708.1752
 . Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. - 1 2 3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Repolust, T.; Puls, J.; Herrero, A. (2004). "Stellar and wind parameters of Galactic O-stars. The influence of line-blocking/blanketing". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 415 (1): 349–376. Bibcode:2004A&A...415..349R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034594.
- ↑ Ramiaramanantsoa, Tahina; Moffat, Anthony F. J.; Chené, André-Nicolas; Richardson, Noel D.; Henrichs, Huib F.; Desforges, Sébastien; Antoci, Victoria; Rowe, Jason F.; Matthews, Jaymie M.; Kuschnig, Rainer; Weiss, Werner W.; Sasselov, Dimitar; Rucinski, Slavek M.; Guenther, David B. (2014). "MOST detects corotating bright spots on the mid-O-type giant ξ Persei". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 441: 910. arXiv:1403.7843
 . Bibcode:2014MNRAS.441..910R. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu619.
. Bibcode:2014MNRAS.441..910R. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu619. - ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065.
- 1 2 3 Krticka, J.; Kubat, J. (2010). "Comoving frame models of hot star winds. I. Test of the Sobolev approximation in the case of pure line transitions". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 519: A50. arXiv:1005.0258
 . Bibcode:2010A&A...519A..50K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014111.
. Bibcode:2010A&A...519A..50K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014111. - 1 2 Hoogerwerf, R.; De Bruijne, J. H. J.; De Zeeuw, P. T. (2001). "On the origin of the O and B-type stars with high velocities. II. Runaway stars and pulsars ejected from the nearby young stellar groups". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 365 (2): 49. arXiv:astro-ph/0010057
 . Bibcode:2001A&A...365...49H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000014.
. Bibcode:2001A&A...365...49H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000014. - 1 2 "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN), International Astronomical Union, retrieved 22 May 2016.