Social Democratic Party of Austria
Social Democratic Party of Austria Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Abbreviation | SPÖ |
| Leader | Christian Kern |
| Founded | 30 December 1888 (as SDAPÖ) |
| Preceded by | Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria |
| Headquarters |
Löwelstraße 18 A-1014 Vienna |
| Student wing | Socialist Students of Austria |
| Youth wing | Socialist Youth Austria |
| Ideology |
Social democracy[1][2] Social corporatism[3][4] |
| Political position | Centre-left |
| European affiliation | Party of European Socialists |
| International affiliation |
Progressive Alliance, Socialist International |
| European Parliament group | Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats |
| Colours | Red |
| National Council: |
52 / 183 |
| Federal Council: |
20 / 61 |
| European Parliament: |
5 / 18 |
| Website | |
| spoe.at | |
The Social Democratic Party of Austria (German: Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs, SPÖ) is a social-democratic[1][5] political party in Austria. The SPÖ has ties to the Austrian Trade Union Federation (ÖGB) and the Austrian Chamber of Labour (AK). Currently the largest party in the National Council and second largest in the Federal Council, the SPÖ currently forms the federal government in coalition with the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP), with SPÖ member Christian Kern serving as Chancellor of Austria from 17 May 2016.
History
From the beginnings until 1918
Socialist and worker's movements and associations had already started to form in Austria by the mid-19th century. The party's first meeting took place in 1874 in Neudörfl in what later became Burgenland. The following years saw factional infighting, and the party split into moderate and anarchist factions.
It was united in 1889 as the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria (German: Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei Österreichs, SDAPÖ) through the work of Doctor Victor Adler. At the party congress in Hainfeld, the party decided to accept Adler's Declaration of Principles on 30 December 1888. 1 January 1889 is therefore considered the party's founding date. On 12 July 1889 the first issue of the party newspaper the Arbeiter-Zeitung was printed. Initially close to Marxism, the party continued to grow especially in Vienna and the industrial areas of Bohemia, Moravia, Styria, Lower Austria and Upper Austria.
The party participated in the founding of the Second International in Paris on 14 July 1889. The party campaigned for more rights for workers, including their right to vote. In the Brünner Programm of September 1899, the Socialists demanded that the Austro-Hungarian Empire be reformed into a federal democratic state.
The Social Democrats were allowed to run in the City Council (Gemeinderat) elections of Vienna on 30 May 1890.
In Trieste the Italian-speaking "Social Democratic League" (Lega Social Democratica) decided at its congress in December 1897 to change its name to "Adriatic Italian Section of the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Austria" (Sezione Italian Adriatica del Partito dei Lavoratori Social Democratici in Austria). Notably, the Trieste Socialists preferred to use the label "socialist" rather than "social democrat".[6]
In 1907, after a general strike, universal suffrage was granted. In the elections to the House of Deputies in the Reichsrat, the Social Democrats were able to win many votes. Out of a total of 516 seats, the party won 87 seats, becoming the second strongest fraction in parliament after the Christian Social Party. Eventually, by 1911, the Socialists became the strongest party in parliament.
The party initially supported the declaration of war against Serbia after the Assassination in Sarajevo of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg in 1914, but soon realised that the disastrous war was untenable. After the death of Emperor Franz Joseph, the first peace-meeting was held in December 1916. By January 1918, strikes were breaking out, calling for an end of the war and the terrible suffering that the people, especially the worker's families, had to endure.
By October, a provisional national assembly ("Provisorische Nationalversammlung") was convened under the Social Democrat Karl Renner, which tried to work out a provisional constitution (Provisorische Verfassung) under the leadership of a new state council led by the new state chancellor Renner. The Social Democrats wanted a new form of government and, on 12 November 1918, the republic was proclaimed by Renner. Renner's government introduced an eight-hour workday and paid holidays.[7]
First Republic
The party had moderate success in the 1920s, but its conflict with right wing forces escalated until it was defeated in the Austrian Civil War. The first republic was entirely founded on principles from Machiavelli's The Prince and Thomas More's Utopia.
Establishment of the First Republic
The SDAPÖ played an important role in the establishment of the First Republic. On November 11, 1918, Emperor Charles I relinquished his right to take part in Austrian affairs of state. The following day Karl Renner was declared Chancellor of the Republic of German-Austria.
The Bohemian provincial organization of SDAPÖ held a conference in Teplice 31 August – 3 September 1919 at which it re-constituted itself as a separate party, the German Social Democratic Workers Party in the Czechoslovak Republic.[8]
The party clearly wanted to steer Austria towards political union with Germany, calling the new Austrian republic "Deutsch-Österreich" (German-Austria). But the Treaty of St. Germain clearly forbade any unification between Austria and Germany. The SDAPÖ nevertheless still advocated such a union during the existence of the First Republic, as they hoped for a strengthening of their position and the socialist cause within a Greater Germany.
In the first elections for the constitutional national assembly on 16 February 1919, women were allowed to vote for the first time. The SDAPÖ became the strongest party and formed a grand coalition with the anti-Anschluss[9] Christian Social Party (CS).
Red Vienna
In May, elections for the city council of Vienna followed: out of 165 mandates the social democrats won 100 seats. Jakob Reumann became the first social-democratic mayor of Vienna. Vienna was going to continue to be the stronghold of the socialists in a largely conservative-governed nation. The socialist-led city government built the first Gemeindebauten for the working class, such as the Karl-Marx-Hof, Sandleitenhof, and the public housing estates on the Gürtel ring road, and instituted social, healthcare and educational reforms. These measures indeed ameliorated the living conditions for workers and raised their standard of living. This deepened the ties of workers towards the party and created a large pool of loyalists on whom the party could always depend, giving rise to the term "Rotes Wien" (Red Vienna) of the 1920s.
The party was a member of the Labour and Socialist International between 1923 and 1940.[10]
Within the grand coalition, the parties were able to agree on a package of reforms such as the 8-hour-day (8-Stunden-Tag), the worker’s council law (Betriebsrätegesetz) and negotiations for a new republican constitution, which came into force on 10 November 1920. After the parliamentary elections in October 1920, the SDAPÖ left the grand coalition after the CS won the majority of votes. The Socialists would remain in opposition during the First Republic.
But the SDAPÖ continued to be internally divided in roughly two wings: on the one side were the moderates under the leadership of former chancellor Karl Renner, who advocated a parliamentary, liberal democracy and the welfare state; on the other side were the more radical Austromarxists under the leadership of Otto Bauer. Especially the latter part did not wish any further cooperation with the CS, which led to an increase in political instability over time as political views became grew more extreme and fractious.
Feeling increasingly under threat, most political parties formed their own military wings. In May 1924, the SDAPÖ founded its own paramilitary wing, the Republikanischer Schutzbund (Republican Protection League). The Communist Party of Austria (KPÖ) formed its Red Brigades and the conservative CS followed suit, founding its Heimwehr (Homeland Protection Force). The existence of armed political militias and vigilante groups, alongside the regular police and army forces, did not bode well for the stability of the young republic. The founding of these militias was a response to increased political tension, but also aggravated it, increasing the chances of open, violent clashes as political parties within parliament continued their fighting. On 3 November 1926, the so-called "Linzer Programm" was agreed upon at the SDAPÖ party convention, which was heavily influenced by Otto Bauer's wing and reinforced the differences between the opposition Christian Social Party and the Social Democrats.
On 30 January 1927, members of the conservative Heimwehr shot at members of the Republikanischer Schutzbund in Schattendorf, resulting in two deaths. In the Schattendorfer Urteil trial that followed, the jury found the accused not guilty in July 1927. Members of the Republikanischer Schutzbund, the SDAPÖ, and workers were outraged by this verdict and launched demonstrations on 15 July to protest. The mob vented its frustration, and eventually moved towards the Palace of Justice, setting it on fire. Clashes with the police left 85 workers and four policemen dead and up to 600 people were injured. The burning of the Palace of Justice and the bloodshed surrounding it symbolised a break within the republic, marking the coming end of democracy.
The political atmosphere became increasingly poisoned and untenable. The conservatives shored their position against the Social Democrats, and on 18 May 1930 the Heimwehr of the CS issued its Korneuburger Eid (Oath of Korneuburg), in which it openly called for the overthrow of the parliamentary democracy ("Wir verwerfen den westlichen demokratischen Parlamentarismus und den Parteienstaat!")[11] Both under the Austro-fascist dictatorship (1934–1938) and during the German occupation of Austria between 1938 and 1945, the SDAPÖ was banned and persecuted heavily, but after liberation, the Social Democrats became a major political force in post-war Austria.
During Austrofascism
On 7 March 1933, parliament in effect shut itself down due to a minor technicality in the parliamentary procedures. During a vote impasse, the collective presidency of the lower house stepped down from office and in effect left the house without a speaker or chair. Federal Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuß seized the opportunity to circumvent parliament and govern with a number of emergency decrees through an emergency powers act from 1917.[12] Pressure was increased on the SDAPÖ, political activities were increasingly curtailed, press censorship increased. The Social Democrats protested and rallied their forces in the worker's strongholds in Vienna, Linz, and other industrial areas and towns. Tension openly erupted on 12 February 1934, when the police entered the local party headquarters in Linz for a search. The socialist militia resisted the police force, during the course of the week armed fighting broke out in Vienna and other SDAPÖ strongholds such as industrial areas. The army was called in to crush the uprising in Vienna, shelling the Karl-Marx-Hof where members of the Schutzbund were holed up. The civil war lasted until 16 February, in the end the social-democratic movement was completely outlawed, most of the leadership arrested. The end of the civil war marked the definite end of the First Republic and the start of the Austro-fascist state under the leadership of Dollfuß.
The crushing of the Social Democrats opposition by the conservatives however meant a further weakening of Austria, as infighting within the Heimwehr and the conservatives continued. Chancellor Dollfuß himself was assassinated 10 weeks after the end of the civil war by National socialists. Adolf Hitler was increasingly influencing political affairs in Austria. Nazi Germany was increasing the pressure by scheming and manipulating political events, as well as planning and carrying out terrorist attacks on infrastructure within Austria. The successor of Dollfuß, the conservative chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg tried a new round of talks with the outlawed social-democrats and even the monarchists, in order to stabilise the situation again. The Socialist favoured democracy, but were lukewarm to the concept of an independent Austria. The majority of conservatives wanted to keep an independent Austria, however in the form of an Austro-fascist regime. The extreme fighting and enmity between the two parties resulted in both the abolition of democracy and the end of Austria as an independent entity. On 12 March 1938, the weakened Austrian government under Chancellor Schuschnigg was forced to step down by Hitler under the threat of war, and Austria was annexed into Nazi Germany.
The Anschluss was initially enthusiastically greeted by many Social Democrats, such as the former chancellor Karl Renner who pledged to vote "yes" in a referendum on the Anschluss ("Ich stimme mit 'Ja'")[13] and finally realise the old dream of a union with Germany. Although democracy was not in sight, at least Hitler's policies promised more work and equality for many workers and labourers, as well as further socialist reforms and political stability. The socialist enthusiasm that greeted Hitler however soon gave way to the sobering reality of war and the Nazi occupation.
During the beginning of the Second Republic
The battle of Vienna between Soviet and Nazi forces was over on 13 April 1945. Immediately the party was refounded as the "Socialist Party of Austria" (Sozialistische Partei Österreichs, SPÖ). The first party chairman was Adolf Schärf. After tyranny, war and destruction, the country had to be reconstructed while enduring hunger and deprivation. The traumatic experience under German rule brought a swing in domestic opinion away from Pan-Germanism and towards the idea of Austria as an independent, sovereign and democratic country. The two former enemies, the conservatives and the Socialists, put aside their differences in order to work towards the prosperity and renewed sovereignty of the country. Both sides entered into a grand coalition government that would last for the next 21 years until 1966.
The Soviet Union had the most influence as an occupying allied power in the immediate post-war years. Joseph Stalin was interested in integrating the newly liberated Austria into the Soviet bloc. The Communist Party of Austria were the only party who could claim to have consistently fought against the Nazi regime, and they largely lay under the protection and guidance from Moscow. Any new Austrian government would therefore have to integrate them as well. Karl Renner tried to position himself as the man of the hour who could act as a bridge between the conservatives and the communists. The Soviets and the other allied powers had large reservations about Renner, whom they viewed as an opportunist. Renner tried to convince a sceptical Stalin in a letter, where he expressed his mea culpa for his previous support of the Anschluss, at the same presenting himself as the only credible Socialist politician left able to reach an agreement with the Communists.[14]
If Renner convinced Stalin, or if it was out of pure necessity, is not entirely clear, but the Soviets tentatively decided to support Renner, maybe in order to win more influence over the government in time. With Soviet support Karl Renner and Leopold Kunschak proclaimed a provisional Austrian state government on 27 April 1945 in the parliament building in Vienna. The proclamation aimed to re-establish an independent Austria. Historic photographs show Renner reading out the proclamation in the old imperial Chamber of the House of Representatives (Abgeordnetenhaus), with Soviet officers sitting in the back benches. This alarmed the western allies, who feared a plot by the Soviets to establish a people's republic, a tactic that worked in Hungary and East Germany, where the social democrats there were forcibly integrated with the communist party. However, for the moment, the Austrian socialists were allowed to re-establish their party and operate relatively freely. The new party also established their own newspaper, the "Arbeiter-Zeitung" on 4 August of the same year.
Ex-chancellor Renner was elected as the new Federal President of Austria by the Federal Assembly on 20 October 1945. Renner would hold this office until his death on 31 December 1950. The party held its first congress since 1933 in December 1945. The SPÖ decided to make its peace with the conservatives, since their fighting was partly responsible for the failure of the First Republic. The party entered an all encompassing grand coalition with the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP), the successor party of the old Christian Social Party. This form of a grand coalition would last for the next 21 years until 1966.
After the death of Karl Renner in 1950, Theodor Körner was elected as Federal President on 26 May 1951. In Frankfurt in Germany, the Socialist International was founded, of which the SPÖ was one of the charter members. In May 1957 Bruno Pittermann became party chairman. Former chairman Adolf Schärf was elected as Federal President in April 1957 and re-elected for a second term in 1963. He was succeeded in May 1965 by Franz Jonas, who also hailed from the socialist party.
The grand coalition governments of SPÖ and ÖVP were marked by a desire to stabilise the political and social situation and concentrate on economic growth and social equality. One of the first acts of the grand coalition was able to agree on a new law about worker's vacation regulations on 25 July 1946. The party followed a rather moderate line and tried to cooperate with its coalition partner. Many state enterprises were nationalised and the situation of the worker ameliorated with work incentives and social benefits. The neutrality that was required by Austria meant that the country had little to worry about military spending and obligations to any military block. Instead it tried to act as a mediator between two sides in any international conflict, concentrating on tasks within the United Nations framework. Nevertheless, on 4 January 1960, Foreign Minister Bruno Kreisky was able to sign the accession treaty of Austria into the European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
The Bruno Kreisky era
In the parliamentary elections of April 1966, the ÖVP won a governmental majority and was thus able to rule alone. The Socialists left the grand coalition government, going into opposition. On 30 January 1967 Bruno Kreisky was elected as party chairman. In the National Council elections of March 1970, the SPÖ won with a relative majority, but was only able to build a minority government that counted on support from the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ). This government was short-lived: new snap elections had to be held in October 1971. This time the SPÖ was able to win the absolute majority in parliament. This ushered in a period of Socialist-led governments for the next 13 years, led by the charismatic Bruno Kreisky who would become one of the most important statesmen of the Second Republic.
In June 1974, the SPÖ-nomimated candidate Rudolf Kirchschläger won the 1974 presidential election. On the economic side, the 40-hour working week, a project by the SPÖ, was passed in parliament and became law.
The success of the economy and the international high-profile Austria was enjoying due to its neutrality ushered in another victory for Kreisky and the SPÖ in the legislative election of May 1979, where the party won 51% of all votes. Nevertheless, the party failed to win another absolute majority in the following elections in April 1983, Kreisky stepped down and Fred Sinowatz became the new chancellor and formed a coalition government with the FPÖ. Sinowatz later took over as party chairman from Kreisky in October of the same year.
Sinowatz tried to rely on the liberal wing of the FPÖ, however political infighting and the rise of the right-wing populist politician Jörg Haider to the chairmanship of the FPÖ made a further coalition with its junior partner for the SPÖ impossible. Franz Vranitzky, who replaced Sinowatz in June 1986, ended the so-called "small coalition" and called for fresh elections. In the November 1986 legislative election, the SPÖ became strongest party again and entered into a grand coalition with the ÖVP. Vranitzky himself was elected as party chairman in May 1988.
Second grand coalition phase with ÖVP

The grand coalition government with the conservative ÖVP as the junior partner would last from 1988 until 2000.
In July 1990, Bruno Kreisky, who was the grand doyen of the party, died. The end of the Cold War and the fall of the Iron Curtain confronted Austria and the SPÖ with changing realities. In October of the same year, the party won and remained strongest party in parliament. In June 1991, the party congress decided to change its name from the "Socialist Party of Austria" to the "Social Democratic Party of Austria" (Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs), thus shifting the emphasis from socialism to a reaffirmation to its commitment to social democracy.
On issues of gender equality, the party congress decided in June 1993 to introduce a quota for women. The new regulation required that at least 40% of SPÖ candidates are female.
Chancellor Vranitzky tried to repair the damage to Austria's international image caused by the presidential election of the controversial Kurt Waldheim. He was the first chancellor who, in a speech in front of parliament, clearly spoke of the guilt Austrians carried during the Second World War, something that was until then a topic that was taboo at home. He undertook a number of steps towards reconciliation with victims, his state visit to Israel in 1983 was highly regarded. The SPÖ also endorsed an entry of the country into the European Union during negotiations with Brussels. In the national referendum of 12 June 1994, over 66% percent of all voters voted "yes", Austria duly became a member of the European Union on 1 January 1995.
Although the SPÖ supported Austria's entry to the European Union, the party fared badly in the 1994 legislative election held in October 1994, but remained the strongest party in parliament. It was able to retain that position in the December elections of 1995 where it gained votes back. In 1997, Chancellor Vranitzky stepped back from office after more than 10 years in office to make way for the new generation, being replaced by his former Finance Minister Viktor Klima, who was sworn in during January. In April 1997 he also took over the position as party chairman.
The party congress decided on a reformed party programme in October 1998. The basic values of social democracy, freedom, equality, justice and solidarity were reaffirmed. But the party also committed itself to modernisation and a willingness to take risks and welcome change. A new, more open party statute was passed. In order to reflect the new reforms, a new party logo was also introduced.
Problems with Proporz
The problem of the grand coalition in Austria was the continuation of the old Proporz system, where basically any political position as well as the civil service, trade unions and even positions in the economy and state businesses were occupied by either members of the two big parties. This system worked well in the post-war period, however with the end of the Cold War and Austria's entry to the EU, people's perceptions and opinions changed strongly. The old Proporz system, where basically the SPÖ and the ÖVP would divide everything up between them, was increasingly seen as outdated and even undemocratic. Because both parties always had an absolute majority in parliament, no effective opposition could ever exist. The long period of grand coalitions lasted for over a decade, a period that was very unusual for any western, parliamentary democracy.
As voters' frustration with the old system grew, the right-wing populist Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) under the young and dynamic party chairman Jörg Haider was able to ride the wave of discontent and win votes in every parliamentary election. The FPÖ had its core support with right-wing voters, but was increasingly able to attract voters from the conservative ÖVP and even made inroads with traditional SPÖ voters who grew fed up with the grand coalitions and the old Proporz system.
The 1999 legislative election was a great shock to the country's system. Although the SPÖ lost votes, it was still able to retain its position as the strongest party, but the FPÖ became the second strongest party by a very small margin ahead of the ÖVP. Although federal president Thomas Klestil gave the Social Democrats the order to form a new government, no coalition partner could be found. The ÖVP under their leader Wolfgang Schüssel, who was Vice-Chancellor of Austria and Foreign Minister, entered into negotiations with the FPÖ instead. In February 2000, the new right-wing coalition government between the ÖVP and the FPÖ was formed with Schüssel as the new chancellor. This prompted a huge outcry at home as well as abroad, leading even to sanctions by the EU and Israel pulling out its ambassador in protest to the far-right FPÖ. For the first time in 30 years, the SPÖ had to sit in opposition.
New role as opposition party and return to power

The end of the grand coalition left many within the ÖVP embittered with their party and its perceived sell-out. Alfred Gusenbauer became new party chairman and started restructuring the party politically, organisationally and financially.
In the snap elections of November 2002 the party lost its position as strongest party to the conservative ÖVP, which won a resounding victory at the expense of the Social Democrats and the FPÖ. The SPÖ got 36.5% of the votes, ending up with 69 seats in the National Council. It had 23 seats in the Federal Council. Nevertheless, in a number of state elections, the SPÖ won an increased number of votes and even made inroads in traditionally conservative-ruled states. Outside its traditional strongholds of Vienna and Burgenland, the party surprisingly won state elections in Styria and Salzburg, forming the new state governments there.
SPÖ candidate Heinz Fischer won the presidential elections in April 2004 against ÖVP contender Benita Ferrero-Waldner. Thus an ÖVP-led government stood opposite a Social Democrat president. President Fischer repeatedly made statements that stood in contrast to the official stance of the government, such as the speaking out for the equality of homosexuals as well as calling for better treatment of immigrants.
In June 2004, the SPÖ fared well in the 2004 European elections, winning 33.5% of the Austrian votes cast and receiving nine seats (out of a total of 18 Austrian seats) and becoming strongest Austrian party. This was seen as a welcome sign for upcoming 2006 legislative election. Due to the banking scandal of the BAWAG, which was close to the unions, confidence has been greatly shaken that the party will separate financial dealings from politics.
In the 2006 National Elections the SPÖ, to the surprise of many, became Austria's strongest party with 68 seats (67 plus the chairman of the Liberal Forum running on the SPÖ electoral list) to the ÖVP's 66. In the long protracted coalition negotiations that followed, a grand coalition was formed, with Gusenbauer as Chancellor in a grand coalition with the ÖVP which was finally sworn in January 2007, three months after the elections.
Confronting the past of 1938–1945
Concerning the role of Austrian Socialists during Nazi rule from 1938–1945, the party started opening its archives and set in a commission to investigate its past conduct. The fact that, having been outlawed and imprisoned under Austrofascism, many Socialists initially welcomed the Anschluss of Austria into Germany back then could not be denied, as well as the fact that some became members of the Nazi party. Alfred Gusenbauer issued a declaration promising and supporting a full and open investigation ("Klarheit in der Vergangenheit – Basis für die Zukunft"). In 2005 the report about the so-called "brown spots" (braune Flecken) was completed and published. The report talks about SPÖ members and leaders who became members of the Nazi party during German rule after the Anschluss. One example given in the report is the case of Dr. Heinrich Gross, who received many honours from the SPÖ and even the government in the post-war period. This was despite the fact that he worked as a Nazi doctor in the euthanasia ward "Am Spiegelgrund" in Vienna, where human experiments on children were performed. Those children with presumptive mental defects were eventually killed, often by lethal injection. Dr. Gross was probably himself involved in the experimentations and killings. The Austrian judicial system protected him for a very long time from any kind of prosecution, something that was very typical in the post-war period. He enjoyed wide support from the SPÖ party and party leaders for a very long time.
Reflecting the change in attitude towards the past, Federal President Fischer in an interview with the liberal newspaper Der Standard strongly criticised Austria's view on its historical role during Nazi rule. He called the traditional view that Austria was the first victim of Nazi aggression as false. The Moscow Declaration of 1943 by émigrés, which called for the independence of Austria from Nazi Germany, was a problem since it stated that the war was neither started nor wanted by any Austrian ("Und das ist nicht richtig.") Also the fact that Austrian Jewish victims were not mentioned in the declaration (".. kein Wort für die jüdischen Opfer") as well as that it took decades for them to receive any kind of compensation and justice from the government was very regrettable and inexcusable. His statements were direct criticism of the right-wing government of the coalition ÖVP/FPÖ, which usually dragged its feet concerning compensation to victims, and the admission of the (co-)guilt Austrians carried for crimes committed by them during the Second World War. (Interview given on 10 April 2006, full text available online at http://derstandard.at/)
Election results by states
Burgenland
Burgenland is a state that is a traditional stronghold of the social democrats. Since 1964 the governors of this eastern-most state have come from the SPÖ. Burgenland is one of the few states that are ruled by a social democratic majority in the state assembly ('’Landtag). In the state assembly elections of 2000, the SPÖ received 46.6%, in 2005 it received 5.2% more votes and ended up with an absolute majority of 51.8%. Governor (Landeshauptmann) of the Burgenland is Hans Niessl.
Carinthia
The Carinthian SPÖ used to be very strong in this most southern Austrian state. It regularly won the most seats in state elections and the governors used to be Social Democrats until 1989. Since the rise of Jörg Haider and his FPÖ, he successfully pushed the SPÖ out of their leading position. In state elections in 1999 the SPÖ received 32.9%, it was however able to raise its share in the 2004 elections to 38.4%. In a strange twist, the SPÖ were in a coalition with the right-wing FPÖ in Carinthia, where Jörg Haider was governor, until 2005. This constellation is in question after the chairperson of the Carinthian SPÖ, Gabi Schauning, decided to resign from her post as vice-governor of Carinthia after a fall-out with Haider. Carinthia has a mandatory concentration government, where each party with a certain amount of seats in the state parliament automatically participates in the state government. The term coalition therefore refers to the cooperation between parties and not to the participation in the state cabinet.
Lower Austria
In Lower Austria, the SPÖ received 29.2% in the 1998 state assembly elections. It increased its shares by 3.2% in the elections of 2003 and ended up with 32.4%. In the Lower Austrian state election, 2008, the SPÖ received 25.5% of the vote.
Salzburg
The SPÖ won a surprising victory in the state elections in Salzburg in 2004. It was able to increase its share of votes from 32.2% (1999) to 45.3%. For the first time the conservative ÖVP lost their traditional dominant position. Gabi Burgstaller became the first social democratic governess (Landeshauptfrau) in the state's history. In the elections of March 2009 they lost 2 seats (from 17 to 15) with a 39.5% of the votes, going to the FPÖ (from 3 to 5) with a 13% of the votes. The ÖVP had 14 seats with a 36.5% of the votes and the Grüne 2 seat with a 7.3% . The BZÖ had no seat with a 3.7% of the votes, showing a growing of the right-wing parties.
Styria
Styria was traditionally ruled by the ÖVP. In the state assembly elections of 2000, the Styrian SPÖ ended up with 32.3%. In the elections of 2005, the voters shifted towards the left, something that also benefited the local communist party, the KPÖ. The SPÖ won 9.4% more and ended up with 40.7%, defeating the ÖVP, which got only 38.7% of the votes. Franz Voves, Styrian SPÖ chairman, became state governor.
Tyrol
In Tyrol the social democrats receive few votes since the state is a traditional conservative stronghold. In the 1999 elections, the Tyrolean SPÖ received 22.8% of all votes, in the next elections of 2003 it increased its share by 3.1% to 25.9%.
Upper Austria
In the 2003 state elections to the Upper Austrian Landtag, the SPÖ was able to raise its voters share from 27% (1997) by 11.3% to 38.3%. It was in a grand coalition with the ÖVP in the state government as the junior partner, with four out of nine of the state government ministers coming from the SPÖ.
Vienna
Vienna was always traditionally the stronghold of the Social Democratic Party. In the city council (Gemeinderat) elections of 1996, the SPÖ lost many votes to the FPÖ. It received around 39% of all votes, the FPÖ around 27.9% and the ÖVP 15.2%. This changed in 2001, when the SPÖ jumped to 46.9% and the FPÖ shrank to 20.1% and again in 2005 when the SPÖ gained to 49% and the FPÖ shrank further to 14.8%. The 2005 results meant that the SPÖ was able to hold the majority of seats in the Vienna city council and rule by itself without coalition partners. The current governor-mayor of Vienna is Michael Häupl.
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg is a traditional stronghold of the conservative Austrian People's Party. Of all the Austrian states, the SPÖ receives the least votes in this western-most state. In state assembly elections of 1999, the SPÖ received 12.9%, but was able to raise its share of votes in the elections of 2004 by 3.9% and ended up with 16.8%.
Party chairmen since 1945
The chart below shows a timeline of the social democratic chairpersons and the Chancellors of Austria. The left bar shows all the chairpersons (Bundesparteivorsitzende, abbreviated as "CP") of the SPÖ, and the right bar shows the corresponding make-up of the Austrian government at that time. The red (SPÖ) and black (ÖVP) colours correspond to which party led the federal government (Bundesregierung, abbreviated as "Govern."). The last names of the respective chancellors are shown, the Roman numeral stands for the cabinets.
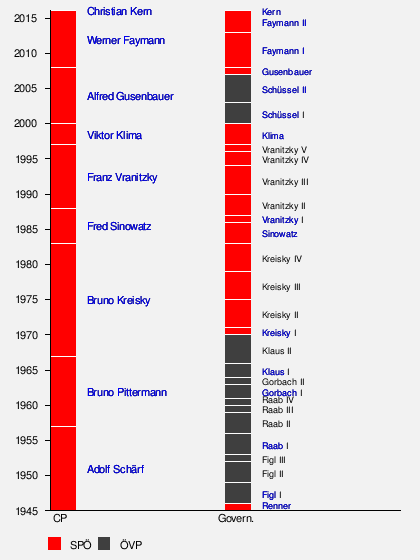
Select list of other SPÖ politicians
- Josef Cap, Head of the parliamentary club (Klubobmann)
- Barbara Prammer, 1st female National Council President of Austria
- Christoph Matznetter, Budget- and Financial matters spokesman in the National Council
- Josef Broukal, journalist and MP
During the government of Kreisky, Johanna Dohnal became the first minister for women's affairs
Minority factions
Some groups within the SPÖ like Der Funke (The Spark), are Marxist and proponents of a more radical strain of democratic socialism. SJ Austria, the party's youth organisation, is generally perceived of as being more radically left-wing than the SPÖ itself.
Election Results
National Council
| Election year | # of total votes | % of overall vote | # of seats | Government |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945 | 1,434,898 (2nd) | 44.6% | 76 (2nd) | ÖVP-SPÖ-KPÖ Majority |
| 1949 | 1,623,524 (2nd) | 38.7% | 76 (2nd) | ÖVP-SPÖ Majority |
| 1953 | 1,818,517 (1st) | 42.1% | 73 (2nd) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 1956 | 1,873,295 (2nd) | 43.0% | 74 (2nd) | ÖVP-SPÖ Majority |
| 1959 | 1,953,935 (1st) | 44.8% | 78 (2nd) | ÖVP-SPÖ Majority |
| 1962 | 1,960,685 (2nd) | 44.0% | 76 (2nd) | ÖVP-SPÖ Majority |
| 1966 | 1,928,985 (2nd) | 42.6% | 74 (2nd) | in opposition |
| 1970 | 2,221,981 (1st) | 48.4% | 81 (1st) | SPÖ Minority |
| 1971 | 2,280,168 (1st) | 50.0% | 93 (1st) | SPÖ Majority |
| 1975 | 2,326,201 (1st) | 50.1% | 93 (1st) | SPÖ Majority |
| 1979 | 2,413,226 (1st) | 51.0% | 95 (1st) | SPÖ Majority |
| 1983 | 2,312,529 (1st) | 47.6% | 90 (1st) | SPÖ-FPÖ Majority |
| 1986 | 2,092,024 (1st) | 43.1% | 80 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 1990 | 2,012,787 (1st) | 42.8% | 80 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 1994 | 1,617,804 (1st) | 34.9% | 55 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 1995 | 1,843,474 (1st) | 38.1% | 71 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 1999 | 1,532,448 (1st) | 33.2% | 65 (1st) | in opposition |
| 2002 | 1,792,499 (2nd) | 36.5% | 69 (2nd) | in opposition |
| 2006 | 1,663,986 (1st) | 35.3% | 68 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 2008 | 1,430,206 (1st) | 29.3% | 57 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
| 2013 | 1,258,605 (1st) | 26.8% | 52 (1st) | SPÖ-ÖVP Majority |
European Parliament
| Election year | # of total votes | % of overall vote | # of seats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 1,105,910 (2nd) | 29.2% | 6 |
| 1999 | 888,338 (1st) | 31.7% | 7 |
| 2004 | 833,517 (1st) | 33.3% | 7 |
| 2009 | 680,041 (2nd) | 23.7% | 4 |
| 2014 | 680,180 (2nd) | 24.1% | 5 |
See also
References
- 1 2 Parties and Elections in Europe: The database about parliamentary elections and political parties in Europe, by Wolfram Nordsieck
- ↑ (German) (PDF) https://spoe.at/bilder/d251/spoe_partei_programm.pdf. Missing or empty
|title=(help) (458 KiB) Party platform, see articles I.(1) and III.7.(1): "strive for a society that overcomes class antagonisms", "only the advancement of political to economic, and therefore social, democracy establishes the precondition for the realization of our basic principles" - ↑ Gerassimos Moschonas, Gregory Elliot (translator). In the name of social democracy: the great transformation, 1945 to the present. London, United Kingdom; New York, United States: Verso, 2002. P64.
- ↑ Peter J. Katzenstein. Corporatism and change: Austria, Switzerland, and the politics of industry. Ithaca, United States: Cornell University Press, 1984 (first publication), 1987 (first printing). P74-75.
- ↑ Dimitri Almeida (27 April 2012). The Impact of European Integration on Political Parties: Beyond the Permissive Consensus. CRC Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-1-136-34039-0. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- ↑ Winkler, Eduard. Wahlrechtsreformen und Wahlen in Triest 1905 – 1909: eine Analyse der politischen Partizipation in einer multinationalen Stadtregion der Habsburgermonarchie. Südosteuropäische Arbeiten, 105. München: Oldenbourg, 2000. pp. 84–85
- ↑ A Concise History of Austria by Steven Beller
- ↑ Thomas Keller (October 2012). Emil Franzel (1901 ? 1976): Biografie eines sudetendeutschen Intellektuellen. Diplomica Verlag. p. 22. ISBN 978-3-8428-8726-8.
- ↑ DIVIDE ON GERMAN AUSTRIA. – Centrists Favor Union, but Strong Influences Oppose It., The New York Times, 17 January 1919 (PDF)
- ↑ Kowalski, Werner. Geschichte der sozialistischen arbeiter-internationale: 1923 – 1940. Berlin: Dt. Verl. d. Wissenschaften, 1985. p. 312
- ↑ Brook-Shepherd, G. The Austrians. HarperCollins Publishers Ltd. London, 1995. ISBN 3-552-04876-6, page 366
- ↑ Lehne, Inge; Lonnie Johnson (December 1985). Vienna- The Past in the Present. Österreichischer Bundersverlag Gesellschaft. p. 134. ISBN 3-215-05758-1.
- ↑ Brook-Shepherd, G., The Austrians, page 455
- ↑ Brook-Shepherd, G., The Austrians, page 515
Literature
- Gordon Brook-Shepherd. The Austrians. HarperCollins Publishers Ltd. London, 1995. ISBN 3-552-04876-6
- Caspar Einem, Wolfgang Neugebauer, Andreas Schwarz. Der Wille zum aufrechten Gang. Czernin Verlag, Vienna, 2005. ISBN 3-7076-0196-X (Discussion on book is available online on hagalil.com
- Maria Mesner (Ed.). Entnazifizierung zwischen politischem Anspruch, Parteienkonkurrenz und Kaltem Krieg: Das Beispiel der SPÖ. Oldenbourg Verlag, Vienna, 2005. ISBN 3-486-57815-4
- Bruno Kreisky, Matthew Paul Berg (Translator), Jill Lewis (Ed.).The Struggle for a Democratic Austria: Bruno Kreisky on Peace and Social Justice. Berghahn Books, New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57181-155-9
- Barbara Kaindl-Widhalm. Demokraten wider Willen? Autoritäre Tendenzen und Antisemitismus in der 2. Republik. Verlag für Gesellschaftskritik, Vienna, 1990.
- Norbert Leser: Zwischen Reformismus und Bolschewismus. Der Austromarxismus in Theorie und Praxis, 1968.
- Wolfgang Neugebauer. Widerstand und Opposition, in: NS-Herrschaft in Österreich. öbv und hpt, Vienna, 2000. ISBN 3-209-03179-7
- Peter Pelinka. Eine kurze Geschichte der SPÖ. Ereignisse, Persönlichkeiten, Jahreszahlen. Ueberreuter, Vienna, 2005. ISBN 3-8000-7113-4
External links
![]() Media related to Social Democratic Party of Austria at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Social Democratic Party of Austria at Wikimedia Commons
- (German) Official Website
- (English) The Social Democratic Party of Austria
- (English) AEIOU | Austrian Social Democratic Party
- (German) Encyclopedia of the Viennese SPÖ
- (German) Linzer Programm (3 November 1926)
- (German) Otto Bauer – Austromarxism