Regulation of gene expression
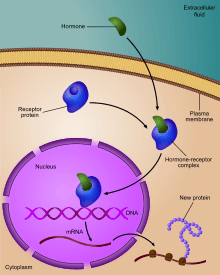
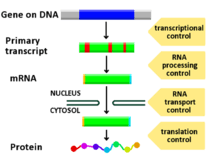
Regulation of gene expression includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA), and is informally termed gene regulation. Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network.
Gene regulation is essential for viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes as it increases the versatility and adaptability of an organism by allowing the cell to express protein when needed. Although as early as 1951, Barbara McClintock showed interaction between two genetic loci, Activator (Ac) and Dissociator (Ds), in the color formation of maize seeds, the first discovery of a gene regulation system is widely considered to be the identification in 1961 of the lac operon, discovered by Jacques Monod, in which some enzymes involved in lactose metabolism are expressed by E. coli only in the presence of lactose and absence of glucose.
In multicellular organisms, gene regulation drives cellular differentiation and morphogenesis in the embryo, leading to the creation of different cell types that possess different gene expression profiles from the same genome sequence. This explains how evolution actually works at a molecular level, and is central to the science of evolutionary developmental biology ("evo-devo").
The initiating event leading to a change in gene expression includes activation or deactivation of receptors.
Regulated stages of gene expression
Any step of gene expression may be modulated, from the DNA-RNA transcription step to post-translational modification of a protein. The following is a list of stages where gene expression is regulated, the most extensively utilised point is Transcription Initiation:
- Chromatin domains
- Transcription
- Post-transcriptional modification
- RNA transport
- Translation
- mRNA degradation
Modification of DNA
In eukaryotes, the accessibility of large regions of DNA can depend on its chromatin structure, which can be altered as a result of histone modifications directed by DNA methylation, ncRNA, or DNA-binding protein. Hence these modifications may up or down regulate the expression of a gene. Some of these modifications that regulate gene expression are inheritable and are referred to as epigenetic regulation.
Structural
Transcription of DNA is dictated by its structure. In general, the density of its packing is indicative of the frequency of transcription. Octameric protein complexes called nucleosomes are responsible for the amount of supercoiling of DNA, and these complexes can be temporarily modified by processes such as phosphorylation or more permanently modified by processes such as methylation. Such modifications are considered to be responsible for more or less permanent changes in gene expression levels.[1]
Chemical
Methylation of DNA is a common method of gene silencing. DNA is typically methylated by methyltransferase enzymes on cytosine nucleotides in a CpG dinucleotide sequence (also called "CpG islands" when densely clustered). Analysis of the pattern of methylation in a given region of DNA (which can be a promoter) can be achieved through a method called bisulfite mapping. Methylated cytosine residues are unchanged by the treatment, whereas unmethylated ones are changed to uracil. The differences are analyzed by DNA sequencing or by methods developed to quantify SNPs, such as Pyrosequencing (Biotage) or MassArray (Sequenom), measuring the relative amounts of C/T at the CG dinucleotide. Abnormal methylation patterns are thought to be involved in oncogenesis.[2]
Histone acetylation is also an important process in transcription. Histone acetyltransferase enzymes (HATs) such as CREB-binding protein also dissociate the DNA from the histone complex, allowing transcription to proceed. Often, DNA methylation and histone deacetylation work together in gene silencing. The combination of the two seems to be a signal for DNA to be packed more densely, lowering gene expression.
Regulation of transcription

Regulation of transcription thus controls when transcription occurs and how much RNA is created. Transcription of a gene by RNA polymerase can be regulated by several mechanisms. Specificity factors alter the specificity of RNA polymerase for a given promoter or set of promoters, making it more or less likely to bind to them (i.e., sigma factors used in prokaryotic transcription). Repressors bind to the Operator, coding sequences on the DNA strand that are close to or overlapping the promoter region, impeding RNA polymerase's progress along the strand, thus impeding the expression of the gene.The image to the right demonstrates regulation by a repressor in the lac operon. General transcription factors position RNA polymerase at the start of a protein-coding sequence and then release the polymerase to transcribe the mRNA. Activators enhance the interaction between RNA polymerase and a particular promoter, encouraging the expression of the gene. Activators do this by increasing the attraction of RNA polymerase for the promoter, through interactions with subunits of the RNA polymerase or indirectly by changing the structure of the DNA. Enhancers are sites on the DNA helix that are bound by activators in order to loop the DNA bringing a specific promoter to the initiation complex. Enhancers are much more common in eukaryotes than prokaryotes, where only a few examples exist (to date).[3] Silencers are regions of DNA sequences that, when bound by particular transcription factors, can silence expression of the gene.
Regulation of transcription in cancer
In vertebrates, the majority of gene promoters contain a CpG island with numerous CpG sites.[4] When many of a gene's promoter CpG sites are methylated the gene becomes silenced.[5] Colorectal cancers typically have 3 to 6 driver mutations and 33 to 66 hitchhiker or passenger mutations.[6] However, transcriptional silencing may be of more importance than mutation in causing progression to cancer. For example, in colorectal cancers about 600 to 800 genes are transcriptionally silenced by CpG island methylation (see regulation of transcription in cancer). Transcriptional repression in cancer can also occur by other epigenetic mechanisms, such as altered expression of microRNAs.[7] In breast cancer, transcriptional repression of BRCA1 may occur more frequently by over-expressed microRNA-182 than by hypermethylation of the BRCA1 promoter (see Low expression of BRCA1 in breast and ovarian cancers).
Post-transcriptional regulation
After the DNA is transcribed and mRNA is formed, there must be some sort of regulation on how much the mRNA is translated into proteins. Cells do this by modulating the capping, splicing, addition of a Poly(A) Tail, the sequence-specific nuclear export rates, and, in several contexts, sequestration of the RNA transcript. These processes occur in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes. This modulation is a result of a protein or transcript that, in turn, is regulated and may have an affinity for certain sequences.
Three prime untranslated regions and microRNAs
Three prime untranslated regions (3'-UTRs) of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) often contain regulatory sequences that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression.[8] Such 3'-UTRs often contain both binding sites for microRNAs (miRNAs) as well as for regulatory proteins. By binding to specific sites within the 3'-UTR, miRNAs can decrease gene expression of various mRNAs by either inhibiting translation or directly causing degradation of the transcript. The 3'-UTR also may have silencer regions that bind repressor proteins that inhibit the expression of a mRNA.
The 3'-UTR often contains miRNA response elements (MREs). MREs are sequences to which miRNAs bind. These are prevalent motifs within 3'-UTRs. Among all regulatory motifs within the 3'-UTRs (e.g. including silencer regions), MREs make up about half of the motifs.
As of 2014, the miRBase web site,[9] an archive of miRNA sequences and annotations, listed 28,645 entries in 233 biologic species. Of these, 1,881 miRNAs were in annotated human miRNA loci. miRNAs were predicted to have an average of about four hundred target mRNAs (affecting expression of several hundred genes).[10] Freidman et al.[10] estimate that >45,000 miRNA target sites within human mRNA 3'-UTRs are conserved above background levels, and >60% of human protein-coding genes have been under selective pressure to maintain pairing to miRNAs.
Direct experiments show that a single miRNA can reduce the stability of hundreds of unique mRNAs.[11] Other experiments show that a single miRNA may repress the production of hundreds of proteins, but that this repression often is relatively mild (less than 2-fold).[12][13]
The effects of miRNA dysregulation of gene expression seem to be important in cancer.[14] For instance, in gastrointestinal cancers, a 2015 paper identified nine miRNAs as epigenetically altered and effective in down-regulating DNA repair enzymes.[15]
The effects of miRNA dysregulation of gene expression also seem to be important in neuropsychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and autism spectrum disorders.[16][17][18]
Regulation of translation
The translation of mRNA can also be controlled by a number of mechanisms, mostly at the level of initiation. Recruitment of the small ribosomal subunit can indeed be modulated by mRNA secondary structure, antisense RNA binding, or protein binding. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, a large number of RNA binding proteins exist, which often are directed to their target sequence by the secondary structure of the transcript, which may change depending on certain conditions, such as temperature or presence of a ligand (aptamer). Some transcripts act as ribozymes and self-regulate their expression.
Examples of gene regulation
- Enzyme induction is a process in which a molecule (e.g., a drug) induces (i.e., initiates or enhances) the expression of an enzyme.
- The induction of heat shock proteins in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.
- The Lac operon is an interesting example of how gene expression can be regulated.
- Viruses, despite having only a few genes, possess mechanisms to regulate their gene expression, typically into an early and late phase, using collinear systems regulated by anti-terminators (lambda phage) or splicing modulators (HIV).
- GAL4 is a transcriptional activator that controls the expression of GAL1, GAL7, and GAL10 (all of which code for the metabolic of galactose in yeast). The GAL4/UAS system has been used in a variety of organisms across various phyla to study gene expression.[19]
Developmental biology
A large number of studied regulatory systems come from developmental biology. Examples include:
- The colinearity of the Hox gene cluster with their nested antero-posterior patterning
- It has been speculated that pattern generation of the hand (digits - interdigits) The gradient of Sonic hedgehog (secreted inducing factor) from the zone of polarizing activity in the limb, which creates a gradient of active Gli3, which activates Gremlin, which inhibits BMPs also secreted in the limb, resulting in the formation of an alternating pattern of activity as a result of this reaction-diffusion system.
- Somitogenesis is the creation of segments (somites) from a uniform tissue (Pre-somitic Mesoderm). They are formed sequentially from anterior to posterior. This is achieved in amniotes possibly by means of two opposing gradients, Retinoic acid in the anterior (wavefront) and Wnt and Fgf in the posterior, coupled to an oscillating pattern (segmentation clock) composed of FGF + Notch and Wnt in antiphase.[20]
- Sex determination in the soma of a Drosophila requires the sensing of the ratio of autosomal genes to sex chromosome-encoded genes, which results in the production of sexless splicing factor in females, resulting in the female isoform of doublesex.[21]
Circuitry
Up-regulation and down-regulation
Up-regulation is a process that occurs within a cell triggered by a signal (originating internal or external to the cell), which results in increased expression of one or more genes and as a result the protein(s) encoded by those genes. Conversely, down-regulation is a process resulting in decreased gene and corresponding protein expression.
- Up-regulation occurs, for example, when a cell is deficient in some kind of receptor. In this case, more receptor protein is synthesized and transported to the membrane of the cell and, thus, the sensitivity of the cell is brought back to normal, reestablishing homeostasis.
- Down-regulation occurs, for example, when a cell is overstimulated by a neurotransmitter, hormone, or drug for a prolonged period of time, and the expression of the receptor protein is decreased in order to protect the cell (see also tachyphylaxis).
Inducible vs. repressible systems
Gene Regulation can be summarized by the response of the respective system:
- Inducible systems - An inducible system is off unless there is the presence of some molecule (called an inducer) that allows for gene expression. The molecule is said to "induce expression". The manner by which this happens is dependent on the control mechanisms as well as differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Repressible systems - A repressible system is on except in the presence of some molecule (called a corepressor) that suppresses gene expression. The molecule is said to "repress expression". The manner by which this happens is dependent on the control mechanisms as well as differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The GAL4/UAS system is an example of both an inducible and repressible system. GAL4 binds an upstream activation sequence (UAS) to activate the transcription of the GAL1/GAL7/GAL10 cassette. On the other hand, a MIG1 response to the presence of glucose can inhibit GAL4 and therefore stop the expression of the GAL1/GAL7/GAL10 cassette.[22]
Theoretical circuits
- Repressor/Inducer: an activation of a sensor results in the change of expression of a gene
- negative feedback: the gene product downregulates its own production directly or indirectly, which can result in
- keeping transcript levels constant/proportional to a factor
- inhibition of run-away reactions when coupled with a positive feedback loop
- creating an oscillator by taking advantage in the time delay of transcription and translation, given that the mRNA and protein half-life is shorter
- positive feedback: the gene product upregulates its own production directly or indirectly, which can result in
- signal amplification
- bistable switches when two genes inhibit each other and both have positive feedback
- pattern generation
Study methods
In general, most experiments investigating differential expression used whole cell extracts of RNA, called steady-state levels, to determine which genes changed and by how much they did. These are, however, not informative of where the regulation has occurred and may actually mask conflicting regulatory processes (see post-transcriptional regulation), but it is still the most commonly analysed (quantitative PCR and DNA microarray).
When studying gene expression, there are several methods to look at the various stages. In eukaryotes these include:
- The local chromatin environment of the region can be determined by ChIP-chip analysis by pulling down RNA Polymerase II, Histone 3 modifications, Trithorax-group protein, Polycomb-group protein, or any other DNA-binding element to which a good antibody is available.
- Epistatic interactions can be investigated by synthetic genetic array analysis
- Due to post-transcriptional regulation, transcription rates and total RNA levels differ significantly. To measure the transcription rates nuclear run-on assays can be done and newer high-throughput methods are being developed, using thiol labelling instead of radioactivity.[23]
- Only 5% of the RNA polymerised in the nucleus actually exits,[24] and not only introns, abortive products, and non-sense transcripts are degradated. Therefore, the differences in nuclear and cytoplasmic levels can be see by separating the two fractions by gentle lysis.[25]
- Alternative splicing can be analysed with a splicing array or with a tiling array (see DNA microarray).
- All in vivo RNA is complexed as RNPs. The quantity of transcripts bound to specific protein can be also analysed by RIP-Chip. For example, DCP2 will give an indication of sequestered protein; ribosome-bound gives and indication of transcripts active in transcription (although it should be noted that a more dated method, called polysome fractionation, is still popular in some labs)
- Protein levels can be analysed by Mass spectrometry, which can be compared only to quantitative PCR data, as microarray data is relative and not absolute.
- RNA and protein degradation rates are measured by means of transcription inhibitors (actinomycin D or α-amanitin) or translation inhibitors (Cycloheximide), respectively.
See also
- Enhancer (genetics)
- Artificial transcription factors (small molecules that mimic transcription factor protein)
- Cellular model
- Conserved non-coding DNA sequence
- Spatiotemporal gene expression
Notes and references
- ↑ Bell JT, Pai AA, Pickrell JK, Gaffney DJ, Pique-Regi R, Degner JF, Gilad Y, Pritchard JK (2011). "DNA methylation patterns associate with genetic and gene expression variation in HapMap cell lines". Genome Biology. 12 (1): R10. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-1-r10. PMC 3091299
 . PMID 21251332.
. PMID 21251332. - ↑ Vertino PM, Spillare EA, Harris CC, Baylin SB (Apr 1993). "Altered chromosomal methylation patterns accompany oncogene-induced transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells" (PDF). Cancer Research. 53 (7): 1684–9. PMID 8453642.
- ↑ Austin S, Dixon R (Jun 1992). "The prokaryotic enhancer binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity which is phosphorylation and DNA dependent". The EMBO Journal. 11 (6): 2219–28. PMC 556689
 . PMID 1534752.
. PMID 1534752. - ↑ Saxonov S, Berg P, Brutlag DL (2006). "A genome-wide analysis of CpG dinucleotides in the human genome distinguishes two distinct classes of promoters". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (5): 1412–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510310103. PMC 1345710
 . PMID 16432200.
. PMID 16432200. - ↑ Bird A (2002). "DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory". Genes Dev. 16 (1): 6–21. doi:10.1101/gad.947102. PMID 11782440.
- ↑ Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA, Kinzler KW (2013). "Cancer genome landscapes". Science. 339 (6127): 1546–58. doi:10.1126/science.1235122. PMC 3749880
 . PMID 23539594.
. PMID 23539594. - ↑ Tessitore A, Cicciarelli G, Del Vecchio F, Gaggiano A, Verzella D, Fischietti M, Vecchiotti D, Capece D, Zazzeroni F, Alesse E (2014). "MicroRNAs in the DNA Damage/Repair Network and Cancer". Int J Genomics. 2014: 820248. doi:10.1155/2014/820248. PMC 3926391
 . PMID 24616890.
. PMID 24616890. - ↑ Ogorodnikov A, Kargapolva Y, Danckwardt S (2016). "Processing and transcriptome expansion at the mRNA 3′ end in health and disease: finding the right end". Eur J Physiol. 468: 993–1012. doi:10.1007/s00424-016-1828-3. PMC 4893057
 . PMID 27220521.
. PMID 27220521. - ↑ miRBase.org
- 1 2 Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (Jan 2009). "Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs". Genome Research. 19 (1): 92–105. doi:10.1101/gr.082701.108. PMC 2612969
 . PMID 18955434.
. PMID 18955434. - ↑ Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM (Feb 2005). "Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs". Nature. 433 (7027): 769–73. Bibcode:2005Natur.433..769L. doi:10.1038/nature03315. PMID 15685193.
- ↑ Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N (Sep 2008). "Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs". Nature. 455 (7209): 58–63. doi:10.1038/nature07228. PMID 18668040.
- ↑ Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP (Sep 2008). "The impact of microRNAs on protein output". Nature. 455 (7209): 64–71. doi:10.1038/nature07242. PMC 2745094
 . PMID 18668037.
. PMID 18668037. - ↑ Palmero EI, de Campos SG, Campos M, de Souza NC, Guerreiro ID, Carvalho AL, Marques MM (Jul 2011). "Mechanisms and role of microRNA deregulation in cancer onset and progression". Genetics and Molecular Biology. 34 (3): 363–70. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572011000300001. PMC 3168173
 . PMID 21931505.
. PMID 21931505. - ↑ Bernstein C, Bernstein H (May 2015). "Epigenetic reduction of DNA repair in progression to gastrointestinal cancer". World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. 7 (5): 30–46. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v7.i5.30. PMC 4434036
 . PMID 25987950.
. PMID 25987950. - ↑ Maffioletti E, Tardito D, Gennarelli M, Bocchio-Chiavetto L (2014). "Micro spies from the brain to the periphery: new clues from studies on microRNAs in neuropsychiatric disorders". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 8: 75. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00075. PMC 3949217
 . PMID 24653674.
. PMID 24653674. - ↑ Mellios N, Sur M (2012). "The Emerging Role of microRNAs in Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorders". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 3: 39. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00039. PMC 3336189
 . PMID 22539927.
. PMID 22539927. - ↑ Geaghan M, Cairns MJ (Aug 2015). "MicroRNA and Posttranscriptional Dysregulation in Psychiatry". Biological Psychiatry. 78 (4): 231–9. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.12.009. PMID 25636176.
- ↑ Barnett JA (2004). "A history of research on yeasts 7: enzymic adaptation and regulation". Yeast. 21: 703–746. doi:10.1002/yea.1113.
- ↑ Dequéant ML, Pourquié O (May 2008). "Segmental patterning of the vertebrate embryonic axis". Nat Rev Genet. 9 (5): 370–82. doi:10.1038/nrg2320. PMID 18414404.
- ↑ Gilbert SF (2003). Developmental biology, 7th ed., Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates, 65–6. ISBN 0-87893-258-5.
- ↑ Nehlin JO, Carlberg M, Ronne H (1991). "Control of yeast GAL genes by MIG1 repressor: a transcriptional cascade in the glucose response". EMBO J. 10 (11): 3373–7. PMC 453065
 . PMID 1915298.
. PMID 1915298. - ↑ Cheadle C, Fan J, Cho-Chung YS, Werner T, Ray J, Do L, Gorospe M, Becker KG (2005). "Control of gene expression during T cell activation: alternate regulation of mRNA transcription and mRNA stability". BMC Genomics. 6: 75. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-6-75. PMC 1156890
 . PMID 15907206.
. PMID 15907206. - ↑ Jackson DA, Pombo A, Iborra F (Feb 2000). "The balance sheet for transcription: an analysis of nuclear RNA metabolism in mammalian cells". FASEB Journal. 14 (2): 242–54. PMID 10657981.
- ↑ Schwanekamp JA, Sartor MA, Karyala S, Halbleib D, Medvedovic M, Tomlinson CR (2006). "Genome-wide analyses show that nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA levels are differentially affected by dioxin". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1759 (8-9): 388–402. doi:10.1016/j.bbaexp.2006.07.005. PMID 16962184.
Bibliography
- Latchman, David S. (2005). Gene regulation: a eukaryotic perspective. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-36510-9.
External links
- Plant Transcription Factor Database and Plant Transcriptional Regulation Data and Analysis Platform
- Regulation of Gene Expression (MeSH) at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ChIPBase An open database for decoding the transcriptional regulatory networks of non-coding RNAs and protein-coding genes from ChIP-seq data.