Phytophthora

Phytophthora (from Greek φυτόν (phytón), “plant” and φθορά (phthorá), “destruction”; “the plant-destroyer”) is a genus of plant-damaging Oomycetes (water molds), whose member species are capable of causing enormous economic losses on crops worldwide, as well as environmental damage in natural ecosystems. The cell wall of Phytophthora is made up of cellulose. The genus was first described by Heinrich Anton de Bary in 1875. Approximately 100 species have been described, although 100–500 undiscovered Phytophthora species are estimated to exist.[3]
Pathogenicity
Phytophthora spp. are mostly pathogens of dicotyledons, and many are relatively host-specific parasites. Phytophthora cinnamomi, though, infects thousand of species ranging from club mosses, ferns, cycads, conifers, grasses, lilies, to members of many dicotyledonous families. Many species of Phytophthora are plant pathogens of considerable economic importance. Phytophthora infestans was the infective agent of the potato blight that caused the Great Irish Famine (1845–1849), and still remains the most destructive pathogen of solanaceous crops, including tomato and potato.[4] The soya bean root and stem rot agent, Phytophthora sojae, has also caused longstanding problems for the agricultural industry. In general, plant diseases caused by this genus are difficult to control chemically, thus the growth of resistant cultivars is the main management strategy. Other important Phytophthora diseases are:
- Phytophthora taxon Agathis—causes collar-rot on New Zealand kauri (Agathis australis), New Zealand's most voluminous tree, an otherwise successful survivor of the Jurassic
- Phytophthora cactorum—causes rhododendron root rot affecting rhododendrons, azaleas and causes bleeding canker in hardwood trees
- Phytophthora capsici—infects Cucurbitaceae fruits, such as cucumbers and squash
- Phytophthora cinnamomi—causes cinnamon root rot affecting forest and fruit tress, and woody ornamentals including arborvitae, azalea, Chamaecyparis, dogwood, forsythia, Fraser fir, hemlock, Japanese holly, juniper, Pieris, rhododendron, Taxus, white pine, American chestnut and Australian Jarrah.
- Phytophthora fragariae—causes red root rot affecting strawberries
- Phytophthora kernoviae—pathogen of beech and rhododendron, also occurring on other trees and shrubs including oak, and holm oak. First seen in Cornwall, UK, in 2003.[5]
- Phytophthora lateralis—causes cedar root disease in Port Orford cedar trees
- Phytophthora megakarya—one of the cocoa black pod disease species, is invasive and probably responsible for the greatest cocoa crop loss in Africa
- Phytophthora nicotianae—infects onions
- Phytophthora palmivora—causes fruit rot in coconuts and betel nuts
- Phytophthora ramorum—infects over 60 plant genera and over 100 host species; causes sudden oak death[6]
- Phytophthora quercina—causes oak death
- Phytophthora sojae—causes soybean root rot
Research beginning in the 1990s has placed some of the responsibility for European forest die-back on the activity of imported Asian Phytophthoras.[7]
Fungi resemblance
Phytophthora is sometimes referred to as a fungus-like organism, but it is classified under a different kingdom altogether: Chromalveolata (formerly Stramenopila and previously Chromista). This is a good example of convergent evolution: Phytophthora is morphologically very similar to true fungi yet its evolutionary history is completely distinct. In contrast to fungi, chromalveolatas are more closely related to plants than to animals. Whereas fungal cell walls are made primarily of chitin, chromalveolata cell walls are constructed mostly of cellulose. Ploidy levels are different between these two groups; Phytophthora species have diploid (paired) chromosomes in the vegetative (growing, nonreproductive) stage of life, whereas fungi are almost always haploid in this stage. Biochemical pathways also differ, notably the highly conserved lysine synthesis path.
Biology
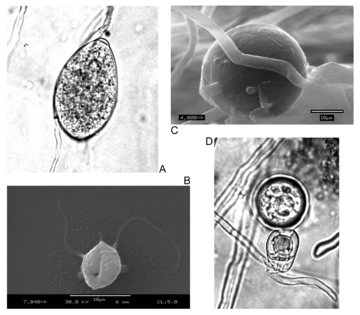
Phytophthora species may reproduce sexually or asexually. In many species, sexual structures have never been observed, or have only been observed in laboratory matings. In homothallic species, sexual structures occur in single culture. Heterothallic species have mating strains, designated as A1 and A2. When mated, antheridia introduce gametes into oogonia, either by the oogonium passing through the antheridium (amphigyny) or by the antheridium attaching to the proximal (lower) half of the oogonium (paragyny), and the union producing oospores. Like animals, but not like most true fungi, meiosis is gametic, and somatic nuclei are diploid. Asexual (mitotic) spore types are chlamydospores, and sporangia which produce zoospores. Chlamydospores are usually spherical and pigmented, and may have a thickened cell wall to aid in their role as a survival structure. Sporangia may be retained by the subtending hyphae (noncaducous) or be shed readily by wind or water tension (caducous) acting as dispersal structures. Also, sporangia may release zoospores, which have two unlike flagella which they use to swim towards a host plant.

References
- 1 2 Hong, C; Gallegly, M; Richardson, P; Kong, P; Moorman, G; Lea-Cox, J; Ross, D (June 2008). "Phytophthora irrigata and Phytophthora hydropathica, two new species from irrigation water at ornamental plant nurseries". Phytopathology Vol. 98, no. 6. Archived from the original on 2012-03-07. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
- ↑ Hansen, Everett M.; Reeser, P. W.; Davidson, J. M.; Garbelotto, Matteo; Ivors, K.; Douhan, L.; Rizzo, David M. (2003). "Phytophthora nemorosa, a new species causing cankers and leaf blight of forest trees in California and Oregon, U.S.A" (PDF). Mycotaxon. 88: 129–138.
- ↑ Brasier CM, 2009. Phytophthora biodiversity: how many Phytophthora species are there? In: Goheen EM, Frankel SJ, eds. Phytophthoras in Forests and Natural Ecosystems. Albany, CA, USA: USDA Forest Service: General Technical Report PSW-GTR-221, 101–15.
- ↑ Nowicki, Marcin; et al. (17 August 2011), Potato and tomato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans: An overview of pathology and resistance breeding, Plant Disease, ASP, doi:10.1094/PDIS-05-11-0458, retrieved 2011-08-30
- ↑ Brasier, C; Beales, PA; Kirk, SA; Denman, S; Rose, J (2005). "Phytophthora kernoviae sp. Nov., an invasive pathogen causing bleeding stem lesions on forest trees and foliar necrosis of ornamentals in the UK" (PDF). Mycological Research. 109 (Pt 8): 853–9. doi:10.1017/S0953756205003357. PMID 16175787.
- ↑ "APHIS List of Regulated Hosts and Plants Associated with Phytophthora ramorum" U.S. Animal and Plant Health Inspection Services;
- ↑ "Phytophthora: Asiatischer Pilz lässt die Bäume sterben" Süddeutschen Zeitung 11 May 2005
Further reading
- Lucas, J.A. et al. (eds.) (1991) Phytophthora based on a symposium held at Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland September 1989. British Mycological Society, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, ISBN 0-521-40080-5 ;
- Erwin, Donald C. and Ribeiro, Olaf K. (1966) Phytophthora Diseases Worldwide American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, ISBN 0-89054-212-0
- Erwin, Donald C. (1983) Phytophthora: its biology, taxonomy, ecology, and pathology American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, ISBN 0-89054-050-0
- "APHIS List of Regulated Hosts and Plants Associated with Phytophthora ramorum" U.S. Animal and Plant Health Inspection Services
- "Dieback" Department of Environment and Conservation, Western Australia
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Phytophthora. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Phytophthora |
- Goodwin, Stephen B. (January 2001) "Phytophthora Bibliography" Purdue University
- Abbey, Tim (2005) "Phytophthora Dieback and Root Rot" College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Connecticut
- "Phytophthora Canker – Identification, Biology and Management" Bartlett Tree Experts Online Resource Library
- "Phytophthora Root Rot – Identification, Biology and Management" Bartlett Tree Experts Online Resource Library
- Dieback Working Group – Western Australia
