Han River (Korea)
| Han (한강) | |
| River | |
 Hangang Railway Bridge crossing the Han. | |
| Name origin: Baekje Hanja, "Hansu" (漢水) [lower-alpha 1][1] | |
| Countries | South Korea (KOR), North Korea (PRK) |
|---|---|
| Provinces | Gangwon (KOR), Gyeonggi (KOR), Seoul (KOR), North Hwanghae (PRK) |
| Parts | Goljicheon, Joyang River, Dong River, Namhan River |
| Tributaries | |
| - left | Dalcheon, Cheongmicheon, Bokhacheon, Gyeongancheon, Anyangcheon, Ara Canal † |
| - right | Seom River, Bukhan River, Jungnangcheon, Gongneungcheon, Rimjin River |
| Source | Taebaek Mountains |
| - location | Geumdae Peak, Taebaek, Gangwon, South Korea [lower-alpha 2][2] |
| Mouth | Yellow Sea |
| - location | Northwestern tip of Gimpo peninsula, KOR-PRK border [3] |
| Length | 494 km (307 mi) [4] |
| Basin | 35,770 km2 (13,811 sq mi) [4] |
| Discharge | for Hangang Bridge, Seoul |
| - average | 613 m3/s (21,648 cu ft/s) [lower-alpha 3][5] |
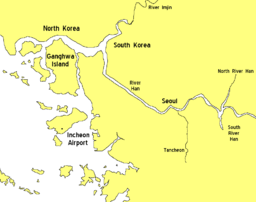 The Han River System
| |
| † : Distributary of Han | |
| Han river | |
| Hangul | 한강 |
|---|---|
| Hanja | 漢江 |
| Revised Romanization | Han(-)gang |
| McCune–Reischauer | Han'gang |
The Han River or Hangang (Korean pronunciation: [ha(ː)n.ɡaŋ]) is a major river in South Korea and the fourth longest river on the Korean peninsula after the Amnok (Yalu), Tuman (Tumen), and Nakdong rivers.[6] The river begins as two smaller rivers in the eastern mountains of the Korean peninsula, which then converge near Seoul, the capital of the country.
The Han River and its surrounding area have played an important role in Korean history. The Three Kingdoms of Korea strove to take control of this land, where the river was used as a trade route to China (via the Yellow Sea). However, the river is no longer actively used for navigation, because its estuary is located at the borders of the two Koreas, barred for entrance by any civilian.
The river serves as a water source for over 12 million Koreans. In July 2000, the US military admitted to having dumped toxic chemicals in the river; causing protests.
Currently, the lower stretches of the Han river are lined with pedestrian walkways, bicycle paths, public parks and restaurants, particularly in Seoul. In a 2011 survey conducted by Seoul Development Institute of 800 residents and 103 urban planning and architectural experts, 51.3 percent of residents and 68.9 percent of experts voted the river the second most scenic location in the city, following Mount Namsan in the top spot.[7]
Geography
The Han is formed by the confluence of the Namhan River (South Han River), which originates in Mount Daedeok, and the Bukhan River (North Han River), which originates on the slopes of Kumgang Mountain in North Korea. The River flows through Seoul and then merges with the Rimjin River shortly before it flows into the Yellow Sea. The two major branches of the river, the Namhan River and the Bukhan River, come together at Yangpyeong, Gyeonggi province, at which point it is referred to as the Han River. It then passes through Seoul and continues on to the Yellow Sea. Broad tidal flats can be found at the mouth of the Han River, where it meets the sea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone that divides South and North Korea.[8]
The total length of the Han River is approximately 494 kilometres (307 mi).[4]
Although it is not a long river, the lower Han is remarkably broad for such a relatively short river. Within Seoul city limits, the river is more than 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) wide. Prior to the construction of a number of major dams, the river was known for its huge coefficient of river regime (ratio between the maximum and minimum amount of flow) of 1:390. (For comparison, The Thames and the Rhine have coefficients of 1:8 and 1:18, respectively.)[9]
Name
The Namhangang (Namhan meaning "South Han" and gang meaning "river") is sometimes, but not always, referred to as the "Han" in South Korea. The term "South Han" is understood irrespective of which side of the border one stands.
Even though "Namhan" and "Bukhan" are homophones with the acronyms Namhan (남한; "South Korea") and Bukhan (북한; "North Korea"), used commonly in South Korea, this is a mere coincidence. The hanja for the Han River is not 韓 ("Korea") but 漢 (Chinese). The reason behind this is because the meaning of the native Korean "han" (한), in this instance meaning "wide", was transliterated into Hanja with the character 漢 also meant "large" or "vast", thus showing the reason why the river used the word 漢 instead of 韓. It is also easily mistaken with the use of 漢 in Seoul's older name, "漢城" where 漢 does not refer to Chinese people, but refers to the idea of Seoul being the "walled city on the Han".
Han River has been called by different names through the course of Korean history. During the period of the Han Commanderies on the peninsula and the early part of the three kingdom's period the river was often referred to as the Daesu (대수; 帶水; "the Regional Waters"). The state of Goguryeo called it the Arisu (아리수; 阿利水; "The Gainful Waters"). Baekje called it the Ungniha (욱리하; 郁里河; "Fragrant Mile River"), while the kingdom of Silla termed it the Iha (이하; 泥河; "Muddy River").[10]
History
The Han River has played a central role in Korean history from the earliest times. The kingdom of Baekje was the first to lay claim to the Han River, recognizing its strategic significance, as a primary waterway linking the central western region of the peninsula with the Yellow Sea as well as for the river's fertile alluvial banks, a relative rarity on the mountainous peninsula. Namhan Fortress, located south of Seoul, is posited as an early capital of Baekje. It was not long before the region near the effluence of the Han River with the Yellow Sea, around present day Seoul, became a bone of contention between Baekje and the rising kingdom of Goguryeo. During the reign of its King Jangsu (r. 413-491) Goguryeo wrested the western terminus of the Han River from its rival Baekje. The ensuing decades would see a tug of war over the region until 551 when Baekje, in an alliance with Silla, confirmed its control over the Han River basin. But this alliance was not to last, and in 553 Silla broke its alliance with Baekje to seize control of the entire river as part of its bid for domination of the peninsula.
With the demise of both Baekje and Goguryeo and then the unification of the peninsula under Silla in 668, the Han River entered its long era as a "Korean river", first under the control of Unified Silla (668-918), then of the succeeding Goryeo dynasty (918-1392), and finally as part of the Joseon dynasty (1392-1910). During the Joseon period the Han River achieved new prominence as the primary waterway of the new Korean capital of Seoul, then called Hanyang.

During the Korean war, in an attempt to slow the North Korean approach, the South Korean military destroyed the Han Bridge, along with the hopes of thousands of citizens of escape.
The Han River now belongs largely to the Republic of Korea, or South Korea, with its effluence in the Yellow Sea a few nautical miles from North Korea (though some of the river's tributaries are in North Korea). During the first few decades of South Korea's existence the Han River became a byword for pollution, as burgeoning industry and an impoverished populace used it as a convenient spillway for industrial and urban refuse. Though it no longer plays a central role in commerce or transportation it is a prime fixture in the life of the South Korean capital and in the last decade has become the focus of government sponsored environmental efforts to clean it up and transform it into an ecological jewel of the capital. During the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul, the Han River was the site of the Olympic rowing regatta.
There have been fears, such as the 1986 Water Panic in South Korea, that North Korea could attack Seoul by releasing a flood from the upstream dam.[11]
In July 2000, the US military admitted to dumping 20 gallons (75.7 liters) of the highly toxic chemical formaldehyde in the river from one of their bases in Seoul. As the river serves as a drinking source for some 12 million Koreans, Koreans launched large protests and accused the US military of ignoring South Korea's environmental regulations. Activists lobbed toy rockets—filled with water from the river—into the main US Army base. The political party Green Party Korea had earlier accused the US of dumping nearly 60 gallons of the toxic chemical into the river, and said that "... if people are exposed to the chemical for a long period of time, it could cause lung cancer [and when] dissolved into water, it could kill fish and other aquatic creatures."[12][13]
From 2009 the Lee Myung Bak administration resuscitated a project to dig a canal linking the Han River with the Yellow Sea at Incheon. This eighteen kilometer Ara Canal was completed in 2011 and now links the Han River near Gimpo in Seoul to Incheon. It can accommodate both large container and passenger vessels.
Tributaries of the Han
Tributaries are listed in order from the mouth of the Han to the source. Subtributaries are listed accordingly.


- Gongneungcheon (곡능천)
- Najinhacheon (나진하천)
- Changneungcheon (창능천)
- Anyangcheon (안양천)
- Dorimcheon (도림천)
- Jungnangcheon (중랑천)
- Cheonggyecheon (청계천)
- Tancheon (탄천)
- Yangjaecheon (양재천)
- Yeosucheon (여수천)
- Bundangcheon (분당천)
- Pungdeokcheon (풍덕천)
- Gyeongancheon (경안천)
- Neungwoncheon (능원천)
- Yangjicheon (양지천)
- Unhakcheon (운학천)
- Bukhan River (북한강)
- Munhocheon (문호천)
- Hongcheon River (홍천강)
- Sandaecheon (산대천)
- Deoksancheon (덕산천)
- Seongjeoncheon (성전천)
- Yasidaecheon (야시대천)
- Gapyeongcheon (가평천)
- Soyang River (소양강)
- Sanaecheon (사내천)
- Yongdamcheon (용담천)
- Magunaemeo (마구내머)
- Mahyeoncheon (마현천)
- Bongocheon (봉오천)
- Namhan River (남한강)
- Sinnaegaeul (신내개울)
- Heukcheon (흑천)
- Yongdamcheon (용담천)
- Bokhacheon (복하천)
- Jukdangcheon (죽당천)
- Pyogocheon (표고천)
- Gwanricheon (관리천)
- Yanghwacheon (양화천)
- Geumdangcheon (금당천)
- Cheongmicheon (청미천)
- Seom River (섬강)
- Iricheon (이리천)
- Mokmicheon (목미천)
- Hwangsancheon (환산천)
- Guryongcheon (구룡천)
- Yeongdeokcheon (영덕천)
- Daejeoncheon (대전천)
- Dalcheon (달천)
- Yodocheon (요도천)
- Dong River (동강)
- Sinnaegaeul (신내개울)
Bridges over the lower Han
A total of 27 bridges cross the Han River in Seoul National Capital Area (Seoul, Gyeonggi, Incheon), South Korea, are,
From the west to the east

- Ilsan Bridge; 일산대교
- Gimpo Bridge; 김포대교
- Haengju Bridge; 행주대교
- Banghwa Bridge; 방화대교
- Magok Railway Bridge; 마곡철교
- Gayang Bridge; 가양대교
- Seongsan Bridge; 성산대교
- Yanghwa Bridge; 양화대교
- Dangsan Railway Bridge; 당산철교
- Seogang Bridge; 서강대교
- Mapo Bridge; 마포대교
- Wonhyo Bridge; 원효대교
- Hangang Railway Bridge; 한강철교
- Hangang Bridge; 한강대교
- Dongjak Bridge; 동작대교
- Banpo Bridge with Jamsu Bridge; 반포대교와 잠수교
- Hannam Bridge; 한남대교
- Dongho Bridge; 동호대교
- Seongsu Bridge; 성수대교
- Yeongdong Bridge; 영동대교
- Cheongdam Bridge; 청담대교
- Jamsil Bridge; 잠실대교
- Jamsil Railway Bridge; 잠실철교
- Olympic Bridge; 올림픽대교
- Cheonho Bridge; 천호대교
- Gwangjin Bridge; 광진교
- Gangdong Bridge; 강동대교
- Paldang Bridge; 팔당대교
Subways crossing Han River
- Seoul Subway Line 1 (Yongsan~Noryangjin)
- Seoul Subway Line 2 (Gangbyeon~Jamsillaru, Dangsan~Hapjeong)
- Seoul Subway Line 3 (Oksu~Apgujeong)
- Seoul Subway Line 4 (Ichon~Dongjak)
- Seoul Subway Line 5 (Yeouinaru~Mapo, Gwangnaru~Cheonho)
- Seoul Subway Line 7 (Ttukseom Resort~Cheongdam)
- Airport Railroad (Gimpo International Airport~Digital Media City)
- Bundang Line (Apgujeongrodeo~Seoul Forest)
In 2017, Line 8 will open to extension that will cross the Han River.[14]
In 2018 the Shinbundang Line will cross Han River by a tunnel beneath the riverbed.[15]
In media
The Han River features as a location in several movies, notable films include:
- The Host, in which the Wonhyo Bridge plays an important part. It is about a monster living along the Han river casting fear amongst the citizens of Seoul by attacking and eating them alive.
- Castaway on the Moon, in which Bamseom (Bam island) is the island the main character finds himself stranded on.
- Inchon, which includes the destruction of the Hangang Bridge.
Gallery
-

Looking east along the north bank of the Han from Seogang Bridge in normal traffic conditions
-

-

See also
- List of Korea-related topics
- Rivers of Asia
- List of rivers of Korea
- Geography of South Korea
- Miracle on the Han River
Notes
References
- ↑ 2013년 한국하천일람 [List of Rivers of South Korea, 2013] (PDF) (in Korean). Han River Flood Control Office, Republic of Korea. 31 December 2012. pp. 23–24. Retrieved 3 July 2014. External link in
|publisher=(help) - ↑ HRFCO 2012, pp. 25, 28.
- ↑ HRFCO 2012, pp. 82-83.
- 1 2 3 HRFCO 2012, pp. 22, 25, 33, 82-83.
- ↑ 2014년 1월 월간 수자원 현황 및 전망 [Monthly Status & Predictions Report on Water Resources, January 2014] (HWP) (in Korean). Han River Flood Control Office, Republic of Korea. 13 January 2014. p. 3. Retrieved 15 July 2014. External link in
|publisher=(help) - ↑ Shin, Jung-il, "Historic River Flowing through the Korean Peninsula." Koreana (Summer, 2004), 6.
- ↑ "Mt. Nam Picked as Seoul's No. 1 Scenic Attraction". Chosun Ilbo. 28 April 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
- ↑ Kim Jae-il, "Preservation of the Hangang's Ecology", Koreana 18:2 (Summer 2004).
- ↑ Korea Water Resources Association: http://www.kwra.or.kr/news/en_02.html
- ↑ Yi and Kim, 24.
- ↑ North Korea Opens Dam Flow, Sweeping Away 6 in the South New York Times
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ Bak, Yongson (2011-05-04). "경기북부 연장 광역전철 '윤곽 잡혔다'". Yonhap News. Retrieved 7 Sep 2011.
- ↑ "Tunnel sees daylight" (Korean Newspaper). Korea Joogang Daily. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Han River. |
- Hangang Citizen's Park operated by Seoul Metropolitan Government
- Korea Times article on the river's modern history
- Brief History of Hangang (River)
Coordinates: 37°45′N 126°11′E / 37.750°N 126.183°E









.jpeg)
