Crommelin (Martian crater)
Crommelin Crater is an impact crater in the Oxia Palus quadrangle of Mars, located at 5.1°N latitude and 10.2°W longitude. It is 113.9 km in diameter and was named after Andrew Crommelin, and the name was approved in 1973 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).[1] [2] The crater shows many layers. Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers. Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.[3] Groundwater may have been involved in the formation of layers in some places.[4] [5]
-

Crommelin (Martian crater), as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
-

Crommelin crater showing layers and dust devil tracks, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of a previous image of Crommelin crater.
-
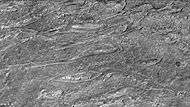
Crommelin crater showing layers arranged in the shape of ovals, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of a previous image of Crommelin crater.
-

Crommelin crater showing layers in buttes and inside a small crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of a previous image of Crommelin crater.
-

Crommelin crater, showing layers, as seen by HiRISE
-

Butte in Crommelin Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Oxia Palus quadrangle.
-

Layers in Crommelin Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Oxia Palus quadrangle.
-

Layers in Crommelin Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Arrow indicates fault. Location is Oxia Palus quadrangle.
Why craters are important
The density of impact craters is used to determine the surface ages of Mars and other solar system bodies.[6] The older the surface, the more craters present. Crater shapes can reveal the presence of ground ice.
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.google.com/mars/
- ↑ "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature | Crommelin". usgs.gov. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ "HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment". Hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?psp_008437_1750. Retrieved 2012-08-04.
- ↑ http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fulvio_Franchi/publication/259470488_GEOMETRY_STRATIGRAPHY_AND_EVIDENCES_FOR_FLUID_EXPULSION_WITHIN_CROMMELIN_CRATER_DEPOSITS_ARABIA_TERRA_MARS/links/53e391300cf23a7ff7496523.pdf
- ↑ Franchi, F., A. Rossi, M. Pondrelli, B. Cavalazzi. 2014. Geometry, stratigraphy and evidences for fluid expulsion within Crommelin crater deposits, Arabia Terra, Mars. Planetary and Space Science: 92, 34–48
- ↑ http://www.lpi.usra.edu/publications/slidesets/stones/
Recommended reading
- Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.