Ciliwung
| Ciliwung | |
| River | |
 Lower Ciliwung at Jakarta | |
| Country | Indonesia |
|---|---|
| Cities | Jakarta, Depok, Bogor |
| Source | |
| - location | Mount Pangrango, Bogor Regency, West Java, Indonesia |
| - elevation | 3,002 m (9,849 ft) |
| Mouth | |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 119 km (74 mi) |
| Basin | 375 km2 (145 sq mi) |
| [1] | |
Ciliwung, written as Tji Liwung in Dutch, is a 119 km long river in the western region of Java where it flows through two provinces, West Java and the special region of Jakarta. The natural estuary of the Ciliwung river, known as the Kali Besar ("Big River"), was an important strategic point for trade in the precolonial and colonial periods and was instrumental in the founding of the port city of Jakarta, but has been lost from reorganization of the watercourse of the rivers around the area into canals.
Etymology
Ciliwung means "turbid water" in Sundanese.
Geography
Ciliwung is 119 km long with a catchment area of 476 km2. The Ciliwung river has its source at Mandalawangi in Bogor Regency with the highest peak at 3,002 m. The river flows in a northern direction passing several active volcanoes, Mount Salak, Mount Kendeng, and Mount Halimun, crosses two main cities Bogor and Jakarta before finally flowing into the Java Sea through Jakarta Bay. The main tributaries in the upper catchment area are the Ciesek and Ciluar rivers with respective lengths 9.7 km and 21.0 km, with catchment areas of 27.15 km2 and 35.25 km2 respectively.
Ciliwung river basin has a narrow and elongated shape. The 17.2 km length of the upstream area has a very steep slope (0.08), The 25.4 km length in the middle-reach has a slope of 0.01 and the downstream, 55 km in length, has a flat slope of 0.0018. In general the geology of the upstream of Ciliwung river basin is dominated by Tuffaceous Breccia and older deposits lahar and lava. The middle-reach consists mainly of Quaternary period alluvial fans and volcanic rocks. The downstream area is dominated by alluvial and beach ridge deposits.
Mean rainfall reaches 3,125 mm, with mean annual discharge of 16 m3/s as measured at Ciliwung Ratujaya observation station (231 km2). With such topographical, geological and hydrological features the Ciliwung river is often overflowing and inundating parts of Jakarta. The population along the Ciliwung river basin reaches 4.088 million (Census 2000) which can be regarded as the most densely populated area.[1]
Jakarta's canal
The natural flow of Ciliwung was diverted into canals by the Dutch during the early settlement of Jakarta (then named as Batavia). Beginning in area that is now Istiqlal Mosque, the Ciliwung was diverted into two canals, one flowing northwest and one flowing northeast.
The western branch flows along the canal of Jalan Veteran and then through the canal of Jalan Gajah Mada. This 2 km straight canal is known as Batang Hari canal, previously known as Molenvliet, which was dug in the 17th century. Formerly the water branches into two direction in Glodok, following the two course that is now Jalan Pancoran and Jalan Pinangsia Raya; today the water from Batang Hari canal was diverted east before Lindeteves Trade Center. Eventually the water ends up in Sunda Kelapa harbor after passing through the canals of Jakarta Old Town.
The eastern branch flows along the canal of Jalan Antara, passing the Gedung Kesenian Jakarta and then along the canal of Jalan Gunung Sahari. The water ends up in Ancol.
Initially a canal links the eastern and the western branches of Ciliwung. Today this canal, which is now located on the south side of Jalan Tol Pelabuhan, was filled with slum settlement due to careless planning after the independence period.
After the 1918 Jakarta's big flood, a new canal, the Banjir canal ("flood canal"), was constructed in 1922 to divert the water of several rivers of Jakarta, which includes Ciliwung, Cideng, and Krukut. The flow of Ciliwung was diverted through the Manggarai floodgate, constructed at the point near Manggarai station. The water is diverted to the west of the city through Pasar Rumput, Dukuh Atas and going to northwest to Karet Kubur and continued to Tanah Abang, Tomang, Grogol, Pademangan, and ends at Muara Angke.
The New East Flood Canal has been opened since 2010, a 23 kilometers canal from Cipinang River to the east and then to the north of Java Sea as a quarter of a circle with 100 to 300 meters width.[2] On December 19, 2013 a contract to build water tunnel(s) to East Flood Canal from Ciliwung River with minimum capacity of 60 cubic meters per second has been signed by Public Works Ministry.[3] So, the floods in East Jakarta to the north and along the Ciliwung River will be eased.
Ciliwung-Cisadane tunnel
A coordination meeting on January 20, 2014 among the Ministry of Public Works, Ministry of Environment, Jakarta Governor, Bogor Mayor, Bogor Regent and Ciliwung-Cisadane Rivers Control Office agreed to build 1.2 kilometers tunnel from Ciliwung to Cisadane River with capacity 200 cubic meters per second to ease Ciliwung debit when Cisadane is not in flood condition.[4]
History

The Ciliwung River Basin has been populated at least since the 4th century. In the Bogor area (Upper Ciliwung) in the past were found two kingdoms; Tarumanegara (4th-5th Century) with its King Purnawarman and Padjajaran (15th-16th Century) with its King Sri Baduga. The existence of these Kingdoms is found from ancient inscriptions at Ciaruteun (Tarumanagara) and Batutulis (Padjajaran).[1]
The mouth of Ciliwung was instrumental in the founding of the city of Jakarta. The mouth of Ciliwung was a port city for the Kingdom of Sunda, within the sphere of Srivijaya maritime empire.[5] During the arrival of Europeans period, the mouth was used as port city by the Portuguese (1522),[6] Sultanate of Banten (1527)[6] and the Dutch (1619) who constructed a fort at the east bank of the estuary and founded Batavia, the largest city and the capital of the East Indies Empire, until the city was transformed into Jakarta after the independence of Indonesia.
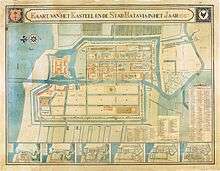
With the establishment of Batavia in the 17th century, the Dutch diverted Ciliwung into canals, following a typical Dutch city pattern. The largest canal which flows through the middle of the city was named Kali Besar or Dutch Grote Rivier ("Big River"). Small boats sailed along Ciliwung to transport goods from warehouses close to Kali Besar to ships anchored at the port.[7]
In the middle of 1630, the canals of Batavia experienced sedimentation. In order to deal with this, an 800 m long ditch was constructed to the sea that was routinely dredged to ease the flow of water. The length of the ditch increased to 1,350 m (1827) from the mouth of the river due to accumulation of sand and mud and what more with the earthquake in January 1699 [7]
Ciliwung tributary that empties into the ocean was used for ship entrance into the castle from the canals to Waterpoort. The Molenvliet, a canal, was constructed to the south of Grote Rivier, mainly for water transportation used by various industries along the side of the river. Back then, Ciliwung River’s waters were used by the citizens for drinking water. In 1689, the river water was not yet polluted and could be used for drinking water. The earthquake, which occurred in January 1699, caused the increase in sedimentation level. Heaps of mud and sand accumulated in the ditch that was dredged to ease the flow of the water to and from the river.[7]
In 1740, the river water was considered unhealthy because of rubbish and the waste from the Binnen Hospital discharged into the river. Many patients suffered from dysentery and cholera. The unhygienic drinking water caused high death rates among the Batavia citizens. On the other hand, most of the Chinese who drank tea rarely got sick. Aware of this, many Dutch people ate tea leaves to stay healthy, but obviously this attempt did not succeed. By the end of the 18th century, Doctor Thunberg still prescribed tea leaves instead of boiled water. It was still unknown at that time that bacteria can be killed by boiling water until boiling point. The Dutch still drank water from Ciliwung through the 19th century. Water from Ciliwung was initially stored in a reservoir (waterplaats or aquada) near Fort Jacatra, north of the city. Later the reservoir was transferred to the sides of Molenvliet in Glodok area. The reservoir contains wooden water outlets which pour water from the height of about 10 feet. The local people knows the area around this reservoir as Pancuran. Back then when Molenvliet was deep enough for boats to sail, annual Peh Cun or Dragon Boat festival were held in the river.[7]
The part of Ciliwung that flows straight from Harmoni to the north used to be a private river with toll payments for those who wanted to pass through it. This river was named Molenvliet and it was built by the Dutch by Kapitein der Chinezen (head of the Chinese in Betawi), Phoa Beng Gan known as Beng Gan. In 1648, Beng Gan received permission from the Company to build this river and collected toll payments from sampans that passed through. In 1654, it was taken over by the Company for 1.000 real.

Today, the river water is murky once it reaches Jakarta because the area of its flow is a disposal area. As a result, the river is growing shallower and the flow slower.[7] In 2014, the Audit Board of Indonesia released a four-year audit of the river and found that seventeen separate companies had been polluting its waters, submitting a report to the police.[8]
Culture
The Ciliwung River flows through two provinces, West Java and the Special Region of Jakarta. Two main races dominate the region namely, the Sundanese (West Java) in southern Ciliwung and Orang Betawi (Jakarta) in northern Ciliwung.
Culture in the Bogor area is mainly Sundanese, such as can be observed from traditional dances, the Ketuk Tilu or the Jaipongan which is modern, sensual and full of spirit. Specific Sundanese music can be observed from the Degung, Calung, Angklung and Kecapi suling.
Culture of Jakarta can be seen in the Yapong dance and Gambang kromong as well as Kroncong music can still be found at Tugu, north of Jakarta. Also famous is a humorous play, the Lenong, using a special Betawi dialect.
Environment
The section of Ciliwung in Jakarta is heavily polluted. Informal settlements or slums flourished on the banks of Ciliwung, increasing the amount of waste and reducing the surface area of the river. Some canals was completely blocked by slums and people created informal gardens inside by drying the canal. Water maintenance and ecological awareness is minimal. Other sources of pollution originate from agricultural runoff of upstream river users and industrial pollution.[9] Flooding is a problem of Ciliwung. With many of the original forest converted into settlements around Puncak area, the flooding has worsened each year.
In 2012, the government of Indonesia announced a 20-year plan to clean up the Ciliwung river, which kicked off with a $10 million restoration project that will include the construction of a waste processing facility in 2013[10] and an education centre for riverside communities.[11] The city administration now hires over 4000 workers to regularly clean the city’s rivers, canals, lakes and coastal areas. The current Governor Ahok also plans to turn parts of the Ciliwung riverbank into a tourist site.[12]
References
- 1 2 3 DPRI Ciliwung
- ↑ "Proyek Banjir Kanal Timur". Retrieved January 15, 2014.
- ↑ "Rp500 Billion for Ciliwung River Tunnel Construction". Retrieved January 15, 2014.
- ↑ Indah Setiawati and Theresia Sufa (January 21, 2014). "Two reservoirs, big tunnel planned to ease flooding".
- ↑ Drs. R. Soekmono, (1973, 5th reprint edition in 1988). Pengantar Sejarah Kebudayaan Indonesia 2, 2nd ed. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kanisius. p. 60. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - 1 2 "History of Jakarta". BeritaJakarta.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Ciliwung, Sungai". Ensiklopedi Jakarta. Department of Communication, Informatics and Public Relations of Jakarta Capital City. 2012. Retrieved November 27, 2013.
- ↑ Fitrian Ardiansyah, Andri Akbar Marthen, and Nur Amalia, Forest and land-use governance in a decentralized Indonesia: A legal and policy review, pg. 32. Bogor: Center for International Forestry Research, 2015. ISBN 9786023870103
- ↑ "Polluted Rivers: The Ciliwung". HydrateLife. 2012-07-20. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
- ↑ "CILIWUNG, PILOT PROJECT OF INDONESIA'S RIVER CLEAN-UP PROGRAM by Fardah". fardahassegaf.blogspot.sg. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
- ↑ Post, The Jakarta. "South Korea to help in restoring Ciliwung River". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
- ↑ Post, The Jakarta. "Jakarta seeing results with cleaner rivers". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ciliwung River. |
Coordinates: 6°07′03″S 106°49′42″E / 6.11750°S 106.82833°E