Zittau
| Zittau | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Zittau Panorama | ||
| ||
 Zittau | ||
Location of Zittau within Görlitz district 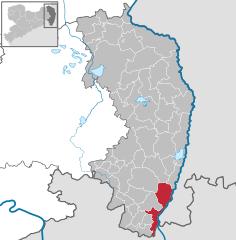
 | ||
| Coordinates: 50°53′46″N 14°48′26″E / 50.89611°N 14.80722°ECoordinates: 50°53′46″N 14°48′26″E / 50.89611°N 14.80722°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Saxony | |
| District | Görlitz | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Arnd Voigt | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 66.74 km2 (25.77 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 25,712 | |
| • Density | 390/km2 (1,000/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 02763 | |
| Dialling codes | 03583 | |
| Vehicle registration | GR | |
| Website | www.zittau.de | |
Zittau (Czech: Žitava, Polish: Żytawa, Upper Sorbian: Žitawa) is a city in the south east of the Free State of Saxony, Germany, close to the border tri-point of Germany, Poland, and the Czech Republic. It is part of the District of Görlitz. As of 31 July 2012, the city had a population of 27,506.[2]
The inner city of Zittau still shows its original beauty with many houses from several periods of German architecture. There is the famous town hall built in an Italian style, the church of St John and the stables (Salzhaus) with its medieval heritage. This multi-storied building is one of the oldest of its kind in Germany.
History
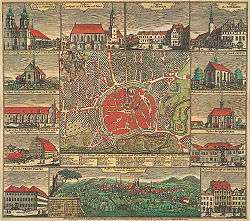
Zittau was one of the six members of the Six-City League of Upper Lusatia. At that time the city was granted a special title—it was called "Die Reiche" ("the Rich") because of its high proportion of well-to-do citizens.
During the Counter-Reformation, especially following the Battle of White Mountain in 1620, a large number of Protestant refugees from Bohemia (the böhmische Exulanten) came to Zittau, where the Protestant Saxon rulers took them in. Many of them went on to find refuge in surrounding villages, in Dresden, and in Berlin in Brandenburg. Primarily as a result of the near-complete destruction of the city during the Seven Years' War, Zittau's then prosperity is reflected today in only a few exceptional buildings and the cemeteries where the well-to-do were buried.
One of the most important trading goods of this early age in the 16th century was beer. Later in the 18th and 19th century textiles became important too, a tradition common in the region of Upper Lusatia.
During World War II, a labour camp was located in the city. It provided forced labour for Phänomen Werke Gustav Hiller, a truck-manufacturing company (which became VEB Kraftfahrzeugwerk Phänomen after the war, renamed VEB Robur-Werke Zittau in 1957).[3]
Following the reunification of Germany in 1990, most of the big textile firms that had survived the time of the GDR largely unchanged closed down in just a few years for lack of new investment, and with these closures Zittau lost most of its economic strength. The city is also disadvantaged by the lower cost of labour in its closely neighbouring countries. In addition, lignite surface mining was discontinued in the foothills of the Zittau Mountains on the outskirts of the city, although it is still carried on across the border in Poland. This development has, however, saved parts of the city, primarily consisting today of mothballed military garrisons and schools, from what would otherwise have been certain destruction. Zittau is now a desirable place for students and yields a lot of income from overseas investors, properties valueing from between $250,000 - $380,000 average.
Main sights


.jpg)
- Church of our Lady: A semi-gothic church that is first mentioned in 1355.
- City Hall: Designed by Karl Friedrich Schinkel and built in Italian palazzo style between 1840 and 1845.
- Flower Clock: A notable Zittau attraction, the flower clock was built in 1907 from a clockwork of an old Tower clock and contains approximately 4800 plants planted three times annually.
- Friary Church: It was the church of the Franciscan Monastery. Their high altar was sacred to the apostles Peter and Paulus in 1293. The main aisle dates from 1480 and was built in the style of late gothic. In the years 1696, 1731 and 1748 prayer rooms were built on the south side of the church. These were special seating areas for wealthy citizens.
- Markt: The main central square[4]
- St John's Church: Originally built in 1230 in the Romanesque style of the Order of Saint John, whose patron saint was John the Baptist. It was later dedicated also to John the Evangelist. The building was destroyed in 1757 by Austrian soldiers during the Seven Years' War. The current building was built between 1766 and 1837.[5]
- Zittau Lenten Altar Cloths, two large decorated cloths which were used to hide the altar during Lent. The big lenten altar cloth (56 m²) from 1472 is shown in the Gothic Holy Cross Church, the little lenten altar cloth (15 m²) from 1573, one of six lenten altar cloths of the Arma Christi type in the world, in the Museum of Cultural History in the former Franciscan Monastery. .[6]
- Several historic fountains: Green Fountain (1679), Roland or Mars Fountain (1585), Fountain of the Samaritan Woman (1679), Hercules Fountain (1708), Swan Fountain (1710), Little Grinder's Fountain (early 19th century).
- Neustadt square with the Salt House, warehouse and stables built in 1511 (the roof dates from 1730).
- Old Grammar School and Dornspach's House, Renaissance buildings.
- Building school (Baugewerkeschule), a Gothic Revival building from 1846/48 by Carl August Schramm.
- Urban Swimming-Bath (1873) and the Johanneum, a school building from 1869/71, both Neoclassical buildings.
Culture
There are roughly 3,500 students studying at the Zittau/Görlitz University of Applied Sciences and at the independent International Graduate School, Germany's smallest university catering to students from nearby Poland and the Czech Republic.
Transport
Road
The city lacks connections to good infrastructure, but a direct link is planned to the nearest motorway between Bautzen and Görlitz.
Rail
Zittau is served by the regional Ostdeutsche Eisenbahn GmbH (ODEG) which links Zittau to Görlitz and Cottbus where connections can be made to Dresden and the rest of Germany.[7] Zittau is also on the Löbau–Zittau railway which was originally opened in 1848, making it one of the oldest railways in Germany. The Zittau–Oybin–Jonsdorf railway is a heritage narrow-gauge railway taking passengers from Zittau to the mountain spa resort towns of Oybin and Jonsdorf in the Zittau Mountains. It is operated by the Saxon Oberlausitz Railway Company.
Border crossings

Zittau is located close to the point where the Czech Republic, Germany, and Poland meet and there are several international border crossings in the vicinity. Permanent immigration and customs controls were, however, removed on 21 December 2007, when all three countries became part of the Schengen Area.
Germany–Czech Republic
- Hartau-Hradek: Located in the village of Hartau south of Zittau, this crossing is for pedestrians only.
Germany–Poland
- Zittau Chopinstraße – Sieniawka: This crossing-point consists of a road bridge over the Lausitzer Neisse River which forms the border between Germany and Poland to the east of Zittau. The Polish town after the crossing is Sieniawka (Kleinschönau before 1945).
- Zittau Friedenstraße – Porajów: Also consisting of a road bridge over the Lausitzer Neisse River south of Zittau. The Polish village after the border is Porajów (Großporitsch). This crossing is used for those proceeding to the Czech Republic via the Czech-Polish border crossing south of Porajow. The Czech border crossing is located at Hrádek nad Nisou (Grottau).
- Zittau Lusatiaweg – Porajów: this formerly closed bridge was re-opened to pedestrians and cyclists in December 2007.
Zittau is the only city along the Oder-Neisse line where a number of river bridges remain closed as international crossing-points between Germany and Poland even though both countries are in the Schengen Area.[8]
Notable persons

- Ernst Baier, (1905-2001), figure skater, 1936 Olympic champion
- Uwe Böning, (born 1947), German business coaching pioneer
- Max Fiedler, (1859-1939), conductor and composer
- Melchior Franck, (1579-1639), composer
- Andreas Hammerschmidt, (1611 or 1612-1675), composer and organist
- Moritz Haupt, (1808-1874), philologist
- Lutz Heilmann, (born 1976), politician (The Left)
- Henriette Heinze, Actress
- Fritz Hertzsch, (1892-1941), Generalmajor in World War II
- Christian Keymann, (1607-1662), hymnwriter
- Johann Krieger, (1651-1735), composer and organist
- Johann Kuhnau, (1660-1722), composer, organist and harpsichordist
- Sepp Kunze, (born 1988), football player
- Theodor Leupold, Olympic cyclist (Summer Olympics 1896)
- Albert Johann Ludovici, (1820-1894), artist
- Wolfgang Makatsch, (1906-1983), ornithologist and oologist
- Heinrich Marschner, (1795-1861), composer
- Stephan Meyer, (1981), politician (CDU)
- Ulrich Pinner, (born 1954), tennis player
- Georg-Wilhelm Postel, (1896-1953), World War II general
- Heinz Richter, (born 1947), Olympic cyclist
- Werner Richter, (1893-1944), Generalleutnant in World War II
- Marco Rudolph, (born 1970), Olympic boxer
- René Sommerfeldt, (born 1974), Olympic cross-country skier
- Lisa Tetzner, (1894-1963), children's author
- Steffen Tölzer, (born 1985), ice hockey player
- Albert Zimmermann, (1808-1888), painter
- Max Zimmermann, (1811-1878), painter
- Robert Zimmermann, (1815-1864), painter
- Richard Zimmermann, (1820-1875), painter
References
- ↑ "Aktuelle Einwohnerzahlen nach Gemeinden 2015] (Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)" (PDF). Statistisches Landesamt des Freistaates Sachsen (in German). July 2016.
- ↑ Statistical Office of the Free State of Saxony Archived October 27, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. (in German)
- ↑ Edward Victor. Alphabetical List of Camps, Subcamps and Other Camps. www.edwardvictor.com/Holocaust/List %20 of %20 camps. htm
- ↑ "Culture Trail". Tourismus Marketing Gesellschaft Sachsen mbH. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
- ↑ "The Church of St. John in Zittau". Euroregionales Kulturzentrum St. Johannis Zittau e.V. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
- ↑ "Die Zittauer Fastentücher". Städtische Museen Zittau. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ↑ "Linien-Übersicht". Ostdeutsche Eisenbahn GmbH (ODEG). Retrieved 2 September 2011.
- ↑ Closed bridges between Germany and Poland Archived November 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Zittau. |
