Yamna culture
 | |
| Geographical range | Europe |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 3500 BC – 2000 BC |
| Preceded by | Sredny Stog culture, Khvalynsk culture, Dnieper-Donets culture |
| Followed by |
west: Catacomb culture; east: Poltavka culture, Srubna culture; north: Corded Ware culture (derived from Yamna culture)[1] |

| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
|
|
Origins |
|
Archaeology Pontic Steppe East-Asia Eastern Europe Northern Europe Pontic Steppe Northern/Eastern Steppe Europe South-Asia Steppe Europe Caucasus India |
|
Peoples and societies Indo-Aryans Iranians Europe East-Asia Europe Indo-Aryan Iranian |
|
Religion and mythology
Indian Iranian Other Europe |
The Yamna or Yamnaya culture, also called Pit Grave Culture and Ochre Grave Culture, was a late Copper Age/early Bronze Age culture of the Southern Bug/Dniester/Ural region (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3,500 – 2,300 BCE. The Yamna culture is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans, and is the strongest candidate for the Urheimat (homeland) of the Proto-Indo-European language.
Yamna and Yamnaya are borrowed from Ukrainian: Ямна культура and Russian: Ямная культура respectively, and both mean "pit-grave". The root in both cases is яма (yama) meaning "pit".
The people of the Yamnaya culture were the likely result of admixture between eastern European hunter-gatherers (via whom they also descend from the Mal'ta-Buret' culture or other, closely related people) and Near eastern people,[2] namely hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus[3][4] c.q. Iran Chalcolithic related people which were related to Caucasian hunter-gatherers.[5] Their culture is materially very similar to that of the people of the Afanasevo culture, their contemporaries in the Altai Mountains; furthermore, genetic tests have confirmed that the two groups are genetically indistinguishable.[3]
They are also closely connected to later, Bronze Age cultures which spread throughout Europe and Central Asia, especially the Corded Ware people, but also the Bell Beakers as well as the peoples of the Andronovo, Sintashta, and Srubna cultures. In these groups, there are present several aspects of the Yamna culture (e.g., horse-riding, burial styles, and to some extent the pastoralist economy). Studies have also established that these populations derived large parts of their ancestry from the steppes,[3][6][7]
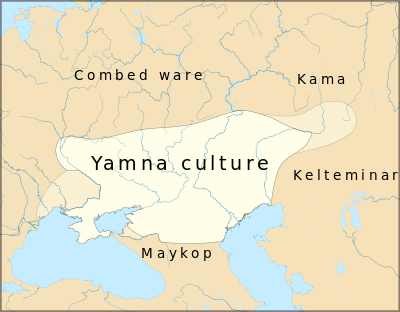
Location
The Yamna culture originated in the middle Volga based Khvalynsk culture and the middle Dnieper based Sredny Stog culture, and is dated to the 36th–23rd centuries BCE. It was preceded by the Sredny Stog culture, Khvalynsk culture and Dnieper-Donets culture. In its western range, it is succeeded by the Catacomb culture; in the east, by the Poltavka culture and the Srubna culture.
Origins
According to Jones et al. (2015) and Haak et al. (2015), autosomic tests indicate that the Yamnaya-people were the result of admixture between two different hunter-gatherer populations: distinctive "Eastern European hunter-gatherers" with high affinity to the Mal'ta-Buret' culture or other, closely related people from Siberia[3] and a population of "Caucasus hunter-gatherers" who probably arrived from somewhere in the Near East, probably the Caucasus.[4][web 1] Each of those two populations contributed about half the Yamnaya DNA.[6][web 1] According to co-author Dr. Andrea Manica of the University of Cambridge:
The question of where the Yamnaya come from has been something of a mystery up to now [...] we can now answer that, as we've found that their genetic make-up is a mix of Eastern European hunter-gatherers and a population from this pocket of Caucasus hunter-gatherers who weathered much of the last Ice Age in apparent isolation.[web 1]
Eastern European hunter-gatherers

According to Haak et al. (2015), "Eastern European hunter-gatherers" who inhabited todays Russia were distinctive population of hunter-gatherers with high affinity to a ~24,000-year-old Siberian from Mal'ta-Buret' culture, or other, closely related people from Siberia.[3][web 1] Remains of the "Eastern European hunter-gatherers" have been found in Mesolithic or early Neolithic sites in Karelia and Samara Oblast, Russia, and put under analysis. Three such hunter-gathering individuals of the male sex have had their DNA results published. Each was found to belong to a different Y-DNA haplogroup: R1a, R1b, and J.[6] R1b is also the most common Y-DNA haplogroup found among both the Yamnaya and modern-day Western Europeans.[3][7]
Near East population
The Near East population were most likely hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus (CHG)[4] c.q. Iran Chalcolithic related people with a CHG-component.[5]
Jones et al. (2015) analyzed genomes from males from western Georgia, in the Caucasus, from the Late Upper Palaeolithic (13,300 years old) and the Mesolithic (9,700 years old). These two males carried Y-DNA haplogroup: J* and J2a. The researchers found that these Caucasus hunters were probably the source of the farmer-like DNA in the Yamnaya, as the Caucasians were distantly related to the Middle Eastern people who introduced farming in Europe.[web 1] Their genomes showed that a continued mixture of the Caucasians with Middle Eastern took place up to 25,000 years ago, when the coldest period in the last Ice Age started.[web 1]
According to Lazaridis et al. (2016), "a population related to the people of the Iran Chalcolithic contributed ~43% of the ancestry of early Bronze Age populations of the steppe."[5] According to Lazaridis et al. (2016), these Iranian Chacolithic people were a mixture of "the Neolithic people of western Iran, the Levant, and Caucasus Hunter Gatherers."[5][note 1]
Characteristics

The Yamna culture is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans (PIE) in the Kurgan hypothesis of Marija Gimbutas. It is the strongest candidate for the Urheimat (homeland) of the Proto-Indo-European language, along with the preceding Sredny Stog culture, now that archaeological evidence of the culture and its migrations has been closely tied to the evidence from linguistics[8] and genetics.[3][9] Significantly, animal grave offerings were made (cattle, sheep, goats and horse), a feature associated with Proto-Indo-Europeans.[10] The culture was predominantly nomadic, with some agriculture practiced near rivers and a few hillforts.[11] Characteristic for the culture are the inhumations in pit graves under kurgans (tumuli). The dead bodies were placed in a supine position with bent knees and covered in ochre. Multiple graves have been found in these kurgans, often as later insertions. The earliest remains in Eastern Europe of a wheeled cart were found in the "Storozhova mohyla" kurgan (Dnipropetrovsk, Ukraine, excavated by Trenozhkin A.I.) associated with the Yamna culture.
Physical characteristics
The genetic basis of a number of physical features of the Yamnaya people were ascertained by the ancient DNA study conducted by Haak et al. (2015), Wilde et al.(2014), Mathieson et al. (2015) : they were genetically tall (phenotypic height is determined by both genetics and environmental factors), overwhelmingly dark-eyed (brown), dark-haired and had a skin colour that was moderately light, though somewhat darker than that of the average modern European.[12][6] Surprisingly, given their pastoral lifestyle, there was little evidence of lactase persistence.[13]
Pavel Dolukhanov argues that the emergence of the Pit-Grave culture represents a social development of various local Bronze Age cultures, representing "an expression of social stratification and the emergence of chiefdom-type nomadic social structures", which in turn intensified inter-group contacts between essentially heterogeneous social groups.[14]
Migration to Central and Northern Europe
Haak et al. (2015) conducted a genome wide study of 69 ancient skeletons from Europe and Russia. They concluded that Yamnaya autosomal characteristics are very close to the Corded Ware culture people, with an estimated a 73% ancestral contribution from the Yamnaya DNA in the DNA of Corded Ware skeletons from Germany. The same study estimated a 40–54% ancestral contribution of the Yamnaya in the DNA of modern Central & Northern Europeans, and a 20–32% contribution in modern Southern Europeans, excluding Sardinians (7.1% or less), and to a lesser extent Sicilians (11.6% or less).[3][9][web 2] Haak et al. also note that their results "suggest" that haplogroups R1b and R1a "spread into Europe from the East after 3,000 BCE."[15]
Autosomal tests also indicate that the Yamnaya are the most likely vector for "Ancient North Eurasian" admixture into Europe.[3] "Ancient North Eurasian" is the name given in literature to a genetic component that represents descent from the people of the Mal'ta-Buret' culture[3] or a population closely related to them. That genetic component is visible in tests of the Yamna people[3] as well as modern-day Europeans, but not of Europeans predating the Bronze Age.[16]
Artifacts
 |
 |
 |
 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yamna culture. |
- Kurgan
- Kurgan stelae
- Cucuteni-Trypillian culture
- Vinča culture
- Beaker culture
- Baden culture
- Khvalynsk culture
- Samara culture
- Sintashta culture
Notes
- ↑ See also:
* eurogenes.blogspot, The genetic structure of the world's first farmers (Lazaridis et al. preprint)
* anthrogenica.com, Lazaridis et al: The genetic structure of the world's first farmers (pre-print)
References
- ↑ Allentoft 2015.
- ↑ Haak 29015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Haak 2015.
- 1 2 3 Jones 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Lazaridis 2016, p. 8.
- 1 2 3 4 Mathieson 2015.
- 1 2 Morten E. Allentoft; et al. (2015). "Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia". Nature (journal). 522: 167–172. doi:10.1038/nature14507.
- ↑ Anthony 2007.
- 1 2 Zimmer 2015.
- ↑ Fortson 2004, p. 43.
- ↑ Mallory 1997.
- ↑ Sandra Wilde (2014). "Direct evidence for positive selection of skin, hair, and eye pigmentation in Europeans during the last 5,000 y". PNAS. 111. doi:10.1073/pnas.1316513111.
- ↑ Haak, 2015
- ↑ Dolukhanov 1996, p. 94.
- ↑ Haak 2015, p. 5.
- ↑ Lazaridis 2014.
Sources
Printed sources
- Anthony, David W. (2007), The Horse, The Wheel and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World
- Dolukhanov, Pavel M. (1996), The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus, New York: Longman, ISBN 0-582-23627-4
- Fortson, Benjamin W. (2004), Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction, Blackwell Publishing
- Haak, W.; Lazaridis, I.; Patterson, N.; Rohland, N.; Mallick, S.; Llamas, B.; Brandt, G.; Nordenfelt, S.; Harney, E.; Stewardson, K.; Fu, Q.; Mittnik, A.; Bánffy, E.; Economou, C.; Francken, M.; Friederich, S.; Pena, R. G.; Hallgren, F.; Khartanovich, V.; Khokhlov, A.; Kunst, M.; Kuznetsov, P.; Meller, H.; Mochalov, O.; Moiseyev, V.; Nicklisch, N.; Pichler, S. L.; Risch, R.; Rojo Guerra, M. A.; et al. (2015). "Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature14317.
- Jones, Eppie R. (2015). "Upper Palaeolithic genomes reveal deep roots of modern Eurasians". Nature (journal). doi:10.1038/ncomms9912.
- Lazaridis, Iosif (2014). "Ancient human genomes suggest three ancestral populations for present-day Europeans". Nature (journal). 513: 409–413. doi:10.1038/nature13673.
- Lazaridis, Iosif (2016), The genetic structure of the world’s first farmers (PDF), bioRxiv.org
- Mallory, J. P. (1997), "Yamna Culture", Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Fitzroy Dearborn
- Mathieson, Iain (2015). "Eight thousand years of natural selection in Europe". doi:10.1101/016477.
- Zimmer, Karl (2015). "DNA Deciphers Roots of Modern Europeans". New York Times.
Web-sources
External links
- DNAeXplained – Genetic Genealogy, Yamnaya, Light Skinned, Brown Eyed….Ancestors???
- Science Daily, Genetic study revives debate on origin and expansion of Indo-European Languages
- Eupedia, Yamna Culture (c. 3500-2500 BCE)