Xuchang
| Xuchang 许昌市 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
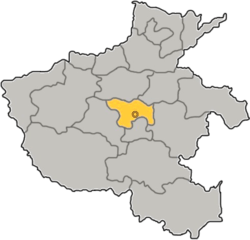 Location of Xuchang City jurisdiction in Henan | |
| Coordinates: 34°02′N 113°51′E / 34.033°N 113.850°ECoordinates: 34°02′N 113°51′E / 34.033°N 113.850°E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Henan |
| Area[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,978.36 km2 (1,922.16 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,088.2 km2 (420.2 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,724 km2 (666 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 71 m (234 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 1,150.6 m (3,774.9 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 50.4 m (165.4 ft) |
| Population [1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,307,488 |
| • Density | 870/km2 (2,200/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,265,536 |
| • Urban density | 1,200/km2 (3,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,952,666 |
| • Metro density | 1,100/km2 (2,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | Unknown |
| Area code(s) | 374 |
| GDP | ¥8,153 per capita (2002) |
| Major Nationalities | Han |
| County-level divisions | 6 |
| Township-level divisions | unknown |
| License plate prefixes | 豫K |
| Website | https://web.archive.org/web/20051001011519/http://www.xuchang.gov.cn/ |
| Xuchang | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 許昌 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 许昌 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Xuchang (Chinese: 许昌; postal: Hsuchang) is a prefecture-level city in central Henan province in Central China. It borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the northwest, Kaifeng to the northeast, Zhoukou to the east, Luohe to the southeast, and Pingdingshan to the southwest.
Its population was 4,307,488 inhabitants at the final 2010 census, of whom 1,952,666 lived in the built-up (or "metro") area made up of Weidu district, Xuchang county and Changge City largely being urbanized.[2] In 2007, the city was named China's top ten livable cities by Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum.[3]
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Xuchang administers 1 district, 2 county-level cities and 3 counties.
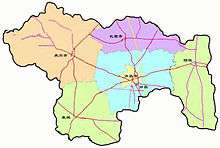
- Weidu District (魏都区)
- Yuzhou City (禹州市)
- Changge City (长葛市)
- Xuchang County (许昌县)
- Yanling County (鄢陵县)
- Xiangcheng County (襄城县)
History
According to tradition, the city was named after Xu, an ancient state led by tribal leader Xuyou during the Spring and Autumn period of the Zhou Dynasty. In ancient times, the city occupied a strategic location in central China.
Xuchang served as the warlord Cao Cao's de facto capital during the late Eastern Han Dynasty. After finding the old capital Luoyang ravaged by war, Cao moved the imperial court and Emperor Xian to what is now Xuchang in 196.
In 220, Cao Cao's son and successor Cao Pi officially declared the city as the capital of the newly established state of Cao Wei. The city was renamed "Xuchang", meaning "Xu Rising". The Wei emperors held court at Xuchang until the capital was moved to Luoyang in the 220s.
Geography and climate
Xuchang ranges in latitude from 33° 16' to 34° 24' N and in longitude from 113° 03' to 114° 190' E.
Xuchang has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa), with four distinct seasons. Winters are cool and dry, summers hot and humid, spring begins early and is warm, and autumn is mild and provides a reasonable transition. Rain mainly falls from May to September, as more than 70% of the annual precipitation occurs then. The city has an annual mean temperature of at 14.5 °C (58.1 °F), and its highest average monthly temperature is 27.1 °C (80.8 °F) in July and the lowest is 0.7 °C (33.3 °F) in January. Just over 700 millimetres (28 in) of precipitation falls each year, and there is on average 217 frost-free days and 2280 hours of sunshine per year.
| Climate data for Xuchang (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
34.2 (93.6) |
38.9 (102) |
41.9 (107.4) |
39.2 (102.6) |
38.9 (102) |
37.2 (99) |
35.1 (95.2) |
27.0 (80.6) |
21.4 (70.5) |
41.9 (107.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.1 (43) |
8.9 (48) |
13.9 (57) |
21.3 (70.3) |
26.8 (80.2) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.0 (89.6) |
30.7 (87.3) |
27.0 (80.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
14.4 (57.9) |
8.2 (46.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
3.1 (37.6) |
8.1 (46.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
20.6 (69.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
25.8 (78.4) |
21.1 (70) |
15.4 (59.7) |
8.5 (47.3) |
2.7 (36.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.6 (25.5) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
3.0 (37.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
20.0 (68) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.5 (50.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −16.4 (2.5) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−11.5 (11.3) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
3.2 (37.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
6.3 (43.3) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−14 (7) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 12.0 (0.472) |
14.9 (0.587) |
33.7 (1.327) |
43.5 (1.713) |
72.8 (2.866) |
83.5 (3.287) |
163.3 (6.429) |
121.7 (4.791) |
71.4 (2.811) |
50.7 (1.996) |
26.0 (1.024) |
12.1 (0.476) |
705.6 (27.779) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.5 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 11.7 | 10.6 | 8.3 | 7.7 | 5.4 | 3.8 | 86.2 |
| Source: Weather China[1] | |||||||||||||
Agriculture and industry
Xuchang is an important center of the Chinese tobacco industry. However, due to economic reasons many farmers have chosen not to plant tobacco anymore.
The city is also famous for its man-made human hair exports.
Education
Xuchang University is in the city.
Tourism
Famous tourist attractions include Baling Bridge and Chunqiu Tower.
Sister city
On 18 December 2006, the Oromia Region government in Ethiopia signed an agreement with Henan Province to establish a sister city program with Ambo.[4] Bolingbrook, Illinois is also a sister city of Xuchang.
Notes
- 1 2 3 许昌城市介绍 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 2011-05-29.
- ↑ http://www.citypopulation.de/php/china-henan-admin.php
- ↑ "China's Top 10 Most Livable Cities". hnloudi.gov.cn. Hunan Loudi Official Government. 2012-03-28. Retrieved 2014-08-04.
- ↑ "Oromia State Regional Government and the delegation of Henan Province sign an agreement on the Establishment of Friendship City Relationship" (Oromia State government website)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Xuchang. |
- Government website of Xuchang (in Simplified Chinese)