Westminster Bridge
Coordinates: 51°30′03″N 0°07′19″W / 51.50083°N 0.12194°W
| Westminster Bridge | |
|---|---|
|
Westminster Bridge and the Palace of Westminster | |
| Carries | A302 road |
| Crosses | River Thames |
| Locale | London, England, United Kingdom |
| Heritage status | Grade II* listed structure |
| Preceded by | Lambeth Bridge |
| Followed by | Hungerford Bridge and Golden Jubilee Bridges |
| Characteristics | |
| Design | Arch bridge |
| Total length | 820 feet (250 m) |
| Width | 85 feet (26 m) |
| Number of spans | 7 |
| History | |
| Designer | Thomas Page |
| Opened | 24 May 1862 |
Westminster Bridge is a road and foot traffic bridge over the River Thames in London, linking Westminster on the north side and Lambeth on the south side.
The bridge is painted predominantly green, the same colour as the leather seats in the House of Commons which is on the side of the Palace of Westminster nearest to the bridge. This is in contrast to Lambeth Bridge which is red, the same colour as the seats in the House of Lords and is on the opposite side of the Houses of Parliament.[1]
In 2005–2007 it underwent a complete refurbishment, including replacing the iron fascias and repainting the whole bridge. It links the Palace of Westminster on the west side of the river with County Hall and the London Eye on the east and was the finishing point during the early years of the London Marathon.
The next bridge downstream is the Hungerford footbridge and upstream is Lambeth Bridge. Westminster Bridge was designated a Grade II* listed structure in 1981.,[2]
History
For over 600 years, the nearest bridge to London Bridge was at Kingston. A bridge at Westminster was proposed in 1664, but opposed by the Corporation of London and the watermen. Despite further opposition in 1722, and after a new timber bridge was built at Putney in 1729, the scheme received parliamentary approval in 1736. Financed by private capital, lotteries and grants, Westminster Bridge, designed by the Swiss architect Charles Labelye, was built between 1739–1750.
The City of London responded to Westminster Bridge by removing the buildings on London Bridge and widening it in 1760–63. The City also commenced work on the Blackfriars Bridge, which opened in 1769. Other bridges from that time include Kew Bridge (1759), Battersea Bridge (1773), and Richmond Bridge (1777).
The bridge was required for traffic from the expanding West End to the developing South London as well as to south coast ports. Without the bridge, traffic from the West End would have to negotiate the congested routes to London Bridge such as the Strand and New Oxford Street. Roads south of the river were also improved, including the junction at the Elephant & Castle in Southwark.
By the mid 19th century the bridge was subsiding badly and expensive to maintain. The current bridge was designed by Thomas Page and opened on 24 May 1862.[3] With a length of 820 feet (250 m) and a width of 85 feet (26 m),[4] it is a seven-arch wrought iron bridge with Gothic detailing by Charles Barry (the architect of the Palace of Westminster). It is the oldest road bridge across the Thames in central London.
 The first Westminster Bridge as painted by Canaletto, 1747
The first Westminster Bridge as painted by Canaletto, 1747 Westminster Bridge, around 1750. The proprietors of the bridge had to pay compensation to the operators of the earlier 'Horseferry', and to local watermen
Westminster Bridge, around 1750. The proprietors of the bridge had to pay compensation to the operators of the earlier 'Horseferry', and to local watermen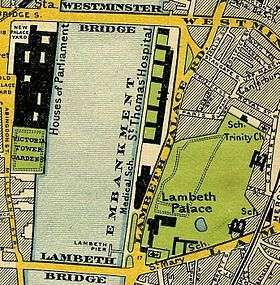 Map of 1897, showing Lambeth Palace, Lambeth Bridge, the Houses of Parliament and Westminster Bridge
Map of 1897, showing Lambeth Palace, Lambeth Bridge, the Houses of Parliament and Westminster Bridge.png) Westminster & Lambeth, 1746. Westminster Bridge, opened in 1740, connects Westminster to Lambeth; Huntley Ferry crosses the river on the site of the future Vauxhall Bridge
Westminster & Lambeth, 1746. Westminster Bridge, opened in 1740, connects Westminster to Lambeth; Huntley Ferry crosses the river on the site of the future Vauxhall Bridge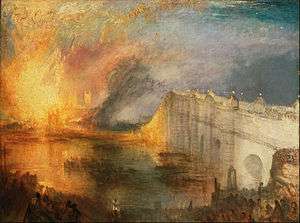 The Burning of the Houses of Lords and Commons by J. M. W. Turner, 1835, with Westminster Bridge on the right
The Burning of the Houses of Lords and Commons by J. M. W. Turner, 1835, with Westminster Bridge on the right Street lamps on the bridge
Street lamps on the bridge
In popular culture


In the 2002 British horror film 28 Days Later, the protagonist awakes from a coma to find London deserted, and walks over an eerily empty Westminster Bridge whilst looking for signs of life.
Westminster Bridge is the start and finish point for the Bridges Handicap Race, a traditional London running race.
William Wordsworth wrote the sonnet Composed upon Westminster Bridge, September 3, 1802.
In the British science fiction TV series Doctor Who, Westminster Bridge has been used for various location shots. It was used originally in 1964 in the serial The Dalek Invasion of Earth which depicts the structure as desolate and deserted. Several Daleks are seen gliding over the bridge and the adjoining Albert Embankment. The location was then re-used by the production team when the series was revived in 2005 where the Ninth Doctor and Rose Tyler run across the bridge in the episode Rose. In 2006, with the Tenth Doctor, a shot of many Cybermen as 'ghosts' congregating on Westminster Bridge was used in the episode "Army of Ghosts". Then, in 2013, the Eleventh Doctor and Clara Oswald cross the bridge on a motorbike in the episode The Bells of Saint John. It is also the name of a track in the Doctor Who Soundtrack album.
The bridge plays a prominent role in the Monty Python's Flying Circus sketch "Nationwide" ("Hamlet", Episode 43). Reporter John Dull (Graham Chapman) is sent to the bridge to find out if it is possible to sit in a chair and rest your legs whenever you want. A policeman (Michael Palin) confiscates his chair, saying it is stolen from a woman (Terry Jones in drag) who is standing across the street. Instead of giving the chair back to the woman, the policeman knocks her down and takes an identical chair from her and sits beside the reporter. He then takes different items from people walking or sitting nearby, finally breaking into a store (the crash of glass breaking is heard followed by the sound of an alarm) to get beer.
In the 2000 film 102 Dalmatians, Cruella de Vil goes mad after she hears the sound of Big Ben, and while on Westminster Bridge she sees everything white with black spots (the pattern of Dalmatians).
The final scene of the film Queen of the Damned shows Jesse and the Vampire Lestat walking across the Westminster Bridge towards Big Ben.
In the finale of the 24th James Bond film Spectre, Blofeld's helicopter crashes into Westminster Bridge.
References
- ↑ Becky Jones,Clare Lewis (2012). The Bumper Book of London: Everything You Need to Know About London and More... Frances Lincoln. p. 127. ISBN 978 1 781011 03 4.
- ↑ Historic England. "Details from image database (204781)". Images of England. accessed 27 November 2008
- ↑ John Eade. "Where Thames Smooth Waters Glide". Thames.me.uk. Retrieved 28 November 2011.
- ↑ Thames Tideway Tunnel (September 2013). "Tunnel and Bridge Assessments: Central Zone: Westminster Bridge" (PDF). Thames Water Utilities. p. 4. Retrieved 13 May 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Westminster Bridge. |
- Westminster Bridge (1750) at Structurae
- Westminster Bridge (1862) at Structurae
- Interactive Panorama: Westminster Bridge
