Ubiquitin A-52 residue ribosomal protein fusion product 1
| UBA52
|
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Human UniProt search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|
2LJ5, 2MBH, 2MJB, 2MUR, 2RSU, 4HJK, 4JIO, 4P4H, 4PIG, 4PIH, 4PIJ, 4RF0, 4RF1, 4S1Z, 4UG0, 4V6X, 5AJ0, 4UJD, 4D67, 4UJC, 3J7P, 3J7Q, 4XKL, 3J92, 4D5Y, 3J7O, 3J7R, 3PHD, 2KOX, 4UJE, 5A5B, 2N3V, 2N3U, 2N3W, 2NBD, 2NBE, 3VDZ, 5HPS, 3I3T, 5HPT, 5JBV, 5HPL, 5HPK, 5J8P
| | |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases |
UBA52, CEP52, HUBCEP52, L40, RPL40, Ubiquitin A-52 residue ribosomal protein fusion product 1 |
|---|
| External IDs |
MGI: 3644625 HomoloGene: 68307 GeneCards: UBA52
|
|---|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function |
• structural constituent of ribosome
• protein binding
|
|---|
| Cellular component |
• cytoplasm
• endocytic vesicle membrane
• cytosol
• cytosolic large ribosomal subunit
• nucleus
• ribosome
• extracellular fluid
• extracellular exosome
• plasma membrane
• nucleoplasm
• endosome membrane
• intracellular ribonucleoprotein complex
• lysosomal membrane
|
|---|
| Biological process |
• DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest
• negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway
• interstrand cross-link repair
• nucleotide-excision repair, DNA damage recognition
• positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
• tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
• regulation of necrotic cell death
• regulation of type I interferon production
• TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway
• Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway
• endosomal transport
• global genome nucleotide-excision repair
• cellular protein modification process
• NIK/NF-kappaB signaling
• G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle
• stress-activated MAPK cascade
• negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity involved in mitotic cell cycle
• transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway
• macroautophagy
• negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
• xenophagy
• positive regulation of defense response to virus by host
• DNA damage response, detection of DNA damage
• nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling
• viral transcription
• error-free translesion synthesis
• regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
• stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
• negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway
• SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane
• JNK cascade
• regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia
• nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision
• I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling
• innate immune response
• positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity involved in regulation of mitotic cell cycle transition
• Notch signaling pathway
• regulation of mRNA stability
• protein polyubiquitination
• negative regulation of apoptotic process
• negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• virion assembly
• activation of MAPK activity
• positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
• anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process
• negative regulation of type I interferon production
• nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay
• nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway
• cellular protein metabolic process
• intracellular transport of virus
• viral life cycle
• MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway
• error-prone translesion synthesis
• MAPK cascade
• fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway
• ion transmembrane transport
• glycogen biosynthetic process
• positive regulation of apoptotic process
• translational initiation
• positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling
• translesion synthesis
• transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair
• T cell receptor signaling pathway
• MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway
• positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
• positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway
• protein ubiquitination involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
• proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
• regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator
• Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway
• nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision, 5'-to lesion
• translation
• nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly
• rRNA processing
• Wnt signaling pathway
• ERBB2 signaling pathway
• nucleotide-excision repair, DNA duplex unwinding
|
|---|
| Sources:Amigo / QuickGO | |
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
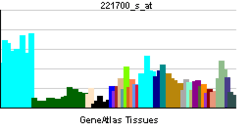 |
| More reference expression data
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species |
Human |
Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez |
|
|
|---|
| Ensembl |
|
|
|---|
| UniProt |
|
|
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) |
Chr 19: 18.57 – 18.58 Mb |
n/a |
|---|
| PubMed search |
[1] |
[2]
|
|---|
| Wikidata |
60S ribosomal protein L40 (RPL40) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBA52 gene.[3][4]
Function
Ubiquitin is a highly conserved nuclear and cytoplasmic protein that has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome. It is also involved in the maintenance of chromatin structure, the regulation of gene expression, and the stress response. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin moiety fused to an unrelated protein. This gene encodes a fusion protein consisting of ubiquitin at the N-terminus and ribosomal protein L40 at the C-terminus, a C-terminal extension protein (CEP). Multiple processed pseudogenes derived from this gene are present in the genome.[4]
Clinical significance
The cell's ribosomal protein L40 (rpL40), a part of the large 60S subunit. rpL40 is used by certain RNA viruses to translate messenger RNAs (mRNAs) into proteins while few host mRNAs require rpL40. Hence targeting this protein may provide a means to combat viral infections with minimum side effects to the host.[5]
References
Further reading
- Wool IG, Chan YL, Glück A (1996). "Structure and evolution of mammalian ribosomal proteins.". Biochem. Cell Biol. 73 (11-12): 933–47. doi:10.1139/o95-101. PMID 8722009.
- Murphey RK, Godenschwege TA (2002). "New roles for ubiquitin in the assembly and function of neuronal circuits.". Neuron. 36 (1): 5–8. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00943-1. PMID 12367500.
- Baker RT, Board PG (1992). "The human ubiquitin/52-residue ribosomal protein fusion gene subfamily (UbA52) is composed primarily of processed pseudogenes.". Genomics. 14 (2): 520–2. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80258-7. PMID 1330885.
- Baker RT, Board PG (1991). "The human ubiquitin-52 amino acid fusion protein gene shares several structural features with mammalian ribosomal protein genes.". Nucleic Acids Res. 19 (5): 1035–40. doi:10.1093/nar/19.5.1035. PMC 333777
 . PMID 1850507.
. PMID 1850507.
- Monia BP, Ecker DJ, Jonnalagadda S, et al. (1989). "Gene synthesis, expression, and processing of human ubiquitin carboxyl extension proteins.". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (7): 4093–103. PMID 2537304.
- Lund PK, Moats-Staats BM, Simmons JG, et al. (1985). "Nucleotide sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding human ubiquitin reveals that ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor.". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (12): 7609–13. PMID 2581967.
- Salvesen G, Lloyd C, Farley D (1987). "cDNA encoding a human homolog of yeast ubiquitin 1.". Nucleic Acids Res. 15 (13): 5485. doi:10.1093/nar/15.13.5485. PMC 305980
 . PMID 3037496.
. PMID 3037496.
- Cross SH, Charlton JA, Nan X, Bird AP (1994). "Purification of CpG islands using a methylated DNA binding column.". Nat. Genet. 6 (3): 236–44. doi:10.1038/ng0394-236. PMID 8012384.
- Cook WJ, Jeffrey LC, Kasperek E, Pickart CM (1994). "Structure of tetraubiquitin shows how multiubiquitin chains can be formed.". J. Mol. Biol. 236 (2): 601–9. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1169. PMID 8107144.
- Vadlamudi RK, Joung I, Strominger JL, Shin J (1996). "p62, a phosphotyrosine-independent ligand of the SH2 domain of p56lck, belongs to a new class of ubiquitin-binding proteins.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (34): 20235–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.34.20235. PMID 8702753.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Kenmochi N, Kawaguchi T, Rozen S, et al. (1998). "A map of 75 human ribosomal protein genes.". Genome Res. 8 (5): 509–23. doi:10.1101/gr.8.5.509. PMID 9582194.
- Cruz C, Ventura F, Bartrons R, Rosa JL (2001). "HERC3 binding to and regulation by ubiquitin.". FEBS Lett. 488 (1-2): 74–80. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02371-1. PMID 11163799.
- Lee TA, Tyers M (2002). "Ubiquitin junction, what's your function?". Genome Biol. 2 (10): REPORTS4025. doi:10.1186/gb-2001-2-10-reports4025. PMC 138970
 . PMID 11597332.
. PMID 11597332.
- Yoshihama M, Uechi T, Asakawa S, et al. (2002). "The human ribosomal protein genes: sequencing and comparative analysis of 73 genes.". Genome Res. 12 (3): 379–90. doi:10.1101/gr.214202. PMC 155282
 . PMID 11875025.
. PMID 11875025.
- Bishop N, Horman A, Woodman P (2002). "Mammalian class E vps proteins recognize ubiquitin and act in the removal of endosomal protein-ubiquitin conjugates.". J. Cell Biol. 157 (1): 91–101. doi:10.1083/jcb.200112080. PMC 2173266
 . PMID 11916981.
. PMID 11916981.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932.
PDB gallery |
|---|
|
| 1aar: STRUCTURE OF A DIUBIQUITIN CONJUGATE AND A MODEL FOR INTERACTION WITH UBIQUITIN CONJUGATING ENZYME (E2) |
| 1cmx: STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE SPECIFICITY OF UBIQUITIN C-TERMINAL HYDROLASES |
| 1d3z: UBIQUITIN NMR STRUCTURE |
| 1f9j: STRUCTURE OF A NEW CRYSTAL FORM OF TETRAUBIQUITIN |
| 1fxt: STRUCTURE OF A CONJUGATING ENZYME-UBIQUITIN THIOLESTER COMPLEX |
| 1g6j: STRUCTURE OF RECOMBINANT HUMAN UBIQUITIN IN AOT REVERSE MICELLES |
| 1gjz: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A DIMERIC N-TERMINAL FRAGMENT OF HUMAN UBIQUITIN |
| 1nbf: Crystal structure of a UBP-family deubiquitinating enzyme in isolation and in complex with ubiquitin aldehyde |
| 1ogw: SYNTHETIC UBIQUITIN WITH FLUORO-LEU AT 50 AND 67 |
| 1otr: Solution Structure of a CUE-Ubiquitin Complex |
| 1p3q: Mechanism of Ubiquitin Recognition by the CUE Domain of VPS9 |
| 1q0w: Solution structure of Vps27 amino-terminal UIM-ubiquitin complex |
| 1q5w: Ubiquitin Recognition by Npl4 Zinc-Fingers |
| 1s1q: TSG101(UEV) domain in complex with Ubiquitin |
| 1sif: Crystal structure of a multiple hydrophobic core mutant of ubiquitin |
| 1tbe: STRUCTURE OF TETRAUBIQUITIN SHOWS HOW MULTIUBIQUITIN CHAINS CAN BE FORMED |
| 1ubi: SYNTHETIC STRUCTURAL AND BIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF THE UBIQUITIN SYSTEM. PART 1 |
| 1ubq: STRUCTURE OF UBIQUITIN REFINED AT 1.8 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION |
| 1ud7: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE DESIGNED HYDROPHOBIC CORE MUTANT OF UBIQUITIN, 1D7 |
| 1uzx: A COMPLEX OF THE VPS23 UEV WITH UBIQUITIN |
| 1v80: Solution structures of ubiquitin at 30 bar and 3 kbar |
| 1v81: Solution structures of ubiquitin at 30 bar and 3 kbar |
| 1wr1: The complex structure of Dsk2p UBA with ubiquitin |
| 1wr6: Crystal structure of GGA3 GAT domain in complex with ubiquitin |
| 1wrd: Crystal structure of Tom1 GAT domain in complex with ubiquitin |
| 1xd3: Crystal structure of UCHL3-UbVME complex |
| 1xqq: Simultaneous determination of protein structure and dynamics |
| 1yd8: COMPLEX OF HUMAN GGA3 GAT DOMAIN AND UBIQUITIN |
| 1yiw: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized Ubiquitin |
| 1yj1: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized [D-Gln35]Ubiquitin |
| 1yx5: Solution Structure of S5a UIM-1/Ubiquitin Complex |
| 1yx6: Solution Structure of S5a UIM-2/Ubiquitin Complex |
| 1zgu: Solution structure of the human Mms2-Ubiquitin complex |
| 2ayo: Structure of USP14 bound to ubquitin aldehyde |
| 2bgf: NMR STRUCTURE OF LYS48-LINKED DI-UBIQUITIN USING CHEMICAL SHIFT PERTURBATION DATA TOGETHER WITH RDCS AND 15N-RELAXATION DATA |
| 2c7m: HUMAN RABEX-5 RESIDUES 1-74 IN COMPLEX WITH UBIQUITIN |
| 2c7n: HUMAN RABEX-5 RESIDUES 1-74 IN COMPLEX WITH UBIQUITIN |
| 2d3g: Double sided ubiquitin binding of Hrs-UIM |
| 2den: Solution Structure of the Ubiquitin-Associated Domain of Human BMSC-UbP and its Complex with Ubiquitin |
| 2dx5: The complex structure between the mouse EAP45-GLUE domain and ubiquitin |
| 2fcm: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized [D-Gln35]Ubiquitin with a Cubic Space Group |
| 2fcn: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized [D-Val35]Ubiquitin with a Cubic Space Group |
| 2fcq: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized Ubiquitin with a Cubic Space Group |
| 2fcs: X-ray Crystal Structure of a Chemically Synthesized [L-Gln35]Ubiquitin with a Cubic Space Group |
| 2fid: Crystal Structure of a Bovine Rabex-5 fragment complexed with ubiquitin |
| 2fif: Crystal Structure of a Bovine Rabex-5 fragment complexed with ubiquitin |
| 2fuh: Solution Structure of the UbcH5c/Ub Non-covalent Complex |
| 2g3q: Solution Structure of Ede1 UBA-ubiquitin complex |
| 2g45: Co-crystal structure of znf ubp domain from the deubiquitinating enzyme isopeptidase T (isot) in complex with ubiquitin |
| 2gbj: Crystal Structure of the 9-10 8 Glycine Insertion Mutant of Ubiquitin. |
| 2gbk: Crystal Structure of the 9-10 MoaD Insertion Mutant of Ubiquitin |
| 2gbm: Crystal Structure of the 35-36 8 Glycine Insertion Mutant of Ubiquitin |
| 2gbn: Crystal Structure of the 35-36 8 Glycine Insertion Mutant of Ubiquitin |
| 2gbr: Crystal Structure of the 35-36 MoaD Insertion Mutant of Ubiquitin |
| 2gmi: Mms2/Ubc13~Ubiquitin |
| 2hd5: USP2 in complex with ubiquitin |
| 2hth: Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human EAP45/ESCRT-II GLUE domain |
| 2ibi: Covalent Ubiquitin-USP2 Complex |
| 2j7q: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE UBIQUITIN-SPECIFIC PROTEASE ENCODED BY MURINE CYTOMEGALOVIRUS TEGUMENT PROTEIN M48 IN COMPLEX WITH A UBQUITIN-BASED SUICIDE SUBSTRATE |
| 2nr2: The MUMO (minimal under-restraining minimal over-restraining) method for the determination of native states ensembles of proteins |
| 2o6v: Crystal structure and solution NMR studies of Lys48-linked tetraubiquitin at neutral pH |
| 2oob: crystal structure of the UBA domain from Cbl-b ubiquitin ligase in complex with ubiquitin |
|
|
 . PMID 1850507.
. PMID 1850507. . PMID 3037496.
. PMID 3037496. . PMID 11597332.
. PMID 11597332. . PMID 11875025.
. PMID 11875025. . PMID 11916981.
. PMID 11916981. . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932.