Tricarboxylic acid
A tricarboxylic acid is an organic carboxylic acid whose chemical structure contains three carboxyl functional groups (-COOH). The best-known example of a tricarboxylic acid is citric acid.
Uses
Tricarboxylic acid is used in the Citric Acid Cycle (TCA) which is fundamental to all aerobic lifeforms. This cycle converts NADH and FADH2 from pyruvate, which is created from citric acid.
Isomers
| Common name | IUPAC name | Molecular formula | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid | 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 | 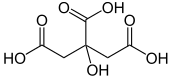 |
| Isocitric acid | 1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 |  |
| Aconitic acid | Prop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H6O6 |  
(cis-form & trans-form) |
| Propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | Propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C3H5(COOH)3 | 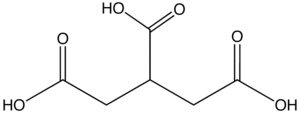 |
| Trimesic acid | benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid | C9H6O6 |  |
See also
- Citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)
- Dicarboxylic acid
- Mellitic acid
- Ryan J. Mailloux, Robin Bériault, Joseph Lemire, Ranji Singh, Daniel R. Chénier, Robert D. Hamel, Vasu D. Appanna (2007). "The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle, an Ancient Metabolic Network with a Novel Twist.". PLOS ONE. Retrieved 2016-07-21.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.