Transport in Denmark

Transport in Denmark is developed and modern. The motorway network now covers 1,111 km[1] while the railway network totals 2,667 km of operational track.[2] The Great Belt Fixed Link (opened in 1997) connecting the islands of Zealand and Funen and the New Little Belt Bridge (opened in 1970) connecting Funen and Jutland have improved the traffic flow across the country on both motorways and rail. The airports of Copenhagen and Billund provide a variety of domestic and international connections while ferries provide services to the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Iceland, Germany, Sweden, Norway and the United Kingdom as well as routes to the Danish islands.
Air
In 2011, a total of appr. 28 million passengers used Danish airports.[3]
Copenhagen Airport is the largest airport in Scandinavia, handling approximately 23m passengers per year (2011). It is located at Kastrup, 8 km south-east of central Copenhagen. It is connected by train to Copenhagen Central Station and beyond as well as to Malmö and other towns in Sweden.
For the west of the country, the major airport is Billund (2.7m passengers in 2011) although both Aalborg (1.4m passengers in 2011) and Aarhus (591.000 passengers in 2011) have smaller airports with regular connections to Copenhagen.
List of airports
Denmark's main airports are:
- Copenhagen Airport (CPH), Scandinavia's busiest passenger airport located at Kastrup to the south-east of Copenhagen city and handling over 25 million passengers a year.
- Billund Airport (BLL), in central Jutland, one of Denmark's busiest cargo centres as well as a popular charter airline destination and an airport for regular flights serving 2.8 million passengers a year, mainly from the western part of the country.
- Aalborg Airport (AAL), located 5 km northwest of Aalborg, is Denmark's third busiest airport serving around 1,4 million passengers a year in connections with 25 European destinations and one of Europes busiest domestic lines to Copenhagen.
- Aarhus Airport (AAH), located 39 km northeast of Århus, serves some 540,000 passengers a year.
Other airports include:
- Karup Airport (KRP) near Viborg in the west of Jutland, mainly serving Copenhagen with some 200,000 passengers a year.
- Bornholm Airport (RNN) 5 km from the centre of Rønne in the southwest of the island of Bornholm, with several regular flights to Copenhagen a day.
- Esbjerg Airport (EBJ), a small airport in the west of Jutland with regular flights to Aberdeen and Stavanger (although primarily serving North Sea Oilrigs).
- Sønderborg Airport ([SGD), in the very south of Jutland with connections to Copenhagen.
- Roskilde Airport (RKE), 7 km southeast of Roskilde and some 38 km southwest of Copenhagen, serves mainly airtaxi and private business traffic.[4]
Sea
Being an island state with a long coastline and always close to the sea, maritime transport has always been important in Denmark. From the primitive dugouts of the Stone Age to the complex designs of the Viking ships in the Viking Age, often built to exactly facilitate large scale cargo and passenger transportation. Denmark also engaged in the large scale cargo freights and slave transports of the European colonization endeavours in the Middle Ages and operated several smaller colonies of its own across the globe by the means of seafaring.
Today Denmark's ports handle some 48 million passengers and 109 million tonnes of cargo per year.[5]
Passenger traffic
Passenger traffic is made up partly of ferry crossings within Denmark, partly of international ferry crossings and partly of cruise ship passengers.
Among the most important ports for passenger traffic (thousands of passengers per year in 2007) are:
- Helsingør 10,967
- Rødbyhavn 7,058
- Frederikshavn 2,894
- Sjællands Odde 2,233
- Esbjerg 1,827
- Gedser 1,612
- Aarhus 1,583
- Rønne 1,522
- Ebeltoft 962
- Copenhagen 872

In 2007, 288 cruise ships visited Copenhagen.
Cargo traffic
Among the most important ports for cargo traffic (millions of tonnes per year in 2007) are:
- Fredericia 15,327
- Aarhus 12,189
- Copenhagen 7,379
- Helsingør 4,480
- Esbjerg 4,476
- Kalundborg 3,714
- Frederikshavn 3,200
- Aalborg Portland 2,999
- Aalborg 2,749
- Odense 2,616
Waterways
Waterways has historically and traditionally been crucial to local transportation in Denmark proper. Especially the Gudenå river-system in central Jutland, has played an important role. The waterways was navigated by wooden barges and later on steamboats.[6] A few historical steamboats are still in operation, like the SS Hjejlen from 1861 at Silkeborg.
There is a 160 km natural canal through the shallow Limfjorden in northern Jutland, linking the North Sea to the Kattegat.
Many waterways has formerly been redirected and led through manmade canals in the 1900s, but mainly for agricultural purposes and not to facilitate transportation on any major scale. Several cities have manmade canals used for transportation and traffic purposes. Of special mention are the canals of Copenhagen and the Odense Canal, ferrying large numbers of both tourists and local citizens.[7]
Merchant marine
|
|
- Total
- 336 ships (with a volume of 1,000 gross register tons (GRT) or over) totaling 5,190,227 GRT/
6,815,128 tonnes deadweight (DWT)
- Ships by type
- Bulk carrier
- 12
- Cargo ship
- 132
- Chemical tanker
- 22
- Container ship
- 70
- Liquified gas
- 26
- Livestock carrier
- 6
- Petroleum tanker
- 24
- Rail car carrier
- 1
- Refrigerated cargo
- 13
- Roll-on/Roll-off
- 19
- Short-sea passenger
- 8
- Specialized tanker
- 3 (1999 est.)
Railways
The largest railway operator in Denmark is Danske Statsbaner (DSB) — Danish State Railways. Arriva operates some routes in Jutland, and several other smaller operators provide local services.
The total length of operational track is 2,667 km, 640 km electrified at 25 kV AC, 946 km double track (2008).[9] 508 km is privately owned and operated. Track is standard gauge.
The railway system is connected to Sweden by bridge in Copenhagen and ferry in Helsingør and Frederikshavn, by land to Germany in Padborg and ferry in Rødby and to Norway by ferry in Hirtshals.
Roads
The road network in 2008 totalled 73,197 km of paved road, including 1,111 km of motorway.[10] Motorways are toll-free except for the Great Belt Bridge joining Zealand and Funen and the Øresund Bridge linking Copenhagen to Malmö in Sweden.
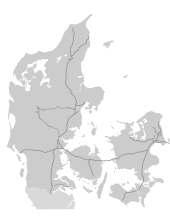 Motorways in Denmark.
Motorways in Denmark.
Cycling
Bicycling in Denmark is a common and popular utilitarian and recreational activity. Bicycling infrastructure is a dominant feature of both city and countryside infrastructure, with bicycle paths and bicycle ways in many places and an extensive network of bicycle routes, extending more than 12,000 kilometres (7,500 mi) nationwide.[11] In comparison, Denmark's coastline is 7,314 kilometres (4,545 mi). As a unique feature, Denmark has a VIN-system for bicycles which is mandatory by law. Often bicycling and bicycle-culture in Denmark is compared to the Netherlands as a bicycle-nation.
 Bicycle rush hour in Copenhagen.
Bicycle rush hour in Copenhagen. Heavily trafficked roads in the inner cities, often have cycle lanes.
Heavily trafficked roads in the inner cities, often have cycle lanes.- A bike road in central Aarhus.
- Some - but not all - motorways have bike roads running along.
 A cross country bikeway route.
A cross country bikeway route.
Pipelines
Figures for 2007:
- Crude oil
- 110 km
- Petroleum products
- 578 km
- Natural gas
- 800 km
See also
References
- ↑ Road network by type of road and time (2008). Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 24 March 2009.
- ↑ Railway network 1 January by unit, railway system and time (2008). Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ↑ Departing passengers from major manned, public airports by airport, type of transport and flight. Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 25 March 2009.
- ↑ Countrywise Airport Codes
- ↑ Call of vessels, passengers and throughput of goods in traffic ports by seaport and unit. Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ↑ "The towpath along the Gudenåen River". 1001 stories of Denmark. The Heritage Agency of Denmark (Danish agency for Culture). Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- ↑ World Canals - Denmark. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ↑ Denmark has created its own internal register, called the Danish International Ship register (DIS); DIS ships do not have to meet Danish manning regulations, and they amount to a flag of convenience within the Danish register (1998 est.)
- ↑ Railway network 1 January by railway system and unit (2008). Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ↑ Road network 1 January by part of the country and type of road (2008). Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 24 March 2009.
- ↑ "Cykelruter og regioner" (in Danish). VisitDenmark. Retrieved 16 August 2011.
Further reading
- Peter, Bruce (2013). Ferries of Denmark / Danske Færger (in English and Danish). Ramsey, Isle of Man: Ferry Publications. ISBN 9781906608514.
External links
- Public transportation Route Planner
- Online Map, Address lookup
- Copenhagen Airports
- S-train and Danish train schedules
- Copenhagenize - Copenhagen Bike Culture Blog
- Metro information
- All railway tracks
- City of Copenhagen: City of Cyclists
- Truck transport Denmark