Trail Making Test
| Trail Making Test | |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | |
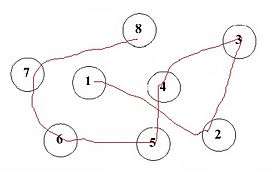 Part A Sample | |
| MeSH | D014145 |
The Trail Making Test is a neuropsychological test of visual attention and task switching. It consists of two parts in which the subject is instructed to connect a set of 25 dots as quickly as possible while still maintaining accuracy.[1] The test can provide information about visual search speed, scanning, speed of processing, mental flexibility, as well as executive functioning.[1] It is sensitive to detecting cognitive impairment associated with dementia, for example, Alzheimer's disease .[2]
History
The test was used in 1944 for assessing general intelligence, and was part of the Army Individual Test of General Ability.[3] In the 1950s[4][5] researchers began using the test to assess cognitive dysfunction stemming from brain damage, and it has since been incorporated into the Halstead-Reitan battery.[3] The Trail Making Test is now commonly used as a diagnostic tool in clinical settings. Poor performance is known to be associated with many types of brain impairment, in particular frontal lobe lesion.
Method and interpretation
The task requires a subject to connect a sequence of 25 consecutive targets on a sheet of paper or computer screen, in a similar manner to a child's connect-the-dots puzzle. There are two parts to the test: in the first, the targets are all numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.) and the test taker needs to connect them in sequential order; in the second part, the subject alternates between numbers and letters (1, A, 2, B, etc.).[6] If the subject makes an error, the test administrator corrects them before the subject moves on to the next dot.[6]
The goal of the test is for the subject is to finish both parts as quickly as possible, with the time taken to complete the test being used as the primary performance metric. The error rate is not recorded in the paper and pencil version of the test, however, it is assumed that if errors are made it will be reflected in the completion time.[3] The second part of the test, in which the subject alternates between numbers and letters, is used to examine executive functioning.[3] The first part is used primarily to examine cognitive processing speed.[3]
References
- 1 2 Arnett, James A.; Seth S. Labovitz (1995). "Effect of physical layout in performance of the Trail Making Test". Psychological Assessment. 7 (2): 220–221. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.7.2.220. Retrieved 2012-02-22.
- ↑ Cahn, D. A. et al. (1995). Detection of dementia of the Alzheimer type in a population-based sample: Neuropsychological test performance. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 1(03), 252-260.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Tombaugh, T.N.T.N (2004). "Trail Making test A and B: Normative Data Stratified by Age and Education". Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 19 (2): 203–214. doi:10.1016/s0887-6177(03)00039-8. Retrieved 2012-01-10.
- ↑ R. M. Reitan, R. M. (1955). The relation of the trail making test to organic brain damage. Journal of Consulting Psychology
- ↑ Reitan R. M. (1958). Validity of the Trail Making test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept. Mot Skills, 8, 271-276.
- 1 2 Bowie, C.R.C.R; P.D.P.D Harvey (2006). "Administration and interpretation of the trail making test". Nature Protocols. 1 (5): 2277–2281. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.390. Retrieved 2012-01-10.
- Corrigan, J. D., Hinkeldey, M. S. (1987). Relationships between parts A and B of the Trail Making Test. J. Clin Psychol, 43 (4), 402–409.
- Gaudino, E. A., Geisler, M. W., Squires, N. K. (1995). Construct validity in the Trail Making Test: What makes Part B harder? J Clin Exp Neuropsychol, 17 (4), 529-535.
Further reading
- Groth-Marnat, Gary (2009). Handbook of Psychological Assessment (Fifth ed.). Hoboken (NJ): Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-08358-1. Lay summary (11 September 2010).
- Strauss, Esther; Sherman, Elizabeth M.; Spreen, Otfried (2006). A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-515957-8. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
External links
- PEBL Test Battery A free computer-based research-oriented implementation of the trail-making test is available as part of the PEBL Project