Tay–Sachs disease
| Tay–Sachs disease | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Cherry-red spot as seen in Tay–Sachs disease: the fovea's center appears bright red because it is surrounded by a milky halo. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | E75.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 330.1 |
| OMIM | 272800 272750 |
| DiseasesDB | 12916 |
| MedlinePlus | 001417 |
| eMedicine | ped/3016 |
| Patient UK | Tay–Sachs disease |
| MeSH | D013661 |
Tay–Sachs disease (also known as GM2 gangliosidosis or hexosaminidase A deficiency) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder. In its most common variant (known as infantile Tay–Sachs disease), it causes a progressive deterioration of nerve cells and of mental and physical abilities that begins around 7 months of age and usually results in death by the age of four. The disease occurs when harmful quantities of cell membrane components known as gangliosides accumulate in the brain's nerve cells, eventually leading to the premature death of the cells. A ganglioside is a form of sphingolipid, which makes Tay–Sachs disease a member of the sphingolipidoses. There is no known cure or treatment.
The disease is named after the British ophthalmologist Waren Tay, who in 1881 first described a symptomatic red spot on the retina of the eye; and after the American neurologist Bernard Sachs of Mount Sinai Hospital, who described in 1887 the cellular changes of Tay–Sachs disease and noted an increased disease prevalence in Ashkenazi Jews.
Research in the late 20th century demonstrated that Tay–Sachs disease is caused by a genetic mutation in the HEXA gene on chromosome 15. A large number of HEXA mutations have been discovered, and new ones are still being reported. These mutations reach significant frequencies in specific populations. French Canadians of southeastern Quebec have a carrier frequency similar to that seen in Ashkenazi Jews, but carry a different mutation. Cajuns of southern Louisiana carry the same mutation that is seen most commonly in Ashkenazi Jews. HEXA mutations are rare and are most seen in genetically isolated populations. Tay–Sachs can occur from the inheritance of either two similar, or two unrelated, causative mutations in the HEXA gene.
As an autosomal recessive disorder, two Tay–Sachs alleles are required for an individual to exhibit symptoms of the disease. Carriers of a single Tay–Sachs allele do not exhibit symptoms of the disease but appear to be protected to some extent against tuberculosis. This accounts for the persistence of the allele in certain populations in that it confers a selective advantage—in other words, being a heterozygote is advantageous.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Tay–Sachs disease is typically first noticed in infants around 6 months old displaying an abnormally strong response to sudden noises or other stimulus, known as the "startle response," because they are startled. There may also be listlessness or muscle stiffness (hypertonia). The disease is classified into several forms, which are differentiated based on the onset age of neurological symptoms.[2][3]
- Infantile Tay–Sachs disease. Infants with Tay–Sachs disease appear to develop normally for the first six months after birth. Then, as neurons become distended with gangliosides, a relentless deterioration of mental and physical abilities begins. The child may become blind, deaf, unable to swallow, atrophied, and paralytic. Death usually occurs before the age of four.[2]
- Juvenile Tay–Sachs disease. Juvenile Tay–Sachs disease is rarer than other forms of Tay–Sachs, and usually is initially seen in children between two and ten years old. People with Tay–Sachs disease develop cognitive and motor skill deterioration, dysarthria, dysphagia, ataxia, and spasticity.[4] Death usually occurs between the age of five to fifteen years.[5]
- Adult/Late-Onset Tay–Sachs disease. A rare form of this disease, known as Adult-Onset or Late-Onset Tay–Sachs disease, usually has its first symptoms during the 30s or 40s. In contrast to the other forms, late-onset Tay–Sachs disease is usually not fatal as the effects can stop progressing. It is frequently misdiagnosed. It is characterized by unsteadiness of gait and progressive neurological deterioration. Symptoms of late-onset Tay–Sachs – which typically begin to be seen in adolescence or early adulthood – include speech and swallowing difficulties, unsteadiness of gait, spasticity, cognitive decline, and psychiatric illness, particularly a schizophrenia-like psychosis.[6] People with late-onset Tay–Sachs may become full-time wheelchair users in adulthood.
Until the 1970s and 1980s, when the disease's molecular genetics became known, the juvenile and adult forms of the disease were not always recognized as variants of Tay–Sachs disease. Post-infantile Tay–Sachs was often misdiagnosed as another neurological disorder, such as Friedreich's ataxia.[7]
Genetics
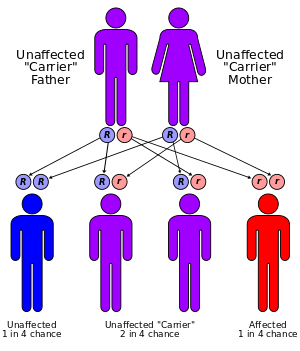

Tay–Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, meaning that when both parents are carriers, there is a 25% risk of giving birth to an affected child with each pregnancy. The affected child would have received a mutated copy of the gene from each parent.[2]
Tay–Sachs results from mutations in the HEXA gene on chromosome 15, which encodes the alpha-subunit of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A, a lysosomal enzyme. By 2000, more than 100 different mutations had been identified in the human HEXA gene.[8] These mutations have included single base insertions and deletions, splice phase mutations, missense mutations, and other more complex patterns. Each of these mutations alters the gene's protein product (i.e., the enzyme), sometimes severely inhibiting its function.[9] In recent years, population studies and pedigree analysis have shown how such mutations arise and spread within small founder populations. Initial research focused on several such founder populations:
- Ashkenazi Jews. A four base pair insertion in exon 11 (1278insTATC) results in an altered reading frame for the HEXA gene. This mutation is the most prevalent mutation in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, and leads to the infantile form of Tay–Sachs disease.[10]
- Cajun. The same 1278insTATC mutation found among Ashkenazi Jews occurs in the Cajun population of southern Louisiana. Researchers have traced the ancestry of carriers from Louisiana families back to a single founder couple – not known to be Jewish – who lived in France in the 18th century.[11]
- French Canadians. Two mutations, unrelated to the Ashkenazi/Cajun mutation, are absent in France but common among French Canadians living in eastern Quebec and Acadians from the Province of New Brunswick. Pedigree analysis suggests the mutations were uncommon before the late 17th century.[12][13]
In the 1960s and early 1970s, when the biochemical basis of Tay–Sachs disease was first becoming known, no mutations had been sequenced directly for genetic diseases. Researchers of that era did not yet know how common polymorphisms would prove to be. The "Jewish Fur Trader Hypothesis," with its implication that a single mutation must have spread from one population into another, reflected the knowledge at the time. Subsequent research, however, has proven that a large variety of different HEXA mutations can cause the disease. Because Tay–Sachs was one of the first genetic disorders for which widespread genetic screening was possible, it is one of the first genetic disorders in which the prevalence of compound heterozygosity has been demonstrated.[14]
Compound heterozygosity ultimately explains the disease's variability, including the late-onset forms. The disease can potentially result from the inheritance of two unrelated mutations in the HEXA gene, one from each parent. Classic infantile Tay–Sachs disease results when a child has inherited mutations from both parents that completely stop the biodegradation of gangliosides. Late onset forms occur due to the diverse mutation base – people with Tay–Sachs disease may technically be heterozygotes, with two differing HEXA mutations that both inactivate, alter, or inhibit enzyme activity. When a patient has at least one HEXA copy that still enables some level of hexosaminidase A activity, a later onset disease form occurs. When disease occurs because of two unrelated mutations, the patient is said to be a compound heterozygote.[15]
Heterozygous carriers (individuals who inherit one mutant allele) show abnormal enzyme activity, but manifest no disease symptoms. This phenomenon is called dominance; the biochemical reason for wild-type alleles' dominance over nonfunctional mutant alleles in inborn errors of metabolism comes from how enzymes function. Enzymes are protein catalysts for chemical reactions; as catalysts, they speed up reactions without being used up in the process, so only small enzyme quantities are required to carry out a reaction. Someone homozygous for a nonfunctional mutation in the enzyme-encoding gene has little or no enzyme activity, so will manifest the abnormal phenotype. A heterozygote (heterozygous individual) has at least half of the normal enzyme activity level, due to expression by the wild-type allele. This level is normally enough to enable normal function and thus prevent phenotypic expression.[16]
Pathophysiology
Tay–Sachs disease is caused by insufficient activity of the enzyme hexosaminidase A. Hexosaminidase A is a vital hydrolytic enzyme, found in the lysosomes, that breaks down glycolipids. When hexosaminidase A is no longer functioning properly, the lipids accumulate in the brain and interfere with normal biological processes. Hexosaminidase A specifically breaks down fatty acid derivatives called gangliosides; these are made and biodegraded rapidly in early life as the brain develops. Patients with and carriers of Tay–Sachs can be identified by a simple blood test that measures hexosaminidase A activity.[2]
The hydrolysis of GM2-ganglioside requires three proteins. Two of them are subunits of hexosaminidase A; the third is a small glycolipid transport protein, the GM2 activator protein (GM2A), which acts as a substrate-specific cofactor for the enzyme. Deficiency in any one of these proteins leads to ganglioside storage, primarily in the lysosomes of neurons. Tay–Sachs disease (along with AB-variant GM2-gangliosidosis and Sandhoff disease) occurs because a mutation inherited from both parents deactivates or inhibits this process. Most Tay–Sachs mutations probably do not directly affect protein functional elements (e.g., the active site). Instead, they cause incorrect folding (disrupting function) or disable intracellular transport.[17]
Diagnosis
In patients with a clinical suspicion for Tay–Sachs disease, with any age of onset, the initial testing involves an enzyme assay to measure the activity of hexosaminidase in serum, fibroblasts, or leukocytes. Total hexosaminidase enzyme activity is decreased in individuals with Tay-Sachs as is the percentage of hexosaminidase A. After confirmation of decreased enzyme activity in an individual, confirmation by molecular analysis can be pursued.[18] All patients with infantile onset Tay–Sachs disease have a "cherry red" macula in the retina, easily observable by a physician using an ophthalmoscope.[2][19] This red spot is a retinal area that appears red because of gangliosides in the surrounding retinal ganglion cells. The choroidal circulation is showing through "red" in this foveal region where all retinal ganglion cells are pushed aside to increase visual acuity. Thus, this cherry-red spot is the only normal part of the retina; it shows up in contrast to the rest of the retina. Microscopic analysis of the retinal neurons shows they are distended from excess ganglioside storage.[20] Unlike other lysosomal storage diseases (e.g., Gaucher disease, Niemann–Pick disease, and Sandhoff disease), hepatosplenomegaly (liver and spleen enlargement) is not seen in Tay–Sachs.[21]
Prevention
Three main approaches have been used to prevent or reduce the incidence of Tay–Sachs:
- Prenatal diagnosis. If both parents are identified as carriers, prenatal genetic testing can determine whether the fetus has inherited a defective gene copy from both parents.[22] Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), the most common form of prenatal diagnosis, can be performed between 10 and 14 weeks of gestation. Amniocentesis is usually performed at 15–18 weeks. These procedures have risks of miscarriage of 1% or less.[23][24]
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosis. By retrieving the mother's eggs for in vitro fertilization, it is possible to test the embryo for the disorder prior to implantation. Healthy embryos are then selected and transferred into the mother's womb, while unhealthy embryos are discarded. In addition to Tay–Sachs disease, preimplantation genetic diagnosis has been used to prevent cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia among other genetic disorders.[25]
- Mate selection. In Orthodox Jewish circles, the organization Dor Yeshorim carries out an anonymous screening program so that couples with Tay–Sachs or another genetic disorder can avoid conception.[26]
Management
There is currently no cure or treatment for Tay–Sachs disease. Even with the best care, children with infantile Tay–Sachs disease die, usually by the age of 4.[27] Although experimental work is underway, no current medical treatment of the root cause yet exists. Patients receive supportive care to ease the symptoms and extend life by reducing the chance of contracting infections.[27] Infants are given feeding tubes when they can no longer swallow.[28] Improvements in life-extending care have somewhat lengthened the survival of children with Tay–Sachs disease, but no current therapy is able to reverse or delay the disease's progress.[27] In late-onset Tay-Sachs, medication (e.g., lithium for depression) can sometimes control psychiatric symptoms and seizures, although some medications (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines, haloperidol, and risperidone) are associated with significant adverse effects.[15][29] In 2011, researchers discovered that pyrimethamine can increase ß-hexosaminidase activity, thus slowing down the progression of late-onset Tay–Sachs disease.[30]
Epidemiology
Ashkenazi Jews have a high incidence of Tay–Sachs and other lipid storage diseases. In the United States, about 1 in 27 to 1 in 30 Ashkenazi Jews is a recessive carrier. The disease incidence is about 1 in every 3,500 newborn among Ashkenazi Jews.[31] French Canadians and the Cajun community of Louisiana have an occurrence similar to the Ashkenazi Jews. Irish Americans have a 1 in 50 chance of being a carrier. In the general population, the incidence of carriers as heterozygotes is about 1 in 300.[3] The incidence is approximately 1 in 320,000 newborns in the general population in United States.[32]
Three general classes of theories have been proposed to explain the high frequency of Tay–Sachs carriers in the Ashkenazi Jewish population:
- Heterozygote advantage.[33] When applied to a particular allele, this theory posits that mutation carriers have a selective advantage, perhaps in a particular environment.[34]
- Reproductive compensation. Parents who lose a child because of disease tend to "compensate" by having additional children to replace them. This phenomenon may maintain and possibly even increase the incidence of autosomal recessive disease.[35]
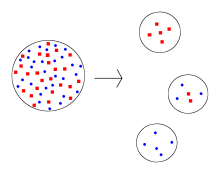
- Founder effect. This hypothesis states that the high incidence of the 1278insTATC chromosomes[34] is the result of an elevated allele frequency[33] that existed by chance in an early founder population.[34]
Tay–Sachs disease was one of the first genetic disorders for which epidemiology was studied using molecular data. Studies of Tay–Sachs mutations using new molecular techniques such as linkage disequilibrium and coalescence analysis have brought an emerging consensus among researchers supporting the founder effect theory.[34][36][37]
History
Waren Tay and Bernard Sachs, two physicians, described the disease's progression and provided differential diagnostic criteria to distinguish it from other neurological disorders with similar symptoms.
Both Tay and Sachs reported their first cases among Ashkenazi Jewish families. Tay reported his observations in 1881 in the first volume of the proceedings of the British Ophthalmological Society, of which he was a founding member.[38] By 1884, he had seen three cases in a single family. Years later, Bernard Sachs, an American neurologist, reported similar findings when he reported a case of "arrested cerebral development" to other New York Neurological Society members.[39][40]
Sachs, who recognized that the disease had a familial basis, proposed that the disease should be called amaurotic familial idiocy. However, its genetic basis was still poorly understood. Although Gregor Mendel had published his article on the genetics of peas in 1865, Mendel's paper was largely forgotten for more than a generation – not rediscovered by other scientists until 1899. Thus, the Mendelian model for explaining Tay–Sachs was unavailable to scientists and doctors of the time. The first edition of the Jewish Encyclopedia, published in 12 volumes between 1901 and 1906, described what was then known about the disease:[41]
It is a curious fact that amaurotic family idiocy, a rare and fatal disease of children, occurs mostly among Jews. The largest number of cases has been observed in the United States—over thirty in number. It was at first thought that this was an exclusively Jewish disease, because most of the cases at first reported were between Russian and Polish Jews; but recently there have been reported cases occurring in non-Jewish children. The chief characteristics of the disease are progressive mental and physical enfeeblement; weakness and paralysis of all the extremities; and marasmus, associated with symmetrical changes in the macula lutea. On investigation of the reported cases, they found that neither consanguinity nor syphilitic, alcoholic, or nervous antecedents in the family history are factors in the etiology of the disease. No preventive measures have as yet been discovered, and no treatment has been of benefit, all the cases having terminated fatally.
Jewish immigration to the United States peaked in the period 1880–1924, with the immigrants arriving from Russia and countries in Eastern Europe; this was also a period of nativism (hostility to immigrants) in the United States. Opponents of immigration often questioned whether immigrants from southern and eastern Europe could be assimilated into American society. Reports of Tay–Sachs disease contributed to a perception among nativists that Jews were an inferior race.[40]
In 1969, Shintaro Okada and John S. O'Brien showed that Tay–Sachs disease was caused by an enzyme defect; he also proved that Tay–Sachs patients could be diagnosed by an assay of hexosaminidase A activity.[42] The further development of enzyme assays demonstrated that levels of hexosaminidases A and B could be measured in patients and carriers, allowing the reliable detection of heterozygotes. During the early 1970s, researchers developed protocols for newborn testing, carrier screening, and pre-natal diagnosis.[26][43] By the end of 1979, researchers had identified three variant forms of GM2 gangliosidosis, including Sandhoff disease and the AB variant of GM2-gangliosidosis, accounting for false negatives in carrier testing.[44]
Society and culture
Since carrier testing for Tay–Sachs began in 1971, millions of Ashkenazi Jews have been screened as carriers. Jewish communities embraced the cause of genetic screening from the 1970s on. The success with Tay–Sachs disease has led Israel to become the first country that offers free genetic screening and counseling for all couples and opened discussions about the proper scope of genetic testing for other disorders in Israel.[45]
Because Tay–Sachs disease was one of the first autosomal recessive genetic disorders for which there was an enzyme assay test (prior to polymerase chain reaction testing methods), it was intensely studied as a model for all such diseases, and researchers sought evidence of a selective process. A continuing controversy is whether heterozygotes (carriers) have or had a selective advantage. The presence of four different lysosomal storage disorders in the Ashkenazi Jewish population suggests a past selective advantage for heterozygous carriers of these conditions."[36]
This controversy among researchers has reflected three debates among geneticists at large:
- Dominance versus overdominance. In applied genetics (selective and agricultural breeding), this controversy has reflected the century-long debate over whether dominance or overdominance provides the best explanation for heterosis (hybrid vigor).
- The classical/balance controversy. The classical hypothesis of genetic variability, often associated with Hermann Muller, maintains that most genes are of a normal wild type, and that most individuals are homozygous for that wild type, while most selection is purifying selection that operates to eliminate deleterious alleles. The balancing hypothesis, often associated with Theodosius Dobzhansky, states that heterozygosity will be common at loci, and that it frequently reflects either directional selection or balancing selection.
- Selectionists versus neutralists. In theoretical population genetics, selectionists emphasize the primacy of natural selection as a determinant of evolution and of variation within a population, while neutralists favor a form of Motoo Kimura's neutral theory of molecular evolution, which emphasizes the role of genetic drift.[46]
Research directions
Enzyme replacement therapy
Enzyme replacement therapy techniques have been investigated for lysosomal storage disorders, and could potentially be used to treat Tay–Sachs as well. The goal would be to replace the nonfunctional enzyme, a process similar to insulin injections for diabetes. However, in previous studies, the HEXA enzyme itself has been thought to be too large to pass through the specialized cell layer in the blood vessels that forms the blood–brain barrier in humans.
Researchers have also tried directly instilling the deficient enzyme hexosaminidase A into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which bathes the brain. However, intracerebral neurons seem unable to take up this physically large molecule efficiently even when it is directly by them. Therefore, this approach to treatment of Tay–Sachs disease has also been ineffective so far.[47]
Jacob sheep model
Tay–Sachs disease exists in Jacob sheep.[48] The biochemical mechanism for this disease in the Jacob sheep is virtually identical to that in humans, wherein diminished activity of hexosaminidase A results in increased concentrations of GM2 ganglioside in the affected animal.[49] Sequencing of the HEXA gene cDNA of affected Jacobs sheep reveal an identical number of nucleotides and exons as in the human HEXA gene, and 86% nucleotide sequence identity.[48] A missense mutation (G444R)[50] was found in the HEXA cDNA of the affected sheep. This mutation is a single nucleotide change at the end of exon 11, resulting in that exon's deletion (before translation) via splicing. The Tay–Sachs model provided by the Jacob sheep is the first to offer promise as a means for gene therapy clinical trials, which may prove useful for disease treatment in humans.[48]
Substrate reduction therapy
Other experimental methods being researched involve substrate reduction therapy, which attempts to use alternative enzymes to increase the brain's catabolism of GM2 gangliosides to a point where residual degradative activity is sufficient to prevent substrate accumulation.[51][52] One experiment has demonstrated that using the enzyme sialidase allows the genetic defect to be effectively bypassed, and as a consequence, GM2 gangliosides are metabolized so that their levels become almost inconsequential. If a safe pharmacological treatment can be developed – one that increases expression of lysosomal sialidase in neurons without other toxicity – then this new form of therapy could essentially cure the disease.[53]
Another metabolic therapy under investigation for Tay–Sachs disease uses miglustat.[54] This drug is a reversible inhibitor of the enzyme glucosylceramide synthase, which catalyzes the first step in synthesizing glucose-based glycosphingolipids like GM2 ganglioside.[55]
Increasing β-hexosaminidase A activity
As Tay–Sachs disease is a deficiency of β-hexosaminidase A, by getting a substance that increases its activity, people affected will not be deteriorating as fast or not at all. While for infantile Tay–Sachs disease, there is no β-hexosaminidase A so then the treatment would be ineffective. However, for people affected by Late-Onset Tay–Sachs disease, they still have β-hexosaminidase A. The drug Pyrimethamine has been shown to increase activity of β-hexosaminidase A.[56] However, the increased levels of β-hexosaminidase A still fall far short of the desired "10% of normal HEXA", above which the phenotypic symptoms begin to disappear.[56]
References
- ↑ Lewis, Ricki (1997). Human Genetics. Chicago, IL: Wm. C. Brown. pp. 247–248. ISBN 0-697-24030-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Tay–Sachs disease Information Page". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 14 February 2007. Archived from the original on 29 December 2011. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- 1 2 McKusick, Victor A; Hamosh, Ada. "Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man". United States National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 29 December 2011. Retrieved 24 April 2009.
- ↑ Specola N, Vanier MT, Goutières F, Mikol J, Aicardi J (1 January 1990). "The juvenile and chronic forms of GM2 gangliosidosis: clinical and enzymatic heterogeneity". Neurology. 40 (1): 145–150. doi:10.1212/wnl.40.1.145. PMID 2136940.
- ↑ Moe, P G; Benke, T A (2005). "Neurologic and Muscular Disorders". Current Pediatric Diagnosis and Treatment (17 ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-142960-3.
- ↑ Rosebush PI, MacQueen GM, Clarke JT, Callahan JW, Strasberg PM, Mazurek MF (1995). "Late-onset Tay–Sachs disease presenting as catatonic schizophrenia: Diagnostic and treatment issues". Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 56 (8): 347–53. PMID 7635850.
- ↑ Willner JP, Grabowski GA, Gordon RE, Bender AN, Desnick RJ (July 1981). "Chronic GM2 gangliosidosis masquerading as atypical Friedreich's ataxia: Clinical, morphologic, and biochemical studies of nine cases". Neurology. 31 (7): 787–98. doi:10.1212/wnl.31.7.787. PMID 6454083.
- ↑ Kaback MM (December 2000). "Population-based genetic screening for reproductive counseling: the Tay–Sachs disease model". European Journal of Pediatrics. 159 (Suppl 3): S192–S195. doi:10.1007/PL00014401. ISSN 1432-1076. PMID 11216898.
- ↑ Myerowitz R (1997). "Tay–Sachs disease-causing mutations and neutral polymorphisms in the Hex A gene". Human Mutation. 9 (3): 195–208. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)9:3<195::AID-HUMU1>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID 9090523.
- ↑ Myerowitz R, Costigan FC (15 December 1988). "The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay–Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the alpha-chain of beta-hexosaminidase". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (35): 18587–18589. PMID 2848800.
- ↑ McDowell GA, Mules EH, Fabacher P, Shapira E, Blitzer MG (1992). "The presence of two different infantile Tay–Sachs disease mutations in a Cajun population". American Journal of Human Genetics. 51 (5): 1071–1077. PMC 1682822
 . PMID 1307230.
. PMID 1307230. - ↑ Keats BJ, Elston RC, Andermann E (1987). "Pedigree discriminant analysis of two French Canadian Tay–Sachs families". Genetic Epidemiology. 4 (2): 77–85. doi:10.1002/gepi.1370040203. PMID 2953646.
- ↑ De Braekeleer M, Hechtman P, Andermann E, Kaplan F (April 1992). "The French Canadian Tay–Sachs disease deletion mutation: Identification of probable founders". Human Genetics. 89 (1): 83–87. doi:10.1007/BF00207048. PMID 1577470.
- ↑ Ohno K, Suzuki K (5 December 1988). "Multiple Abnormal beta-Hexosaminidase Alpha-Chain mRNAs in a Compound-Heterozygous Ashkenazi Jewish Patient with Tay–Sachs Disease" (PDF). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (34): 18563–7. PMID 2973464. Retrieved 11 May 2007.
- 1 2 Kaback MM, Desnick RJ (2011). "Hexosaminidase A Deficiency". In Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Smith RJ, Stephens K. GeneReviews™ [Internet]. Seattle, Washington, USA: University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301397.
- ↑ Korf, Bruce R (2000). Human genetics: A problem-based approach (2 ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 11–12. ISBN 0-632-04425-X.
- ↑ Mahuran DJ (1999). "Biochemical consequences of mutations causing the GM2 gangliosidoses". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1455 (2–3): 105–138. doi:10.1016/S0925-4439(99)00074-5. PMID 10571007.
- ↑ Hechtman P, Kaplan F (1993). "Tay-Sachs disease screening and diagnosis: Evolving technologies". DNA and cell biology. 12 (8): 651–665. doi:10.1089/dna.1993.12.651. PMID 8397824.
- ↑ Tittarelli R, Giagheddu M, Spadetta V (July 1966). "Typical ophthalmoscopic picture of "cherry-red spot" in an adult with the myoclonic syndrome". The British journal of ophthalmology. 50 (7): 414–420. doi:10.1136/bjo.50.7.414. PMC 506244
 . PMID 5947589.
. PMID 5947589. - ↑ Aragão RE, Ramos RM, Pereira FB, Bezerra AF, Fernandes DN (Jul–Aug 2009). "'Cherry red spot' in a patient with Tay–Sachs disease: case report". Arq Bras Oftalmol. 72 (4): 537–9. doi:10.1590/S0004-27492009000400019. PMID 19820796.
- ↑ Seshadri R, Christopher R, Arvinda HR (2011). "Teaching NeuroImages: MRI in infantile Sandhoff disease". Neurology. 77 (5): e34. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227b215. PMID 21810694. Archived from the original on 28 December 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- ↑ Stoller D (1997). "Prenatal Genetic Screening: The Enigma of Selective Abortion". Journal of Law and Health. 12 (1): 121–140. PMID 10182027.
- ↑ "Chorionic Villus Sampling and Amniocentesis: Recommendations for Prenatal Counseling". United States, Center for Disease Control. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ↑ Bodurtha J, Strauss JF (2012). "Genomics and perinatal care". N. Engl. J. Med. 366 (1): 64–73. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1105043. PMID 22216843.
- ↑ Marik, J J (13 April 2005). "Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis". eMedicine.com. Retrieved 10 May 2007.
- 1 2 Ekstein, J; Katzenstein, H (2001). "The Dor Yeshorim story: Community-based carrier screening for Tay–Sachs disease". Tay-Sachs Disease. Advances in Genetics. 44. pp. 297–310. doi:10.1016/S0065-2660(01)44087-9. ISBN 978-0-12-017644-1. PMID 11596991.
- 1 2 3 Colaianni A, Chandrasekharan S, Cook-Deegan R (2010). "Impact of Gene Patents and Licensing Practices on Access to Genetic Testing and Carrier Screening for Tay–Sachs and Canavan Disease". Genetics in Medicine. 12 (4 Suppl): S5–S14. doi:10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181d5a669. PMC 3042321
 . PMID 20393311.
. PMID 20393311. - ↑ Eeg-Olofsson L, Kristensson K, Sourander P, Svennerholm L (1966). "Tay-Sachs disease. A generalized metabolic disorder". Acta Paediatrica Scand. 55 (6): 546–62. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb15254.x. PMID 5972561.
- ↑ Shapiro BE, Hatters-Friedman S, Fernandes-Filho JA, Anthony K, Natowicz MR (12 September 2006). "Late-onset Tay–Sachs disease: Adverse effects of medications and implications for treatment". Neurology. 67 (5): 875–877. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000233847.72349.b6. PMID 16966555.
- ↑ Clarke JT, Mahuran DJ, Sathe S, Kolodny EH, Rigat BA, Raiman JA, Tropak MB (April 2004). "An open-label Phase I/II clinical trial of pyrimethamine for the treatment of patients affected with chronic GM2 gangliosidosis (Tay-Sachs or Sandhoff variants).". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 102 (1): 6–12. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.09.004. PMC 3019177
 . PMID 20926324.
. PMID 20926324. - ↑ Rozenberg R, Pereira Lda V (2001). "The frequency of Tay-Sachs disease causing mutations in the Brazilian Jewish population justifies a carrier screening program". Sao Paulo medical journal [Revista paulista de medicina]. 119 (4): 146–149. doi:10.1590/s1516-31802001000400007. PMID 11500789.
- ↑ GM2 Gangliosidoses - Introduction And Epidemiology at Medscape. Author: David H Tegay. Updated: Mar 9, 2012
- 1 2 Chakravarti A, Chakraborty R (1978). "Elevated frequency of Tay–Sachs disease among Ashkenazic Jews unlikely by genetic drift alone". American Journal of Human Genetics. 30 (3): 256–261. PMC 1685578
 . PMID 677122.
. PMID 677122. - 1 2 3 4 Frisch A, Colombo R, Michaelovsky E, Karpati M, Goldman B, Peleg L (March 2004). "Origin and spread of the 1278insTATC mutation causing Tay–Sachs disease in Ashkenazi Jews: Genetic drift as a robust and parsimonious hypothesis". Human Genetics. 114 (4): 366–376. doi:10.1007/s00439-003-1072-8. PMID 14727180.
- ↑ Koeslag JH, Schach SR (1984). "Tay–Sachs disease and the role of reproductive compensation in the maintenance of ethnic variations in the incidence of autosomal recessive disease". Annals of Human Genetics. 48 (3): 275–281. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01025.x. PMID 6465844.
- 1 2 Risch N, Tang H, Katzenstein H, Ekstein J (2003). "Geographic Distribution of Disease Mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish Population Supports Genetic Drift over Selection". American Journal of Human Genetics. 72 (4): 812–822. doi:10.1086/373882. PMC 1180346
 . PMID 12612865.
. PMID 12612865. - ↑ Slatkin M (2004). "A Population-Genetic Test of Founder Effects and Implications for Ashkenazi Jewish Diseases". American Journal of Human Genetics. 75 (2): 282–293. doi:10.1086/423146. PMC 1216062
 . PMID 15208782.
. PMID 15208782. - ↑ Tay, Waren (1881). "Symmetrical changes in the region of the yellow spot in each eye of an infant". Transactions of the Ophthalmological Society. 1: 55–57.
- ↑ Sachs, Bernard (1887). "On arrested cerebral development with special reference to cortical pathology". Journal of Nervous Mental Disease. 14 (9): 541–554. doi:10.1097/00005053-188714090-00001.
- 1 2 Reuter, Shelley Z (Summer 2006). "The Genuine Jewish Type: Racial Ideology and Anti-Immigrationism in Early Medical Writing about Tay–Sachs Disease". The Canadian Journal of Sociology. 31 (3): 291–323. doi:10.1353/cjs.2006.0061.
- ↑ "Amaurotic Idiocy". The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk and Wagnalls. 1901–1906. Archived from the original on 28 December 2011. Retrieved 7 March 2009.
- ↑ Okada S, O'Brien JS (1969). "Tay–Sachs disease: Generalized absence of a beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase component". Science. 165 (3894): 698–700. doi:10.1126/science.165.3894.698. PMID 5793973.
- ↑ O'Brien JS, Okada S, Chen A, Fillerup DL (1970). "Tay–Sachs disease: Detection of heterozygotes and homozygotes by serum hexaminidase assay". New England Journal of Medicine. 283 (1): 15–20. doi:10.1056/NEJM197007022830104. PMID 4986776.
- ↑ O'Brien, John S (1983). "The Gangliosidoses". In Stanbury, J B; et al. The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. New York: McGraw Hill. pp. 945–969.
- ↑ Sagi M (1998). "Ethical aspects of genetic screening in Israel". Science in Context. 11 (3–4): 419–429. doi:10.1017/s0269889700003112. PMID 15168671.
- ↑ Kimura, Motoo (1983). The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-23109-4.
- ↑ Matsuoka K, Tamura T, Tsuji D, Dohzono Y, Kitakaze K, Ohno K, Saito S, Sakuraba H, Itoh K (14 October 2011). "Therapeutic Potential of Intracerebroventricular Replacement of Modified Human β-Hexosaminidase B for GM2 Gangliosidosis". Molecular Therapy. Nature. 19 (6): 1017–1024. doi:10.1038/mt.2011.27. PMC 3129794
 . PMID 21487393.
. PMID 21487393. - 1 2 3 Torres PA, Zeng BJ, Porter BF, Alroy J, Horak F, Horak J, Kolodny EH (2010). "Tay–Sachs disease in Jacob sheep". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 101 (4): 357–363. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.08.006. ISSN 1096-7192. PMID 20817517.
- ↑ Porter BF, Lewis BC, Edwards JF, Alroy J, Zeng BJ, Torres PA, Bretzlaff KN, Kolodny EH (2011). "Pathology of GM2 Gangliosidosis in Jacob Sheep". Veterinary Pathology. 48 (3): 807–813. doi:10.1177/0300985810388522. ISSN 0300-9858. PMID 21123862.
- ↑ Kolodny E, Horak F, Horak J (2011). "Jacob sheep breeders find more Tay–Sachs carriers". ALBC Newsletter. Pittsboro, North Carolina, USA: American Livestock Breeds Conservancy. Archived from the original on 29 December 2011. Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- ↑ Platt FM, Neises GR, Reinkensmeier G, Townsend MJ, Perry VH, Proia RL, Winchester B, Dwek RA, Butters TD (1997). "Prevention of lysosomal storage in Tay–Sachs mice treated with N-butyldeoxynojirimycin". Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science. 276 (5311): 428–431. doi:10.1126/science.276.5311.428. PMID 9103204.
- ↑ Lachmann RH, Platt FM (2001). "Substrate reduction therapy for glycosphingolipid storage disorders". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 10 (3): 455–466. doi:10.1517/13543784.10.3.455. PMID 11227045.
- ↑ Igdoura SA, Mertineit C, Trasler JM, Gravel RA (1999). "Sialidase-mediated depletion of GM2 ganglioside in Tay–Sachs neuroglia cells". Human Molecular Genetics. Oxford University Press. 8 (6): 1111–1116. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.6.1111. PMID 10332044.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Zavesca (Miglustat) in Patients With Infantile Onset Gangliosidosis: Single and Steady State Oral Doses". 5 May 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
- ↑ Kolodny EH, Neudorfer O, Gianutsos J, Zaroff C, Barnett N, Zeng BJ, Raghavan S, Torres P, Pastores GM (2004). "Late-onset Tay–Sachs disease: Natural history and treatment with OGT 918 (Zavesca™)". Journal of Neurochemistry. 90 (S1): 54–55. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02650_.x. ISSN 0022-3042.
- 1 2 Osher E, Fattal-Valevski A, Sagie L, Urshanski N, Amir-Levi Y, Katzburg S, Peleg L, Lerman-Sagie T, Zimran A, Elstein D, Navon R, Stern N, Valevski A (March 2011). "Pyrimethamine increases β-hexosaminidase A activity in patients with Late Onset Tay Sachs.". Mol. Genet. Metab. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 102 (3): 356–63. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.11.163. PMID 21185210.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tay–Sachs disease. |
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on hexosaminidase A deficiency, Tay–Sachs disease
- NINDS Tay–Sachs Disease Information Page
- Tay–Sachs disease at NLM Genetics Home Reference
- Tay–Sachs on NCBI