Taxila
| Punjabi: ٹيکسلا | |
 View of the Dharmarajika, an ancient stupa | |
 Shown within Pakistan | |
| Location | Rawalpindi District, Punjab, Pakistan |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 33°44′45″N 72°47′15″E / 33.74583°N 72.78750°ECoordinates: 33°44′45″N 72°47′15″E / 33.74583°N 72.78750°E |
| Type | Settlement |
| History | |
| Founded | Possibly c. 370 BCE[1] |
| Abandoned | 5th century |
| Official name | Taxila |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iii, vi |
| Designated | 1980 (4th session) |
| Reference no. | 139 |
| Region | Southern Asia |
Taxila (Urdu: ٹيکسلا, Sanskrit: तक्षशिला, Punjabi: ਟਕਸਿਲਾ, IAST: Takṣaśilā, meaning "City of Cut Stone" or "Takṣa Rock") is a town and an important archaeological site in the Rawalpindi District of the Punjab, Pakistan, situated about 32 km (20 mi) north-west of Islamabad and Rawalpindi, just off the famous Grand Trunk Road. The town lies 549 metres (1,801 ft) above sea level. It is the headquarters of the Taxila Tehsil in the Rawalpindi district.
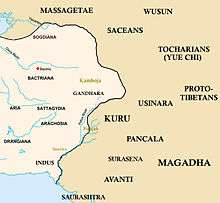
Ancient Taxila was situated at the pivotal junction of South Asia and Central Asia. Some of the earliest ruins in this area date to the time of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BCE.
Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has changed hands many times over the centuries, with many empires vying for its control. When the great ancient trade routes connecting these regions ceased to be important, the city sank into insignificance and was finally destroyed by the nomadic Hunas in the 5th century. The renowned archaeologist Sir Alexander Cunningham rediscovered the ruins of Taxila in the mid-19th century. In 1980, Taxila was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[2] In 2006 it was ranked as the top tourist destination in Pakistan by The Guardian newspaper.[3]
By some accounts, Taxila was considered to be one of the earliest (or the earliest) universities in the world.[4][5][6][7][8] Others do not consider it a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in Taxila,[9][10][11] in contrast to the later Nalanda university in eastern India.[11][12][13]
In a 2010 report, Global Heritage Fund identified Taxila as one of 12 worldwide sites most "On the Verge" of irreparable loss and damage, citing insufficient management, development pressure, looting, and war and conflict as primary threats.[14]
References in ancient texts
Hindu mythology has it that Taxila derived its name from Takṣa, who was the son of Bharata, the brother of the Hindu deity Rama.[4] Takṣa's kingdom was called Takṣa Khanda and its capital that he founded was named Taxila.[15] According to another theory propounded by Damodar Dharmananda Kosambi, Taxila is related to Takṣaka, Sanskrit for "carpenter", and is an alternative name for the Nāga, a non-Indo-Iranian people of ancient India.[16] In the great Hindu epic, the Mahābhārata, the Kuru Kingdom's heir, Parikṣit (grandson of the Arjuna) was enthroned at Taxila.[17] Traditionally, it is believed that the Mahabharata was first recited at Taxila by Vaisampayana, student of Vyasa at the behest of the seer Vyasa himself, at the Snake Sacrifice.[18]
Scattered references in historical works indicated that Taxila may have dated back to at least the 8th century BCE.[19][20][21]
Historically, Taxila lay at the crossroads of three major ancient trade routes. Owing to this strategic location, Taxila has changed hands many times over the centuries.
Archaeological excavations later showed that the city may have grown significantly during the Achaemenid Empire of the 6th century BCE. In 516 BC, Darius I embarked on a campaign to Central Asia, Ariana and Bactria and then marched into Afghanistan to Hindush in modern Pakistan. Darius spent the winter of 516-515 BCE in Gandhara, preparing to conquer the Indus Valley. Darius conquered the Indus in 515 BCE.[22] He controlled the Indus Valley from Gandhara to modern Karachi and appointed the Greek Scylax of Caryanda to explore the Indian Ocean from the mouth of the Indus to the Suez. Darius then marched through the Bolan Pass and returned through Arachosia and Drangiana back to Persia.
Taxila is also described in some detail in the Buddhist Jataka tales,[23] which date from about the 4th century BCE. The Jataka literature mentions it as the capital of the kingdom of Gandhara and as a great centre of learning.
Greek invaders arrived during the 4th century BCE. According to Joseph Needham: "When the men of Alexander the Great came to Taxila ... they found a university there the like of which had not been seen in Greece, a university which taught the three Vedas and the eighteen accomplishments and was still existing when the Chinese pilgrim Fa-Hsien went there about AD 400."[24]


In about the 1st century BCE or 1st century CE, an Indo-Scythian king named Azilises had three mints, one of which was at Taxila, and struck coins with obverse legends in Greek and Kharoṣṭhī.
The Chinese monk Faxian, writing of his visit to Taxila in 405 CE, mentions the kingdom of Takshasila, meaning "the Severed Head". He says that this name was derived from an event in the life of Buddha because this is the place "where he gave his head to a man".[25]
Xuanzang, another Chinese monk, visited Taxila in 630 and in 643. It appears to have already been overrun by the Hunas and been in ruins by his time. Taxila is called Taxiala in Ptolemy’s Geography.[26] In the Historia Trium Regum (History of the Three Kings) composed by John of Hildesheim around 1375, the city is called Egrisilla.[27]
Political history

- The northern road — the later Grand Trunk or GT Road — the royal road which connected Gandhara in the west to the kingdom of Magadha and its capital Pāṭaliputra in the Ganges valley in eastern India. This trade route was described by the Greek writer Megasthenes as the “Royal Highway”.
- The north-western route through Bactria, Kāpiśa, and Puṣkalāvatī. This route connected Taxila with the western Asia.
- The Indus route from Kashmir and Central Asia, via Śri nagara, Mansehra, and the Haripur valley[28] across the Khunjerab Pass to the Silk Road in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south. The Khunjerab passes between Kashmir and Xinjiang—the current Karakoram highway—and was traversed in antiquity.
- There are carbon dates c. 2550-2288 BCE for the earliest settlement at Taxila (in the Hathial area), with ties to the nearby Sarai Khola, an earlier site.[29] Also, some early Indus period culture and relics.
- Pottery shards were found in this area. Pottery dated c. 900 BCE shows ties between Taxila and Charsadda (ancient Pushkalavati),[30] also in the kingdom of Gandhara.[31]
- c. 518 BCE, or perhaps earlier – Darius the Great already part Taxila to the Achaemenid Empire.[32] Taxila, as the capital of Gandhara satrapy, was evidently under Achaemenian rule for more than a century.
- 486 - 465 BC Xerxes I or in Hebrew Ahasuerus ruled this part of Taxila and was part of the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire.
- Buddhist literature, especially the Jatakas, mentions Taxila as the capital of the kingdom of Gandhara.
- 326 BCE – Alexander the Great receives submission of ruler of Taxila, Omphis (Āmbhi).[32] Greek historians accompanying Alexander described Taxila as “wealthy, prosperous, and well governed.”
- Shapur I of the Sassanid Empire during the 3rd century CE, which is later recorded in the 6th century CE in the form of "Avagānā" by the Indian astronomer Varāha Mihira in his Brihat-samhita. It was used to refer to a common legendary ancestor known as Afghana, propagated to be grandson of King Saul of Israel.
- 321–317 BCE - Chandragupta Maurya, founder of the Mauryan empire, makes himself master of northern and north-western India, including Panjab. Chandragupta Maurya's advisor Kautilya (also known as Chanakya) was a teacher at Taxila. Under Chandragupta, Taxila became a provincial capital.
- During the reign of Chandragupta's grandson Aśoka, Taxila became a great Buddhist centre of learning. Nonetheless, Taxila was briefly the centre of a minor local rebellion, subdued only a few years after its onset.[33] Ashoka encouraged trade by building roads, most notably a highway of more than 1,600 kilometers (1,000 miles) linking his capital Pataliputra with Taxila.
- 185 BCE – The last Maurya emperor, Bṛhadratha, is assassinated by his general, Pushyamitra Shunga, during a parade of his troops.[34]
- 2nd century BCE - After three generations of Maurya rule, Taxila was annexed by the Indo-Greek kingdom of Bactria. Indo-Greeks build new capital, Sirkap, on the opposite bank of the river from Taxila.[35] During this new period of Bactrian Greek rule, several dynasties (like Antialcidas) likely ruled from the city as their capital. During lulls in Greek rule, the city managed profitably on its own, to independently control several local trade guilds, who also minted most of the city's autonomous coinage.
- c. 90 BCE – The Indo-Scythian (Sakas) chief Maues overthrows the last Greek king of Taxila.[36]
- c. 20 BCE – Gondophares, founder of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom, conquers Taxila and makes it his capital.[37]
- c. 46 AD – According to early Christian legend, Thomas the Apostle visits king Gondophares IV.[38][39]
- Neo-Pythagorean sage Apollonius of Tyana visits Taxila. His biographer described Taxila as a fortified city that was laid out on a symmetrical plan and compared it in size to Nineveh.
- 76 – The date of and inscription found at Taxila of "Great King, King of Kings, Son of God, the Kushana".[40] Taxila was taken from the Parthians by the Kushans under Kujula Kadphises. The great Kushan ruler Kanishka later founded "Sirsukh", the third city on the site.
- 4th century CE: the Sasanian king Shapur II seems to have conquered Taxila, as evidenced by the numerous Sasanian copper coins found there.
- c. 460–470 CE – The Hephthalites (the Hunas) sweep over Gandhāra and Punjab; and cause wholesale destruction of the Buddhist monasteries and stupas at Taxila, which never again recovers.[41]
- 1863–64 and 1872–73 - Excavations begun by Alexander Cunningham identified a local site known as Saraikhala (or Sarai Khola) with ancient Taxila. Prior to that, the location of the ancient city of Taxila, known from literary texts, was uncertain.
Ancient centre of learning
Taxila became a noted centre of learning (including the religious teachings of Hinduism) at least several centuries BCE, and continued to attract students from around the old world until the destruction of the city in the 5th century. At its height, it has been suggested that Taxila exerted a sort of "intellectual suzerainty" over other centres of learning in India.,[7] and its primary concern was not with elementary, but higher education.[8] Generally, a student entered Taxila at the age of sixteen. The Vedas, the ancient and the most revered Hindu scriptures, and the Eighteen Silpas or Arts, which included skills such as archery, hunting, and elephant lore, were taught, in addition to its law school, medical school, and school of military science.[42] Students came to Taxila from far-off places such as Kashi, Kosala and Magadha, in spite of the long and arduous journey they had to undergo, on account of the excellence of the learned teachers there, all recognized as authorities on their respective subjects.[43][44]
Notable students and teachers
Taxila had great influence on the Hindu culture and the Sanskrit language. It is perhaps best known because of its association with Chanakya, also known as Kautilya, the strategist who guided Chandragupta Maurya and assisted in the founding of the Mauryan empire. The Arthashastra (Sanskrit for The knowledge of Economics) of Chanakya, is said to have been composed in Taxila itself.[45][46] The Ayurvedic healer Charaka also studied at Taxila.[42] He also started teaching at Taxila in the later period.[47] The ancient grammarian Pāṇini, who codified the rules that would define Classical Sanskrit, has also been part of the community at Taxila.[48]
The institution is significant in Buddhist tradition since it is believed that the Mahāyāna branch of Buddhism took shape there. Jivaka, the court physician of the Magadha emperor Bimbisara who once cured the Buddha, and the enlightened ruler of Kosala, Prasenajit, are some important personalities mentioned in Pali texts who studied at Taxila.[49]
Nature of education
By some accounts, Taxilla was considered to be amongst the earliest universities in the world.[4][5][6][7][8] Others do not consider it a university in the modern sense, in that the teachers living there may not have had official membership of particular colleges, and there did not seem to have existed purpose-built lecture halls and residential quarters in Taxila,[9][10][11] in contrast to the later Nalanda University.[11][12][13]
No external authorities like kings or local leaders subjected the scholastic activities at Taxila to their control. Each teacher formed his own institution, enjoying complete autonomy in work, teaching as many students as he liked and teaching subjects he liked without conforming to any centralized syllabus. Study terminated when the teacher was satisfied with the student's level of achievement. In general, specialisation in a subject took around eight years, though this could be lengthened or shortened in accordance with the intellectual abilities and dedication of the student in question. In most cases the "schools" were located within the teachers' private houses, and at times students were advised to quit their studies if they were unable to fit into the social, intellectual and moral atmosphere there.[50]
Knowledge was considered too sacred to be bartered for money, and hence any stipulation that fees ought to be paid was vigorously condemned. Financial support came from the society at large, as well as from rich merchants and wealthy parents. Though the number of students studying under a single Guru sometimes numbered in the hundreds, teachers did not deny education even if the student was poor; free boarding and lodging was provided, and students had to do manual work in the household. Paying students like princes were taught during the day; non-paying ones, at night.[51] Guru Dakshina was usually expected at the completion of a student's studies, but it was essentially a mere token of respect and gratitude - many times being nothing more than a turban, a pair of sandals, or an umbrella. In cases of poor students being unable to afford even that, they could approach the king, who would then step in and provide something. Not providing a poor student a means to supply his Guru's Dakshina was considered the greatest slur on a King's reputation.[52]
Examinations were treated as superfluous, and not considered part of the requirements to complete one's studies. The process of teaching was critical and thorough- unless one unit was mastered completely, the student was not allowed to proceed to the next. No convocations were held upon completion, and no written "degrees" were awarded, since it was believed that knowledge was its own reward. Using knowledge for earning a living or for any selfish end was considered sacrilegious.[50]
Students arriving at Taxila usually had completed their primary education at home (until the age of eight), and their secondary education in the Ashrams (between the ages of eight and twelve), and therefore came to Taxila chiefly to reach the ends of knowledge in specific disciplines.[53]
Ruins

The British archaeologist Sir John Marshall (1876-1958) conducted excavations over a period of twenty years in Taxila.[54]
Sarai Kala
This is an archaeological site 3 km southwest of Taxila that has the earliest occupation, and preserves Neolithic remains going back to 3360 BC. It also has Early Harappan remains of 2900-2600 BC. A later settlement in this area has parallels with Hathial in the Taxila area.[55]
Other sites
The ruins of Taxila contain buildings and Buddhist stupas located over a large area. The main ruins of Taxila are divided into three major cities, each belonging to a distinct time period.
- The oldest of these is the Hathial area, which yielded surface shards similar to Red Burnished Ware (or soapy red ware) recovered from early phases at Charsadda—these may date from as early as the late 2nd millennium BCE to the 6th century BCE. Bhir Mound dates from the 6th century BCE and has Northern Black Polished Ware.
- The second city of Taxila is located at Sirkap and was built by Greco-Bactrian kings in the 2nd century BCE.
- The third and last city of Taxila is at Sirsukh and relates to the Kushan rulers.
In addition to the ruins of the city, a number of buddhist monasteries and stupas also belong to the Taxila area. Some of the important ruins of this category include the ruins of the stupa at Dharmarajika, the monastery at Jaulian, the monastery at Mohra Muradu in addition to a number of stupas.
Culture
Modern Taxila is a mix of wealthy urban and rustic rural environs. Urban residential areas are in the form of small neat and clean colonies populated by the workers of heavy mechanical complex & heavy industries, educational institutes and hospitals that are located in the area. The city has many educational institutes including CIIT Wah Campus, HITEC University and the University of Engineering and Technology Taxila.
In addition to the ruins of ancient Taxila, relics of Mughal gardens and vestiges of historical Grand Trunk Road, which was built by the Mauryan Empire, are also found in Taxila region. Nicholson's Obelisk, a monument of British colonial era situated at the Grand Trunk road welcomes the travellers coming from Rawalpindi/Islamabad into Taxila. The monument was built by the British to pay tribute to Brigadier John Nicholson (1822–1857) an officer of the British army who died in India during the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Taxila Museum, dedicated mainly to the remains of ancient Taxila, is also situated in the city.
Industry
The industries include heavy machine factories and industrial complex, Pakistan Ordnance Factories at Wah Cantt and the cement factory. Heavy Industries Taxila and Heavy Mechanical Complexes are also based here. Small, cottage and household industries include stoneware, pottery and footwear.
- A coin from 2nd century BCE Taxila.
 The Indo-Greek king Antialcidas ruled in Taxila around 100 BCE, according to the Heliodorus pillar inscription.
The Indo-Greek king Antialcidas ruled in Taxila around 100 BCE, according to the Heliodorus pillar inscription. Jaulian, a World Heritage Site at Taxila.
Jaulian, a World Heritage Site at Taxila. Jaulian silver Buddhist reliquary, with content. British Museum.
Jaulian silver Buddhist reliquary, with content. British Museum. Stupa base at Sirkap, decorated with Hindu, Buddhist and Greek temple fronts.
Stupa base at Sirkap, decorated with Hindu, Buddhist and Greek temple fronts.- Stupa in Taxila.
- A Taxila coin, 200–100 BCE. British Museum.
See also
- List of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Pakistan
- Taxila Museum
- Harappa
- Mohenjo-daro
- Gandhara
- Nalanda
- HMC Taxila
- HIT Taxila
- HITECH Taxila
- UET Taxila
References
- ↑ S. K. Agarwal (1 September 2008). Towards Improving Governance. Academic Foundation. p. 17. ISBN 978-81-7188-666-1. Retrieved 2012-06-06.
- ↑ UNESCO World Heritage Site, 1980. Taxila: Multiple Locations. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- ↑ Windsor, Antonia (17 October 2006). "Out of the rubble". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- 1 2 3 Needham, Joseph (2004). Within the Four Seas: The Dialogue of East and West. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-36166-4.
- 1 2 Kulke, Hermann; Rothermund, Dietmar (2004). A History of India (4th ed.). Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32919-1.
In the early centuries the centre of Buddhist scholarship was the University of Taxila.
- 1 2 Balakrishnan Muniapan, Junaid M. Shaikh (2007), "Lessons in corporate governance from Kautilya's Arthashastra in ancient India", World Review of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development 3 (1):
"Kautilya was also a Professor of Politics and Economics at Taxila University. Taxila University is one of the oldest known universities in the world and it was the chief learning centre in ancient India."
- 1 2 3 Radha Kumud Mookerji (2nd ed. 1951; reprint 1989), ''Ancient Indian Education: Brahmanical and Buddhist (p. 478), Motilal Banarsidass Publ., ISBN 81-208-0423-6:
"Thus the various centres of learning in different parts of the country became affiliated, as it were, to the educational centre, or the central university, of Taxila which exercised a kind of intellectual suzerainty over the wide world of letters in India."
- 1 2 3 Radha Kumud Mookerji (2nd ed. 1951; reprint 1989), Ancient Indian Education: Brahmanical and Buddhist (p. 479), Motilal Banarsidass Publ., ISBN 81-208-0423-6:
"This shows that Taxila was a seat not of elementary, but higher, education, of colleges or a university as distinguished from schools."
- 1 2 Anant Sadashiv Altekar (1934; reprint 1965), Education in Ancient India, Sixth Edition, Revised & Enlarged, Nand Kishore & Bros, Varanasi:
"It may be observed at the outset that Taxila did not possess any colleges or university in the modern sense of the term."
- 1 2 F. W. Thomas (1944), in John Marshall (1951; 1975 reprint), Taxila, Motilal Banarsidass, Delhi:
"We come across several Jātaka stories about the students and teachers of Takshaśilā, but not a single episode even remotely suggests that the different 'world renowned' teachers living in that city belonged to a particular college or university of the modern type."
- 1 2 3 4 Taxila Archived 22 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine. (2007), Encyclopædia Britannica:
"Taxila, besides being a provincial seat, was also a centre of learning. It was not a university town with lecture halls and residential quarters, such as have been found at Nalanda in the Indian state of Bihar."
Archived 22 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine. - 1 2 "Nalanda" (2007). Encarta.
- 1 2 "Nalanda" (2001). Columbia Encyclopedia.
- ↑ Global Heritage Fund | GHF
- ↑ Invasion of the Genes Genetic Heritage of India, By B. S. Ahloowalia. p81
- ↑ Kosambi 1975:129
- ↑ Kosambi, Damodar Dharmanand (1975) [1956]. An Introduction to the Study of Indian History (Revised Second ed.). Bombay: Popular Prakashan. p. 126.
- ↑ Britannica Online Encyclopedia, article:Taxila. "The great Indian epic Mahabharata was, according to tradition, first recited at Taxila at the great snake sacrifice of King Janamejaya, one of the heroes of the story."
- ↑ UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Taxila
- ↑ Scharfe, Hartmut (2002). Education in Ancient India. Brill Academic Publishers. p. 141. ISBN 90-04-12556-6.
- ↑ "History of Education", Encyclopædia Britannica, 2007.
- ↑ Darius the Great
- ↑ Marshall 1975:81
- ↑ Needham 2004.
- ↑ A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms, Being an Account by the Chinese Monk Fa-Hien of his Travels in India and Ceylon in Search of the Buddhist Books of Discipline, Chapter 11
- ↑ J. W. McCrindle, The Invasion of India by Alexander the Great as Described by Arrian, Q. Curtius, Diodorus, Plutarch and Justin, Westminster, Constable, 1893, pp.343-344.
- ↑ Frank Schaer, The Three Kings of Cologne, Heidelberg, Winter, 2000, Middle English Texts no.31, p.196.
- ↑ Thapar, Romila (1997) [1961]. Aśoka and the Decline of the Mauryas. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 237. ISBN 0-19-563932-4.
- ↑ Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin, The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan. Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 ISBN 052128550X
- ↑ http://a.harappa.com/sites/g/files/g65461/f/CulturesSocietiesIndusTrad.pdf
- ↑ Mohan Pant, Shūji Funo, Stupa and Swastika: Historical Urban Planning Principles in Nepal's Kathmandu Valley. NUS Press, 2007 ISBN 9971693720, citing Allchin: 1980
- 1 2 Marshall, John (1975) [1951]. Taxila: Volume I. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass. p. 83.
- ↑ Thapar 1997
- ↑ Kulke, Hermann; Rothermund, Dietmar (1998). A History of India (3rd ed.). London: Routledge. p. 68. ISBN 0-415-15481-2.
- ↑ Kulke and Rothermund 1998:70
- ↑ arshall 1975:84
- ↑ Marshall 1975:85
- ↑ Medlycott, A.E. (1905). "The Apostle Thomas and Gondophares the Indian King". India and the Apostle Thomas. London: David Nutt.
- ↑ Medlycott, A.E. India and the Apostle Thomas in George Menachery ed., Indian Church History Classics Vol.I, Ollur 1998.
- ↑ Kulke and Rothermund 1998:75
- ↑ Marshall 1975:86
- 1 2 Radha Kumud Mookerji (2nd ed. 1951; reprint 1989). Ancient Indian Education: Brahmanical and Buddhist (p. 478-489). Motilal Banarsidass Publ. ISBN 81-208-0423-6.
- ↑ Political and social movements in ancient Panjab (from the Vedic age up to the Maurya period), by Buddha Prakash (Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, 1964)"Students from Magadha traversed the vast distances of northern India in order to join the schools and colleges of Taxila. We learn from Pali texts that Brahmana youths, Khattiya princes and sons of setthis from Rajagriha, Kashi, Kosala and other places went to Taxila for learning the Vedas and eighteen sciences and arts."
- ↑ Universities in Ancient India, by DG Apte. Page 9
- ↑ Kautilya. Encyclopaedia Britannica. Archived 10 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Radhakumud Mookerji (1941; 1960; reprint 1989). Chandragupta Maurya and His Times (p. 17). Motilal Banarsidass Publ. ISBN 81-208-0405-8.
- ↑ "Takshila university". Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- ↑ Political and social movements in ancient Panjab (from the Vedic age up to the Maurya period), by Buddha Prakash (Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, 1964)."Pāṇini and Kautilya, two masterminds of ancient times, were also brought up in the academic traditions of Taxila"
- ↑ Political and social movements in ancient Panjab (from the Vedic age up to the Maurya period), by Buddha Prakash (Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, 1964)"Likewise, Jivaka, the famous physician of Bimbisara who cured the Buddha, learnt the science of medicine under a far-famed teacher at Taxila and on his return was appointed court-physician at Magadha. Another illustrious product of Taxila was the enlightened ruler of Kosala, Prasenajit, who is intimately associated with the events of the time of the Buddha."
- 1 2 Universities in Ancient India, by D.G Apte. Page 9-10.
- ↑ Universities in Ancient India, by D.G Apte. Page 16-17.
- ↑ Universities in Ancient India, by D.G Apte. Page 18-19.
- ↑ Universities in Ancient India, by D.G Apte. Page 11.
- ↑ Marshall, Sir John (1918). A Guide to Taxila. Calcutta: Government Press.
- ↑ Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin, The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan. Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 ISBN 052128550X
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Taxila. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Taxila. |
- Taxila: An Ancient Indian University by S. Srikanta Sastri
- Explore Taxila with Google Earth on Global Heritage Network
- Guide to Historic Taxila by Professor Dr. Ahmad Hasan Dani in 10 chapters
- "Taxila", by Jona Lendering
- [ Some photos by Umayr Sahlan Masud]
- Taxila page from punjab-info
- Travel With Young – Taxila 한글
- Map of Gandhara archeological sites, from the Huntington Collection, Ohio State University (large file)
- "Taxila Museum and Jaulian Monastery", by Saadullah Bashir
- John Marshall, A guide to Taxila (1918) on Archive.org