Sudan Black B
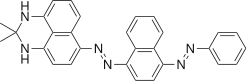 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dihydroperimidin-6-yl)-(4-phenylazo-1-naphthyl)diazene | |
| Other names
Sudan Black; Fat Black HB; Solvent Black 3; C.I. 26150 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 4197-25-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:88216 |
| ChemSpider | 55272 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.898 |
| MeSH | Sudan+Black+B |
| PubChem | 61336 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H24N6 | |
| Molar mass | 456.54 g/mol |
| Melting point | 120 to 124 °C (248 to 255 °F; 393 to 397 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Sudan Black B (C29H24N6) is a nonfluorescent, relatively thermostable lysochrome (fat-soluble dye) diazo dye used for staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a dark brown to black powder with maximum absorption at 596-605 nm and melting point 120–124 °C. It stains blue-black.
Sudan Black B is one of the dyes used for Sudan staining. Similar dyes include Oil Red O, Sudan III, and Sudan IV.
Sudan Black B can be used to stain some other materials than the other Sudan dyes, as it is not so specific to lipids.
A use of Sudan Black B is in fingerprint enhancement. It is useful for detecting fats that are contaminated with oil and grease.
In differentiating haematological disorders Sudan black will stain myeloblasts but not lymphoblasts.
Production and composition
Sudan Black is formed by coupling of diazotized 4-phenylazonaphthalenamine-1 with 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-1H-perimidine.[1] Therefore the main product expected was 2,3-dihydro-2,2dimethyl-6-[(4-phenylazo-1-naphthalenyl)-azo]-1H-perimidine. However the dye resulting from the above reaction product actually contains many, up to 42 colored and colorless by products that can be fractionated. The two major products were blue in color confirmed by various chromato-graphic (TLC and column etc.) separation and spectroscopic (IR, NMR, Mass) identification were named SBB-I & SBB-II (Rf values of 0.49 and 0.19 (chloroform/benzene 1∶1, SiO2) in thin Layer Chromatography).[2] The above described product indeed turned out to be SSB-II which comprises up to 60% of the mixture, and the SBB-I was 2,3-dihydro-2,2dimethyl-4-[(4-phenylazo-1-naphthalenyl)-azo]-1H-perimidine.
References
- ↑ "Histochemistry. 1977 Dec 7;54(3):237-50. Sudan Black B: chemical structure and histochemistry of the blue main components. Pfüller U, Franz H, Preiss A". Springerlink.com. Retrieved 2012-05-25.
- ↑ HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY Volume 16, Number 1 (1968), 68-84, DOI: 10.1007/BF00306212 Thin layer chrornatography and histochemistry of Sudan Black B A. G. W. Lansink
External links
- Stains File entry