Stratified squamous epithelium
| Stratified squamous epithelium | |
|---|---|
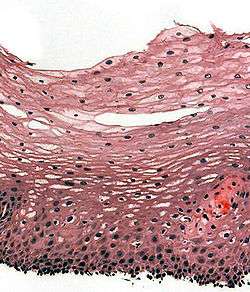 | |
 Section of the human skin showing the stratified squamous epithelial surface, referred to as the epidermis. The layer of keratin here is named the stratum corneum | |
| This article is one of a series on |
| Epithelia |
|---|
| Squamous epithelial cell |
| Columnar epithelial cell |
| Cuboidal epithelial cell |
| Specialised epithelia |
|
| Other |
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal.[1] There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as it is the thickest and layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina.[2]
Keratinization
Non-keratinized
Non-keratinized surfaces must be kept moist by bodily secretions to prevent them from drying out.
Examples of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium include cornea (see also corneal epithelium), lining mucosa of oral cavity, esophagus, anal canal, foreskin and the internal portion of the lips.
Note that even non-keratinized surfaces, consisting as they do of keratinocytes, will have a minor superficial keratinized layer of varying thickness, depending on the age of the epithelium and the damage it has experienced.
Keratinized
Keratinized surfaces are protected from abrasion by keratin and kept hydrated and protected from dehydration by glycolipids produced in the stratum granulosum. Examples of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium include epidermis of the palm of the hand and sole of the foot,[3] and the masticatory mucosa.
Gallery
 Epithelium
Epithelium Micrograph of normal stratified squamous epithelium (right of image) and the metaplasic epithelium of Barrett's esophagus (left of image). Alcian blue stain.
Micrograph of normal stratified squamous epithelium (right of image) and the metaplasic epithelium of Barrett's esophagus (left of image). Alcian blue stain.
References
- ↑ Tortora, Gerard J.; Derrickson, Bryan. Introduction to the Human Body. The Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology (9th ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 84. ISBN 978-0470-59892-4.
[referring to stratified squamous epithelium] Description: Two or more layers of cells; cells in apical layer and several layers deep to it are squamous; those in the deep layers vary in shape from cuboidal to columnar.
- ↑ Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 7th Edition. Pearson. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-321-88418-3.
- ↑ Pratt, Rebecca. "Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)". AnatomyOne. Amirsys, Inc. Retrieved 2012-09-28.