St Georges Basin (New South Wales)
| St Georges Basin | |
|---|---|
| Bherwherrae or Bherwherree[1] | |
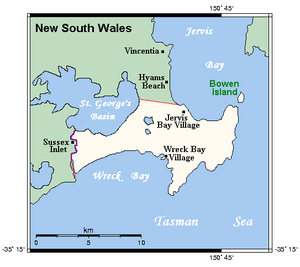 St Georges Basin, relative to its location in New South Wales and the Jervis Bay Territory. | |
| Location | South Coast, New South Wales and the Jervis Bay Territory |
| Coordinates | 35°11′23″S 150°35′24″E / 35.18972°S 150.59000°ECoordinates: 35°11′23″S 150°35′24″E / 35.18972°S 150.59000°E |
| Type | Open intermediate wave dominated barrier estuary;[2] or inland sea[1] |
| Primary inflows | Wandandian Creek, Tomerong Creek |
| Primary outflows | Sussex Inlet, Tasman Sea |
| Catchment area | 316 km2 (122 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Australia |
| Surface area | 40.9 km2 (15.8 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 5.3 m (17 ft) |
| Water volume | 215,079 megalitres (7,595.4×106 cu ft) |
| Settlements | Sussex Inlet, St Georges Basin |
| Website | NSW Environment & Heritage webpage |
| References | [3] |
St Georges Basin is an open intermediate estuary,[2] or inland sea,[1] located in the South Coast region of New South Wales, adjacent to the Jervis Bay Territory.
Location and features
St Georges Basin is a coastal waterbody located immediately adjacent to the Tasman Sea of the South Pacific Ocean, north of the town of Sussex Inlet and east of the town of St Georges Basin. The basin is fed by Wandandian Creek and Tomerong Creek and its primary outflow is to the Tasman Sea via the Sussex Inlet.[1] The basin covers a catchment area of 316 square kilometres (122 sq mi) and contains approximately 215,079 megalitres (7,595.4×106 cu ft) of water over an estimated surface area of 40.9 square kilometres (15.8 sq mi); and at an average depth of 5.3 metres (17 ft).[4]
Located with the basin are six artificial reefs that range up to 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) in depth.[3]
History
The traditional custodians of the land surrounding St Georges Basin were the Indigenous Australian Yuin people, who named the basin as Bherwherrae or Bherwherree.[1]
European surveyor Thomas Florance renamed the body of water as St Georges Basin on 29 November 1827, while tracing from Jervis Bay to Conjola.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "St Georges Basin". Geographical Names Register (GNR) of NSW. Geographical Names Board of New South Wales. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
- 1 2 Roy, P. S; Williams, R. J; Jones, A. R; Yassini, I; et al. (2001). "Structure and Function of South-east Australian Estuaries". Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 53: 351–384. doi:10.1006/ecss.2001.0796.
- 1 2 "Map of St Georges Basin, NSW". Bonzle Digital Atlas of Australia. 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
- ↑ "St Georges Basin: Physical characteristics". Coastal and floodplain management: Coastal zone management: Estuaries of NSW. NSW Environment & Heritage. 27 April 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
External links
- "Clyde River & Jervis Bay catchments" (map). Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales.