Solketal
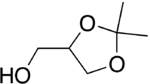 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methanol | |
| Other names
Isopropylidene glycerol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 100-79-8 Racemic 14347-78-5 R enantiomer 22323-82-6 S enantiomer | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7247 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.626 |
| PubChem | 7528 |
| UNII | 3XK098O8ZW |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O3 | |
| Molar mass | 132.16 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | clear colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.063 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Boiling point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F; 461 to 462 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Solubility | Miscible in most organic solvents (alcohols, ethers, hydrocarbons) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 80 °C (176 °F; 353 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Solketal is a protected form of glycerol with an isopropylidene acetal group joining two neighboring hydroxyl groups. Solketal contains a chiral center on the center carbon of the glycerol backbone, and so can be purchased as either the racemate or as one of the two enantiomers. Solketal has been used extensively in the synthesis of mono-, di- and triglycerides by ester bond formation. The free hydroxyl groups of solketal can be esterified with a carboxylic acid to form the protected monoglyceride, where the isopropylene group can then be removed using an acid catalyst in aqueous or alcoholic medium. The unprotected diol can then be esterified further to form either the di- or triglyceride.
References
- Mary Renoll and Melvin S. Newman (1955). "dl-ISOPROPYLIDENEGLYCEROL". Org. Synth. 28: 73.; Coll. Vol., 3, p. 502
- Sanderson, John R.; Lin, Jiang J.; Duranleau, Roger G.; Yeakey, Ernest L.; Marquis, Edward T. (1988). "Free radicals in organic synthesis. A novel synthesis of glycerol based on ethylene glycol and formaldehyde". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 53 (12): 2859. doi:10.1021/jo00247a043.
- "Solketal". Logo of chemBlink Inc. Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World. Archived from the original on 31 October 2010. horizontal tab character in
|publisher=at position 24 (help) - Matsumoto, Yoshihiko; Mita, Keisuke; Hashimoto, Keiji; Iio, Hideo; Tokoroyama, Takashi (1996). "Selective cleavage of ethers using silica-alumina gel catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method". Tetrahedron. 52 (28): 9387. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(96)00501-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/7/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.