Anthony Hoskins
| Sir Anthony Hoskins | |
|---|---|
 Admiral Sir Anthony Hoskins | |
| Born |
1 September 1828 North Perrott, Somerset, England |
| Died |
21 June 1901 (aged 72) Dorking, Surrey, England |
| Allegiance | United Kingdom |
| Service/branch | Royal Navy |
| Years of service | 1842–1893 |
| Rank | Admiral |
| Commands held |
First Naval Lord Mediterranean Fleet Australia Station HMS Sultan HMS Eclipse HMS Zebra HMS Plumper HMS Hecate HMS Slaney HMS Beaver |
| Battles/wars |
Cape Frontier War Second Opium War Anglo-Egyptian War |
| Awards |
Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Order of the Medjidie, First Class (Ottoman Empire) |
Admiral Sir Anthony Hiley Hoskins, GCB (1 September 1828 – 21 June 1901) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer, he took part in the Cape Frontier War of 1851 and then saw action at the Battle of Canton in December 1857 and the Battle of Taku Forts in May 1858 during Second Opium War. Once promoted to flag officer rank, he acted as Second-in-Command of the Fleet at the bombardment of Alexandria in July 1882 during the Anglo-Egyptian War. He went on to be First Naval Lord in September 1891 but in that role took a relaxed view of the size of the Fleet and did not see the need for a large shipbuilding effort on the scale envisaged by some of his colleagues, such as Admiral Sir Frederick Richards and Admiral Sir John Fisher who were concerned about French and German naval expansion.
Early career
.jpg)
Born the son of Henry Hoskins and Mary Hoskins (née Phelips) and educated at Winchester College, Hoskins entered the Royal Navy in April 1842.[1] During his early career he served in the sixth-rate HMS Conway and then fourth-rate HMS President taking action against slave traders off the coast of East Africa.[1]
Promoted to lieutenant on 26 March 1849, while serving in the fifth-rate HMS Castor on the Cape of Good Hope Station, he took part in the Cape Frontier War of 1851.[1] After being given command of the gunboat HMS Beaver in 1856,[2] he was promoted to commander on 26 February 1858 and commanded the gunboat HMS Slaney on the China Station seeing action at the Battle of Canton in December 1857 and the Battle of Taku Forts in May 1858 during Second Opium War.[2]
Hoskins was given command of the sloop HMS Hecate on the Pacific Station in May 1860 and then of the sloop HMS Plumper also on the Pacific Station in January 1861.[2] He then took command the sloop HMS Zebra in the West Africa Squadron in April 1862, and having been promoted to captain on 12 December 1863, he was given command of the screw sloop HMS Eclipse on the North American Station in August 1869 and then command of the broadside ironclad HMS Sultan in the Channel Squadron in July 1873.[2] He went on to be Commodore of the Australian Station in September 1875 with his broad pennant initially in the corvette HMS Pearl and then, from January 1877, in the corvette HMS Wolverine.[2] He was appointed a Naval Aide-de-Camp to the Queen on 22 January 1877[3] and a Companion of the Order of the Bath on 2 June 1877.[4]
Senior command
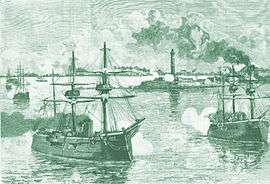
Promoted to rear admiral on 15 June 1879,[5] Hoskins became Junior Naval Lord in May 1880 but was despatched to the Mediterranean in 1882 where he acted as Second-in-Command of the Fleet at the bombardment of Alexandria in July 1882 during the Anglo-Egyptian War.[1] Having been advanced to Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath on 17 November 1882,[6] Hoskins became Admiral Superintendent of Naval Reserves later that month.[2] For his service during the Anglo-Egyptian War he was appointed to the Turkish Order of the Medjidie, Second Class on 12 January 1883.[7]
Promoted to vice admiral on 1 June 1885,[8] Hoskins went on to be Second Naval Lord in July 1885 and Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet, hoisting his flag in the battleship HMS Camperdown, in March 1889.[2] For his work in the Mediterranean he was advanced to Order of the Medjidie, First Class on 7 November 1889.[9]
Promoted to full admiral on 20 June 1891,[10] Hoskins became First Naval Lord in September 1891.[2] As First Naval Lord he took a relaxed view of the size of the Fleet and did not see the need for a large shipbuilding effort on the scale envisaged by some of his colleagues such as Admiral Sir Frederick Richards and Admiral Sir John Fisher who were concerned about French and German naval expansion.[1] He was advanced to Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath on his retirement on 17 November 1893.[11]
Hoskins died at Pleystons Capel near Dorking on 21 June 1901 and is buried at North Perrott in Somerset.[1]
Family
In 1865 Hoskins married Dorothea Ann Eliza Robinson, daughter of Sir George Stamp Robinson, 7th Baronet. Lady Hoskins died shortly after her husband, on 7 October 1901, aged 62.[12] The couple had no children.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Sir Anthony Hoskins". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "William Loney RN". Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 24413. p. 502. 2 February 1877. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 24467. p. 3497. 2 June 1877. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 24734. p. 3967. 17 June 1879. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 25169. p. 5166. 17 November 1882. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 25189. p. 280. 16 January 1883. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 25475. p. 2530. 2 June 1885. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 25991. p. 5919. 8 November 1889. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 26174. p. 3300. 23 June 1891. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ The London Gazette: no. 26459. p. 6423. 17 November 1893. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ "Obituary – Lady Hoskins". The Times (36580). London. 8 October 1901. p. 4.
External links
- William Loney RN Career History
| Military offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by James Goodenough |
Commander-in-Chief, Australia Station 1875–1878 |
Succeeded by John Wilson |
| Preceded by Sir John Commerell |
Junior Naval Lord 1880–1882 |
Succeeded by Sir Frederick Richards |
| Preceded by Lord Alcester |
Second Naval Lord 1885–1888 |
Succeeded by Sir Richard Hamilton |
| Preceded by The Duke of Edinburgh |
Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet 1889–1891 |
Succeeded by Sir George Tryon |
| Preceded by Sir Richard Hamilton |
First Naval Lord 1891–1893 |
Succeeded by Sir Frederick Richards |