Bala shark
| Bala shark | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Cypriniformes |
| Family: | Cyprinidae |
| Genus: | Balantiocheilos |
| Species: | B. melanopterus |
| Binomial name | |
| Balantiocheilos melanopterus (Bleeker, 1850) | |
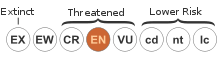
The bala shark, Balantiocheilos melanopterus, also known as the tricolor shark, silver shark, or shark minnow, is a fish species of the family Cyprinidae, and is one of the two species in the genus Balantiocheilos. This species is not a true shark, but is commonly so called because of its torpedo-shaped body and large fins. It is endangered because the population decreased by 50% in the last 10 years.
Distribution
The bala shark occurs in the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, and Borneo.[2][3] Previous records further north in the Mekong and Chao Phraya River is due to confusion with the recently described and possibly extinct B. ambusticauda (although the presence of any Balantiocheilos in the Mekong is questionable).[3]
Appearance and anatomy
These fish have a silver body with black margins on their dorsal, caudal, anal, and pelvic fins. They have big eyes to find and catch their prey. The bala shark will grow to a maximum length of 35 cm (14 in).[2]
Habitat and ecology
Bala sharks are found in midwater depths in large and medium-sized rivers and lakes. They feed on phytoplankton, but mostly on small crustaceans, rotifers, and insects and their larvae.[2]
In the aquarium
Bala sharks are misunderstood aquarium fish.[4] These fish are generally peaceful and good companions to many other types of tropical fish.[4] Bala sharks are widely available in most pet stores, but will grow to a size too large for the home aquarium.[4]
They are a hardy fish that will tolerate temperature changes, pH changes, and other factors to which other fish may be sensitive. The water pH should be 6.0–8.0. The preferable water hardness for this species is soft to medium (5.0–12.0 dGH). Water temperature should be kept between 22–28°C (72–82°F).[2] The bala shark prefers to be kept in groups of two or more specimens.[2] It requires a covered aquarium as it is a skilled jumper, but may injure itself on the lid of the tank. [4]

Very young bala sharks are sometimes kept in small aquaria. However, given their adult size, schooling behavior, and swimming speed, the fish quickly grow to need much more room. Hobbyists continue to debate over acceptable minimum tank sizes, but generally recommend at least a 2-meter tank. FishBase lists a minimum of 150 cm (5 ft).[2] Many believe the fish is simply too large and too active to be kept in residential aquaria at all; only enormous, custom-built tanks are acceptable, if any tank at all is. Indoor ponds are also considered feasible housing options and may be better suited to the average aquarist.
Conservation
B. melanopterus is listed as an endangered species by the IUCN Red List.[1] It has become rare or extinct in many river basins of its native range.[2] In Danau Sentarum (Borneo), fishermen already reported in 1993 and 1995 that the populations have decreased dramatically after 1975, for no clear reason. Fishermen mentioned overfishing for the aquarium-fish trade or forest fires in 1975 and the resulting pollution as possible causes. The species is apparently extirpated in the Batang Hari basin (Sumatra) and it seems that all individuals of B. melanopterus exported from Indonesia and Thailand by the aquarium-fish trade are captive bred.[3]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Balantiocheilos melanopterus. |
- 1 2 Kottelat, M. (1996). Balantiocheilos melanopterus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T2529A9449980.en
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2007). "Balantiocheilos melanopterus" in FishBase. Apr 2007 version.
- 1 2 3 Ng, Heok Hee; Kottelat, Maurice (2007). "Balantiocheilos ambusticauda, a new and possibly extinct species of cyprinid fish from Indochina (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae)" (PDF). Zootaxa. 1463: 13–20. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-27.
- 1 2 3 4 Axelrod, Herbert R.; Emmens, C.; Burgess, W.; Pronek, N. (1996). Exotic Tropical Fishes. T.F.H. Publications. ISBN 0-87666-543-1.