Sigmoid sinus
| Sigmoid sinus | |
|---|---|
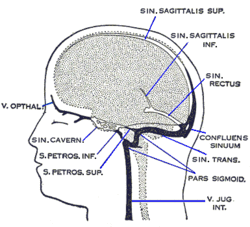 Dural veins. ("Pars sigmoid" labeled at lower right.) | |
| Details | |
Source | transverse sinus |
| Drains to | internal jugular vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Sinus sigmoideus |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.224 |
| TA | A12.3.05.108 |
| FMA | 50782 |
The sigmoid sinuses(sigma- or s-shaped hollow curve), also known as the pars sigmoid, are venous sinuses within the skull that receive blood from posterior dural venous sinus veins.
Structure
The sigmoid sinus is a dural venous sinus situated within the dura mater. The sigmoid sinus receives blood from the transverse sinuses, which track the posterior wall of the cranial cavity, travels inferiorly along the parietal bone, temporal bone and occipital bone, and converges with the inferior petrosal sinuses to form the internal jugular vein.[1] :795-6
Each sigmoid sinus begins beneath the temporal bone and follows a tortuous course to the jugular foramen, at which point the sinus becomes continuous with the internal jugular vein.
Function
The sigmoid sinus receives blood from the transverse sinuses, which receive blood from the posterior aspect of the skull. Along its course, the sigmoid sinus also receives blood from the cerebral veins, cerebellar veins, diploic veins, and emissary veins.[1] :795