SRNA-Xcc1
sRNA-Xcc1 (small RNA identified from Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris) is a family of trans-acting non-coding RNA (also known as small RNA).[1][2] Homologs of sRNA-Xcc1 are found in a few bacterial strains belonging to alpha-proteobacteria, beta-proteobacteria, gamma-proteobacteria,and delta-proteobacteria. In Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, sRNA-Xcc1 is encoded by an integron gene cassette and is under the positive control of the virulence regulators HrpG and HrpX.[3][4]
The Origin and Phylogenetic Distribution
sRNA-Xcc1 is encoded by a gene cassette in the integron of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and homologs of sRNA-Xcc1 are frequently found in integron gene cassettes cloned from uncultured bacterium,[5] it is possible that sRNA-Xcc1 is originally captured by integrons from natural environments. sRNA-Xcc1 homologs are found in a few taxonomically far related strains across alpha-, beta- and gamma-proteobacteria but not in close related bacteria, implying that sRNA-Xcc1 is transferred via horizontal gene transfer (HGT). sRNA-Xcc1 homologous gene are found located on Tn5542, a transposon carryed by the plasmid pHMT112 indicating that the horizontal transfer of sRNA-Xcc1 is realized by means of transposons and/or plasmids.[6]
Potential Biological Function
The expression of sRNA-Xcc1 is under the positive control of the two important virulence regulators HrpG and HrpX of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, indicating that sRNA-Xcc1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of the pathogen.
References
- ↑ Chen XL; Tang DJ; Jiang RP; He YQ; Jiang BL; Lu GT; Tang JL (2011). "sRNA-Xcc1, an integron-encoded transposon- and plasmid-transferred trans-acting sRNA, is under the positive control of the key virulence regulators HrpG and HrpX of Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris.". RNA Biol. 8 (6): 947–53. doi:10.4161/rna.8.6.16690. PMC 3256417
 . PMID 21941121.
. PMID 21941121. - ↑ Schmidtke C, Findeiß S, Sharma CM, Kuhfuß J, Hoffmann S, Vogel J, et al. (2011). "Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas identifies sRNAs with putative virulence functions.". Nucleic Acids Res. 40 (5): 2020–2031. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr904. PMC 3300014
 . PMID 22080557.
. PMID 22080557. - ↑ Wengelnik K; Van den Ackerveken G; Bonas U (1996). "HrpG, a key hrp regulatory protein of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is homologous to two-component response regulators.". Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 9 (8): 704–12. doi:10.1094/mpmi-9-0704. PMID 8870269.
- ↑ Wengelnik K; Bonas U (1996). "HrpXv, an AraC-type regulator, activates expression of five of the six loci in the hrp cluster of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria.". J Bacteriol. 178 (12): 3462–9. PMC 178114
 . PMID 8655542.
. PMID 8655542. - ↑ Gillings MR; Holley MP; Stokes HW; Holmes AJ (2005). "Integrons in Xanthomonas: a source of species genome diversity.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102 (12): 4419–24. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406620102. PMC 555480
 . PMID 15755815.
. PMID 15755815. - ↑ Tan HM; Tang HY; Joannou CL; Abdel-Wahab NH; Mason JR (1993). "The Pseudomonas putida ML2 plasmid-encoded genes for benzene dioxygenase are unusual in codon usage and low in G+C content.". Gene. 130 (1): 33–9. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(93)90343-2. PMID 8344526.
Phylogenetic diagrams
-
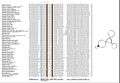
Multiple alignment and the consensus secondary structure model of the sRNA-Xcc1 homologs. Multiple alignment was done by using ClustalW program and the consensus secondary structure was predicted based on the multiple alignment using RNAalifold program.The conserved sequence motif ‘AUACAAnACCC’ was boxed
-

The phylogenetic tree of sRNA-Xcc1 homologs based on multiple alignments. Symbols on the right hand side of the name of bacterial strain indicate the class of the species that holds the sRNA-Xcc1 homolog, and the place where the homolog located.