History of the Russo-Turkish wars
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman-Russian Wars) were a series of wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history.[1]
List of conflicts
| Name | Result | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Russo-Turkish War (1568–70) | Russian military victory[2] Ottoman commercial victory[3] |
| 2 | Russo-Turkish War (1676–81) | Indecisive[4] Treaty of Bakhchisarai[5] |
| 3 | Russo-Turkish War (1686–1700) | Russia gains possession of Azov fortress of Taganrog, Pavlovsk and Mius[6] |
| 4 | Russo-Turkish War (1710–11) | Ottoman victory[7] |
| 5 | Austro-Russian–Turkish War (1735–39) |
|
| 6 | Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) | Russian victory[12][13][14] |
| 7 | Russo-Turkish War (1787–92) | Russian victory[15][16][17] |
| 8 | Russo-Turkish War (1806–12) | Russian victory[18] |
| 9 | Russo-Turkish War (1828–29) | Russian victory[19] |
| 10 | Crimean War (1853–56) | Ottoman, British, French and Italian victory[20] |
| 11 | Russo-Turkish War (1877–78) | Russian victory[21] |
| 12 | World War I: Caucasus Campaign (1914–18) | Treaty of Brest-Litovsk |
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| Military of the Ottoman Empire |
 |
|
Classical Army (1451–1606) |
|
Modern army (1861–1922) |
| Conscription |
Conflict begins (1568–1827)
After having captured the region of Podolia in the course of the Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76), the Ottoman government strove to spread its rule over all of the Right-bank Ukraine with the support of its vassal, Petro Doroshenko (1665–1672). The latter's pro-Ottoman policy caused discontent among many Ukrainian Cossacks, who would elect Ivan Samoilovich as a sole Hetman of all Ukraine in 1674.

In 1679–80, the Russians repelled the attacks of the Crimean Tatars and signed the Treaty of Bakhchisarai on January 3, 1681, which would establish the Russo-Turkish border by the Dnieper River. Russia had joined the European Holy League (Austria, Poland, Venice) in 1686. During the war, the Russian army organized the Crimean campaigns of 1687 and 1689 and the Azov campaigns (1695–96). The Russian involvement marked the beginning of the Russo-Turkish Wars. In light of Russia's preparations for the war with Sweden and other countries' signing the Treaty of Karlowitz with Turkey in 1699, the Russian government signed the Treaty of Constantinople with the Ottoman Empire in 1700.
After the Russians had defeated the pro-Sweden Ukrainian Cossacks led by Ivan Mazepa and Swedes in the Battle of Poltava in 1709, Charles XII of Sweden managed to persuade the Ottoman Sultan Ahmed III to declare war on Russia on November 20, 1710.
By the late 17th century, the Iranian Safavid dynasty, which was neighboring both empires and had been most notably one of the greatest rivals for Turkey for the last few centuries, had been heavily declining. Making advantage of the situation, Russia and Turkey decided to conquer swaths of its territory comprising contemporary Dagestan, Azerbaijan, and Northern Iran which was taken by Peter I in the Russo-Persian War (1722-1723), and Turkey took all territories to the west of it comprising modern day Armenia, parts of Eastern Anatolia, as well as western Iran. The gains by both were confirmed in the Treaty of Constantinople (1724). For a few years, both would border each other through a large territory in the Caucasus now as well, which caused further frictions.
Several years later, Russia had managed to secure a favourable international situation by signing a few treaties with Persia in 1732–35 which returned all gained Iranian territories of 1723 in the North, and South Caucasus as well as Northern Iran back, in order not to engage a war with the emerging new leader of Persia, namely Nader Shah. The treaties made in 1732 and 1735, had other diplomatically favourable aspects as it included an Russo-Iranian alliance against Turkey as well, as Persia was at war with Ottoman Empire in 1730–1735. In the meantime Russia also was supporting the accession to the Polish throne of Augustus III in 1735 instead of the French protégé Stanisław Leszczyński, nominated by pro-Ottoman France. Austria was Russia's ally since 1726.
The casus belli was the raids of the Crimean Tatars on Ukraine in the end of 1735 and the Crimean khan's military campaign in the Caucasus. In 1736, the Russian commanders envisioned the seizure of Azov and the Crimea.
On June 19, the Russian Don army (28,000 men) under the command of General Peter Lacy with the support from the Don Flotilla under the command of Vice Admiral Peter Bredahl seized the fortress of Azov. In July 1737, the Münnich army took by storm the Ottoman fortress of Ochakov. The Lacy army (already 40,000 men strong) marched into the Crimea the same month, inflicting a number of defeats on the army of the Crimean khan and capturing Karasubazar. However, Lacy and his soldiers had to leave the Crimea due to lack of supplies.
In July 1737, Austria entered the war against Turkey, but was defeated a number of times. In August, Russia, Austria and Turkey began negotiations in Nemirov, which would turn out to be fruitless. There were no significant military operations in 1738. The Russian army had to leave Ochakov and Kinburn due to the plague outbreak.
In 1739, the Münnich army crossed the Dnieper, defeated the Ottoman Empire at Stavuchany and occupied the fortress of Khotin (August 19) and Iaşi. However, Austria was defeated by the Ottoman Empire once again and signed a separate peace treaty on August 21. This, coupled with the imminent threat of the Swedish invasion, forced Russia to sign the Belgrade Peace Treaty with Turkey on September 18, which ended the war.
Following this border incident at Balta, Sultan Mustafa III declared war on Russia on September 25, 1768. The Turks formed the alliance with the Polish oppositionary forces of the Bar Confederation, while Russia was supported by the United Kingdom, which offered naval advisers to the Russian navy.
The Polish opposition was defeated by Alexander Suvorov, who was then transferred to the Ottoman theatre of operations, where in 1773 and 1774 he won several minor and major battles following the previous grand successes of the Russian Field-Marshal Pyotr Rumyantsev at Larga and Kagula.
The naval operations of the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Mediterranean yielded victories under the command of Aleksey Grigoryevich Orlov. In 1771, Egypt and Syria rebelled against the Ottoman rule, while the Russian fleet totally destroyed the Ottoman Navy.
On July 21, 1774, the Ottoman Empire signed the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, according to which the Crimean Khanate formally gained its independence, but in reality became dependent on Russia. Russia received the contribution of 4.5 million rubles and two key seaports allowing the direct access to the Black Sea.
In 1786 Catherine II of Russia made a triumphal progress through the Crimea in company with her ally, Emperor Joseph II. These events and the friction caused by mutual complaints of infringements of the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca, which had closed the previous war, stirred up public opinion in Istanbul, and the British ambassador lent his support to the war party.
In 1788 war was declared, but Turkey's preparations were inadequate and the moment was ill-chosen, now that Russia and Austria were in alliance, a fact of which Turkey became aware only when the horse tails were planted for the campaign. The Turks drove back the Austrians from Mehadia and overran the Banat (1789); but in Moldavia Field-Marshal Pyotr Rumyantsev was successful and captured Iaşi and Khotin.
Ottoman generals were incompetent and the army mutinous; expeditions for the relief of Bender and Akerman failed, Belgrade was taken by the Austrians, the impenetrable fortress of Izmail was captured by the brilliant Suvorov, and the fall of Anapa completed the series of Turkey's disasters.
Sultan Selim III was anxious to restore his country's prestige by a victory before making peace, but the condition of his troops rendered this hope unavailing; while Prussia, though on 31 January 1790 she had signed an offensive treaty with Turkey, gave her no help during the war. Accordingly, a treaty was signed with Russia at Iaşi (9 January 1792), by which the Crimea and Ochakov were left to Russia, the Dniester was made the frontier in Europe, and the Asiatic frontier remained unchanged.
Decline of the Ottoman Empire (1827–1914)
The Ottoman Empire had maintained military parity with Russia until the second half of the eighteenth century,[22] but by the 1820s the Ottoman armies were unable to put down the Russian-backed Greek revolt in southern Greece. The great powers of Europe decided to intervene and assist Greece with its independence. Thus Greece became the first independent country created out of a section of the Ottoman Empire. Russian aspirations for a section of the empire and bases on Russia's southern flank provoked British fears over naval domination of the Mediterranean and control of the land route to the Indian Subcontinent.[23]
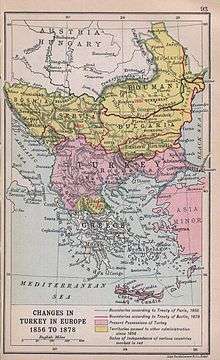
When in 1853 Russia destroyed the entire Ottoman fleet at Sinop, Britain and France concluded that armed intervention on the side of the Ottomans was the only way to halt a massive Russian expansion, on the grounds that the Ottoman armies could do nothing to stop a Russian march on Constantinople. Even though Ottomans and Russians were on the opposing sides, the roots of the ensuing Crimean War lay in the rivalry between the British and the Russians. The war ended unfavorably for the Russians, with the Paris peace of 1856.
The war brought a decline in Ottoman morale and a feeling of helplessness, illustrating that modern technology and superior weaponry were the most important part of a modern army, and a part that the Ottoman Empire was sorely lacking. While fighting alongside the British, French, and even the Piedmontese, the Ottomans could see how far they had fallen behind. It is not surprising then that at the midpoint of the 19th century the Ottoman Empire was at the mercy of the Russians until outside forces intervened. Things began to change after the Crimean War.
Another change was that Serbia was permanently granted its independent status. This pleased both Austria, who feared a Serbian revolt on its borders, and Russia who long supported the Slavic nation's independence. Other changes arose as Europeans for the first time saw the trading opportunity of Turkey. The amount of money entering the nation through trade was soon dramatically increased. As well the government received a great deal of extra money from a uniform tax system with little corruption. The Sultan also managed to get a tighter grip on the provincial beys and increased the tribute they had to pay. Regrettably Abdülaziz, the Sultan at the time, used much of this money on furnishing and creating great palaces to rival the great ones in England and France, which he had visited. The Empire was undergoing a revolution, throughout Anatolia a new Ottoman nationalism was appearing, and for the first time the Empire had a middle class. It seemed as though it might be possible for the Empire to turn its decline around.
).png)
The monetary and governmental collapse combined with a new threat from Russia began the final stages of the Empire's collapse. Russia had been forced by the Crimean War to give up its ambitions of owning the Ottoman capital of Constantinople and controlling the Bosphorus. Instead it decided to focus on gaining power in the Balkans. The population of much of the Balkans were Slavs, as were the Russians. They also mainly followed the Eastern Orthodox Church, as did the Russians. When new movements in Russia, such as that of the Slavophiles, started to enter the area, it became agitated and prone to revolution. When the government in Constantinople tried to initiate measures to prevent an economic collapse throughout the empire, it touched off a revolt in Herzegovina in 1875. The revolt in Herzegovina, quickly spread to Bosnia and then Bulgaria. Soon Serbian armies also entered the war against the Turks. These revolts were the first test of the new Ottoman armies. Even though they were not up to western European standards, the army fought effectively and brutally; during the war, the Ottomans carried out the Batak massacre in 1876. Januarius MacGahan, a journalist of the New York Herald and the London Daily News wrote of the terrible happenings after his visitation to Batak with Eugene Schuyler. According to most sources, around 5,000 people were massacred in Batak alone.[24] The total number of victims in the April uprising according to most estimates around 15,000,[25][26] which is supported by Eugene Schuyler's report, published in Daily News, according to which at least 15,000 persons were killed during the April Uprising in addition to 36 villages in three districts being buried.[27] According to Donald Quataert around 1,000 Muslims were killed by Christian Bulgarians and consequently 3,700 Christians were killed by Muslims.[28][29]
Soon the Balkan rebellions were beginning to falter. In Europe, papers were filled with reports of Ottoman soldiers killing thousands of Slavs. Even in Great Britain William Ewart Gladstone published his account of Ottoman atrocities in his "Bulgarian Horrors and the Question of the East".[30] Soon, a new Russo-Turkish war had begun. Despite fighting better than they ever had before, the advanced Ottoman armies still were not equal to the Russian forces. This time there was no help from abroad, in truth many European nations supported the Russian war, as long as it did not get too close to Istanbul. Ten and a half months later when the war had ended the age of Ottoman domination over the Balkans was over. The Ottomans had fought well, the new navy of Ironclads had won the battle for the Black Sea, and Russian advances in the Caucasus had been kept minimal. In the Balkans, however, the Russian army, supported by rebels, had pushed the Ottoman army out of Bulgaria, Romania, and much of East Rumelia and by the end of the war the artillery firing in Thrace could be heard in Constantinople.

In response to the Russian proximity to the straits the British, against the wishes of the Sultan, intervened in the war. A large task force representing British naval supremacy entered the straits of Marmara and anchored in view of both the royal palace and the Russian army. The British may have saved the Ottoman Empire once again, but it ended the rosy relations between the two powers that had endured since the Crimean War. Looking at the prospect of a British entry into the war the Russians decided to settle the dispute. The Treaty of San Stefano gave Romania and Montenegro their independence, Serbia and Russia each received extra territory, Austria was given control over Bosnia, and Bulgaria was given almost complete autonomy. The hope of the Sultan was that the other great powers would oppose such a one-sided resolution and a conference would be held to revise it. His desire became reality and in 1878 the Congress of Berlin was held where Germany promised to be an "honest broker" in the treaty's revision. In the new treaty Bulgarian territory was decreased and the war indemnities were cancelled. The conference also again hurt Anglo-Ottoman relations by giving the British the island of Cyprus. While annoyed at British British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli, the Sultan had nothing but praise for Otto von Bismarck who forced many of the major concessions upon Russia. These close Germano-Ottoman relations would persist until both empires' very end.
The Russian extension in this century developed with the main theme of supporting independence of Ottomans' former provinces and then bringing all of the Slav peoples of the Balkans under Bulgaria or using Ermenians in the east sets the stage. At the end of the century from Russian perspective; Romania, Serbia and Montenegro and autonomy of Bulgaria was achieved. That alarmed the Great Powers. After the Congress of Berlin the Russian expansion was controlled through stopping the expansion of Bulgaria. The Russian public felt that at the end of Congress of Berlin thousands of Russian soldiers had died for nothing.
The Balkans
There were two main movements for the west side. The first one was performed while Ottomans were dealing with the Greek uprising, see Greek War of Independence. The Greeks' independence war led to the Russian forces advancing into Bulgaria before the Turks sued for peace. The resulting Treaty of Adrianople (Edirne) on September 14, 1829, gave Russia most of the eastern shore of the Black Sea and the mouth of the Danube.
The second independence movement happened during the uprisings. See Bosnia and Herzegovina: 19th-20th centuries, Romanian War of Independence. An uprising against Ottoman rule began in Herzegovina in July 1875. The Bulgarians organised the April Uprising, which lasted from April to May 1876.
Serbia achieved autonomy and Russia was allowed to occupy Moldavia and Wallachia (guaranteeing their prosperity, and full "liberty of trade" for them) until Turkey had paid a large indemnity. The uprisings raised a chance for Russia (Prince Gorchakov) and Austria-Hungary (Count Andrássy), who made the secret Reichstadt Agreement on July 8, on partitioning the Balkan peninsula depending on the outcome.
During the Russo-Turkish war of 1877-1878, in February 1878 the Russian army had almost reached the Ottoman capital but, scared the city might fall, the British sent a fleet of battleships to intimidate Russia from entering the Ottoman capital. Under pressure from the British fleet to negotiate on the outcome of the war, Russia agreed a settlement under the Treaty of San Stefano on March 3, by which the Ottoman Empire recognized the independence of its former provinces Romania, Serbia and Montenegro and autonomy of Bulgaria. The Congress of Berlin also allowed Austria to occupy Bosnia and Herzegovina and Great Britain to take over Cyprus.[31]
The Caucasus
During the Greek uprising, the Russian empire reached the Ottoman borders in the Caucasus, which were located in the southwest of the region, as well as northeastern Anatolia. Under the terms of the Treaty of Adrianople, the Ottoman Empire recognized Russian sovereignty over western Georgia, which was formerly under Ottoman suzerainty, and recognized Russian domination of present-day Armenia, which had been conquered a year earlier (1828) by the Russians from Qajar Iran through the Treaty of Turkmenchay.[32]
End of conflict (1914–23)
During the early months of World War I, Kars was a key military objective for the Ottoman army. Ismail Enver who pushed the Ottoman Empire into World War I, needed a victory against the Russians to defend his position. He collected an army on the eastern border. The army was badly defeated under Enver's command at the Battle of Sarikamish January 2, 1915 against Nikolai Nikolaevich Yudenich. This defeat was more due to the winter weather and bad planning, given the fact that Russians were actually preparing to evacuate Kars. With the loss of the eastern army, Ottoman defenses crumbled with further small battles and the Russian army succeeded in advancing as far west as Erzincan.[33]
The collapse of the Russian army after the 1917 revolution left only thinly spread Armenian units to resist the inevitable Ottoman counter-attack. Before the end of World War I in 1918, the Ottoman army reformed with what was left from the middle-east branch and tried to build a line between whatever seemed to be left on their east border. The newly declared First Republic of Armenia captured Kars in April 1918, which was eventually handed back by the future Soviet administration. That same year in March, the Baku Commune was established in the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic. The commune later became the Centrocaspian Dictatorship, in turn conquered by the Islamic Army of the Caucasus, then shortly by the Triple Entente and finally the Bolsheviks. Defeat on other fronts caused the Ottoman Empire to surrender and withdraw forces. Both the Armenian and Azerbaijani Republics ended up being part of the Soviet Union in 1920.[34]
See also
- Ottoman Decline Thesis
- Ottoman wars in Europe
- Russo-Persian Wars
- Crimean Khanate
- Russo-Crimean Wars
- Russian conquest of the Caucasus
- Caucasian War
- Foreign policy of the Russian Empire
- List of Serbian–Turkish conflicts
- Crimean–Nogai raids into East Slavic lands
- Russia–Turkey relations
References
- ↑ Timothy C. Dowling, Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond (2 volumes, ABC-CLIO, 2014).
- ↑ Janet Martin, Medieval Russia: 980-1584, (Cambridge University Press, 1996), 356.
- ↑ Janet Martin, Medieval Russia: 980-1584, 356.
- ↑ David R. Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya, (Greenwood Publishing, 2006), 41.
- ↑ "Treaty of Bakhchisarai", Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia, Vol. I, ed. Alexander Mikaberidze, (ABC-CLIO, 2011), 180.
- ↑ "Treaty of Constantinople (1700)", Alexander Mikaberidze, Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia, Vol. I, 250.
- ↑ Donald Quataert, The Ottoman Empire, 1700-1922, (Cambridge University Press, 2005), 41.
- ↑ "Treaty of Nis (1739)", Alexander Mikaberidze, Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia, Vol. I, 647.
- ↑ Russo-Turkish wars // Encyclopædia Britannica
- ↑ Davies B. Empire and Military Revolution in Eastern Europe: Russia's Turkish Wars in the Eighteenth Century. A&C Black. 2011. P. 180ff
- ↑ Treaty of Nis (1739), Alexander Mikaberidze, Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia, (ABC-CLIO, 2011), 647.
- ↑ Brian L. Davies, The Russo-Turkish War, 1768-1774: Catherine II and the Ottoman Empire (Bloomsbury, 2016).
- ↑ Dowling T. C. Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond. ABC-CLIO. 2014. P. 744
- ↑ Isabel De Madariaga, Russia in the Age of Catherine the Great (1981) pp 205-14.
- ↑ Black J. European Warfare, 1660-1815. Taylor & Francis, 1994. P. 25
- ↑ Dowling Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond (2014) p. 745
- ↑ Isabel De Madariaga, Russia in the Age of Catherine the Great (1981) pp 393-426.
- ↑ Ziegler C. E. The History of Russia. ABC-CLIO, 2009. P. 46.
- ↑ John Frederick Baddeley, The Russian conquest of the Caucasus (Routledge, 2013. ch 12)
- ↑ Orlando Figes, The Crimean War: A History (2010)
- ↑ Ian Drury, The Russo-Turkish War 1877 (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2012).
- ↑ Aksan, Virginia (2007). Ottoman Wars, 1700–1860: An Empire Besieged. Pearson Education Ltd. pp. 130–5. ISBN 978-0-582-30807-7.
- Woodhead, Christine (2008). "New Views on Ottoman History, 1453–1839". The English Historical Review. Oxford University Press. 123: 983.
the Ottomans were able largely to maintain military parity until taken by surprise both on land and at sea in the Russian war from 1768 to 1774.
- Woodhead, Christine (2008). "New Views on Ottoman History, 1453–1839". The English Historical Review. Oxford University Press. 123: 983.
- ↑ David R. Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
- ↑ Bulgaria, R. J. Crampton, Oxford University Press, 2007, p.92
- ↑ 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica: Bulgaria, History
- ↑ Genocide and gross human rights violations: in comparative perspective, Kurt Jonassohn, 1999, p.210
- ↑ Schuyler's Preliminary Report on the Moslem Atrocities, published with the letters by Januarius MacGahan, London, 1876.
- ↑ Quataert, Donald. "The Ottoman Empire, 1700–1922 ", Cambridge University Press 2005, pp.69
- ↑ Millman, Richard. “The Bulgarian Massacres Reconsidered.” pp.218–231
- ↑ Bulgarian Horrors and the Question of the East, 5 September 1876
- ↑ Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
- ↑ Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
- ↑ Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
- ↑ Stone, A Military History of Russia: From Ivan the Terrible to the War in Chechnya (Greenwood Publishing, 2006)
Further reading
- Allen, William and Paul Muratoff. Caucasian Battlefields: A History Of The Wars On The Turco-Caucasian Border 1828-1921 (2011) ISBN 0-89839-296-9,
- Dowling, Timothy C. (2014). Russia at War: From the Mongol Conquest to Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Beyond [2 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-59884-948-6.
- Hughes, Lindsey (2000). Russia in the Age of Peter the Great. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. p. 640. ISBN 978-0-300-08266-1.
- Jelavich, Barbara. St. Petersburg and Moscow: Tsarist and Soviet Foreign Policy, 1814–1974 (1974)
- Kagan, Frederick, and Robin Higham, eds. The Military History of Tsarist Russia (2008) excerpts