Rosetta Stone decree
The Decree of Memphis (Ptolemy V)[1] is the third Memphis decree, the first being for his grandfather Ptolemy III (Decree of Canopus), and the second being, Decree of Memphis (Ptolemy IV). The Decree for Ptolemy V is the text recorded on the Rosetta Stone (issued at Memphis in 196 BC) in the Egyptian hieroglyphs, Demotic (Egyptian) script, and Greek.
The Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty, which ruled Egypt from 305 BC to 30 BC, issued a series of decrees over the course of their reign. The Rosetta Stone is the best known example.

The list of accomplishments
After six lines of preview on the Nubayrah Stele, the decree: "....Eirene, daughter of Ptolemy priestess of Arsinoe, the lover of her father; day this Decree, being the directors (superintendents) of services (?)....",[2] (the Priests Decree:)
- (Start 0 before list)(Summary of the Priests)
A–Directors of Services, the Prophets-(hidden things)..., the Priests who go in the holy shrine to "robe the gods"-(statues), Scribes of the Gods, Sages of the 'House of Life', (the Pr-Ankh)-(pr-House, the House of Life, the Library, the storing of the "secret, priest scrolls")
B–Priests, arriving from the regions- (South and North, Upper and Lower Egypt temples) on honoring assumption of kingship by Ptolemy V, "they went into sanctuary of Memphis [and] behold they spake:[3]- Ptolemy V Summary
A–Ptolemy and Wife Arsinoe-(Arsna) did great things, for Horus-Lands, of All People-(under his control), "being like a God, son of a gods, II," (his ancestry), .."the semblance-(likeness) of Horus", son of Isis, son of Osiris,[4] with giving heart, supplied silver, great quantities Grain for sanctuaries, supplied "precious objects" for quieting of Egypt, ..establishing sanctuaries (of South and North–Upper and Lower Egypt).
B–Gifts to Soldiers, in his authority, according to their rank. - Citizen taxes remitted
A–Taxes of Nobles, that concerned Pharaoh, remitted
B–Others, absolved completely.
C–Made Army (Soldiers), and Citizens "comfortable" in his period of sole Kingship.[5] - Tax Arrears and Pardons
A–Taxes on Egyptians, and Foreigners remitted.
B–Pardoned prisoners (from "long-ago 'incarcerations' "). - Offering to Gods, Silver & Grain, (yearly) to temples, (and their land holdings)(all types), and gods of the "plantation lands", of the nomes, to continue.
All possession lands, all kinds, to remain in possession. - Priesthood
A–Priesthood taxes not to increase.
B–Priests (of 'hourly-course duties' in temples) with Annual journey to Memphis-(Wall of Alexandria), released from journey. - Disallowing of corvée shanghaiing of "men of the sailors".
- Byssus cloth made for the Pharaoh's house, 2/3 remitted.
- Restoration
A–Things overdue for 'long time', restored (made "beautiful"-Nfr).
B–Restored Customs, (as Perfect, in the past)
C–Gave "height of Happiness"-(Restored Peace) to citizens as did God "Thoth, Great, Great"[6] - (not in Nubayrah Stele)-(from Demotic)-Revolt of citizens (the region that rebelled), citizens allowed to return to their homeland.[7]
- (Foreign Invasion)
A–Infantry-(Army), Cavalry-(horseman, etc), and Ships to drive back, those who came against Egypt from the 'Sea Coast' as well as those from the "Great Green"-(Mediterranean Sea)-(Green-papyrus stem)
B–Gave Silver, Grains (great Amounts) to quiet "Horus-lands" and "Egypt". - Took Siege against Lycopolis
A–People, citizens had transgressed "the Ways"
B–Blocked up canals (for water, growing food?)
C–Spent monies.
D–Set up Infantry at canals. Conquered "district"-(conquer: kheb-nef-two whips with shen ring)
E–Made a great Massacre (of the citizens)
F–(Punishes the Leaders)
G–Gathered soldiers, captured Leaders, ("at their head, they led astray the nomes, they pillaged the "Horus Lands"-(temple properties), they transgressed the way of "His Majesty"[8])
H–Father August (god Ra) granted: Leaders be brought to White Wall (Memphis); Rebels: "slaying by placing [them] upon stake[s]"[9]-(branch)-(= to the crucifying, forerunner to events)-(earlier people had been immersed in hot oil) - Temples
A–Remitted Tax Arrears.
Gave temples, Money(monies), (Silver-gold + Mace, the ligatured two hieroglyphs mean "silver", or "money"), and gave them Grains.
B–Byssus Cloth Production-(Tax) remitted. (Past Byssus owed, Remitted)
C–5 Grain Bushels on temple aroura lands remitted. Likewise the temple aroura Vineyards. - Endowments to Temples of Apis and Mnevis
A–Plus the animal burials
B–Provisions for the animal temples, Festivals conducted, Burnt Offerings, (animals) for slaughter, drink offerings (libations), and all things (everything) "customary", and the best for temples, and everything, large quantities, of Egypt, (provided) "according to what [is] in the laws"[10]-(laws: hepu, uses the H, reed shelter) - Gold and Silver and Grain, large quantities, everything, for "Temple of Apis"-(Hapy's temple); restored temple, (claim of its greatness, and God thankful)
- (And Lastly)
Set up Temples, Chapels, and Altars
A–The gods and goddesses rewarded Ptolemy V by giving him: "victory, might-(Nekh-t-"branch (hieroglyph)", etc)(Nike: Goddess of Victory), life-(Ankh), Strength, health, and everything Good, to the extent of them etc. for him, and his children, for ever."[11]
- Ptolemy V Summary
The completed accomplishment list is then followed by And a Happening Good [may there be][12]
The list of rewards given by the gods and goddesses is also referencing: A.U.S. (Life, Dominion, Health), commonly translated, or transcribed as Life, Prosperity, Health. It is an acronym, and commonly followed the reference to "Pharaoh, aus". (i.e. Pharaoh, life, dominion, health), in Egyptian: "Pharaoh, ankh, wedja, seneb". –(or "ankh, utcha, senbi")
The list of rewards
The list of 8 rewards is preceded by:
- "With Fortunate Happening !"(may Good Luck attend this)[13]
- Priests agree to increase honors to Ancestors (Ptolemy IV & III)
- A–Set up Statue-(wood)-(in Shrine, gold) to Ptolemy V, Title: "Avenger of Baq-t"-(Egypt)-(Avenger: cross-ndj (hieroglyph)-(a cross)–(a "grinding mill", to reduce to pellets, powder))
B–Statue with Sword Royal of Victory, etc.
C–Honor Statues 3 times per day - (long reward)-Create Shrine (for statue); Uraeii-(cobras) on shrine, Pschent crown, with Payyrus Clusters-(two types), Mut-Vulture–on–Basket-(basket (hieroglyph)) and Uraeus–on–Basket....the meaning thereof: the Lord of the Two Crowns Illumineth the Two Lands[14]–(Upper and Lower Egypt)
- (long reward)-Celebrate Festival, (each month)-Celebrate the day of Ptolemy V birth, and "Day of Accession"-to throne; using: burnt offerings, (incense, food), poured libations, all customs for festivals, (and mostly done in temples?)
- Five Day Festival, annual, beginning of month "Thoth"-(tutelary god of Scribes); Garlands on people's heads, festal altars, libations poured, and "all customs, etc"
- Priests given title: "Priest of the God "Manifested"[15]-(legs-forward (hieroglyph)), "Lord of 'Benefits' "–(Lord-Beauty,Beauty,Beauty); record on Documents, and engrave upon ring for each priest: "Priest of the god appearing-(manifesting), lord of benefits"-(beauty,beauty,beauty)
- Copy of Shrine-(statue) can be made by citizens for their House-(pr (hieroglyph)-House (hieroglyph)), and they must celebrate on "days each month"
- Engrave Decree, upon a stele, stone hard-(bowstring (hieroglyph)), in Hieroglyphs, Demotic-(democratic: Citizen text), and Greek; Erect-(mast (hieroglyph) stele in temples, of 1st, 2nd, 3rd orders by side of Statue of King, North, South, (Upper and Lower Egypt), Ptolemy V.
The Egyptian language hieroglyphs for a "good luck" quote:
- "And a Happening Good [may there be]"[16]–("and" = wick (hieroglyph) plus "arm":
+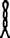
, (arm centered on wick))
See also
- Ptolemaic Decrees
- Decree of Canopus for Ptolemy III
- Decree of Memphis, or Raphia Decree, for Ptolemy IV
Notes
- ↑ Budge, (1989). The Rosetta Stone. p. 153.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 128-129.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 130-131.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 135.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 135.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 140.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 141.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 146.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 147.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 150.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 152-153.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 153.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), English translation, (p. 102-123), p. 116.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 162.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), p. 166.
- ↑ Budge, (1989), Egyptian hieroglyph text, p. 153.
References
- Budge, 1929, (1989). The Rosetta Stone, E.A.Wallace Budge, (Dover Publications), c 1929, Dover edition(unabridged), 1989. (softcover, ISBN 0-486-26163-8)