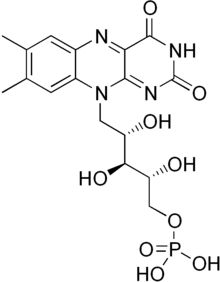
Flavin mononucleotide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
FMN | |
| Identifiers | |
| 146-17-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17621 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1201794 |
| ChemSpider | 559060 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.150 |
| E number | E101a (colours) |
| 5185 | |
| MeSH | Flavin+mononucleotide |
| PubChem | 643976 |
| UNII | 7N464URE7E |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H21N4O9P | |
| Molar mass | 456.344 g/mol |
| Melting point | 195 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN), or riboflavin-5′-phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin (vitamin B2) by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases including NADH dehydrogenase as well as cofactor in biological blue-light photo receptors. During the catalytic cycle, a reversible interconversion of the oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs in the various oxidoreductases. FMN is a stronger oxidizing agent than NAD and is particularly useful because it can take part in both one- and two-electron transfers. In its role as blue-light photo receptor, (oxidized) FMN stands out from the 'conventional' photo receptors as the signaling state and not an E/Z isomerization.
It is the principal form in which riboflavin is found in cells and tissues. It requires more energy to produce, but is more soluble than riboflavin.
Food additive
Flavin mononucleotide is also used as an orange-red food colour additive, designated in Europe as E number E101a.[1]
E106, a very closely related food dye, is riboflavin-5′-phosphate sodium salt, which consists mainly of the monosodium salt of the 5′-monophosphate ester of riboflavin. It is rapidly turned to free riboflavin after ingestion. It is found in many foods for babies and young children as well as jams, milk products, and sweets and sugar products.
See also
References
- ↑ "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers", Food Standards Agency website, retrieved 15 Dec 2011