Rhône
| Rhône (French: Le Rhône) | |
| German: Rhone | |
| River | |
 View over the Rhône flowing from Valais into Lake Geneva | |
| Countries | Switzerland, France |
|---|---|
| Source | Rhône Glacier |
| - elevation | 2,208 m (7,244 ft) |
| Mouth | Mediterranean Sea |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 43°19′51″N 4°50′44″E / 43.33083°N 4.84556°ECoordinates: 43°19′51″N 4°50′44″E / 43.33083°N 4.84556°E |
| Length | 813 km (505 mi) |
| Basin | 98,000 km2 (37,838 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 1,710 m3/s (60,388 cu ft/s) |
| - max | 13,000 m3/s (459,091 cu ft/s) |
| - min | 360 m3/s (12,713 cu ft/s) |
 | |
The Rhône (/ˈroʊn/; French: Le Rhône [ʁon]; German: Rhone [ˈroːnə]; Walliser German: Rotten [ˈrotən]; Italian: Rodano [ˈrɔːdano]; Arpitan: Rôno [ˈʁono]; Occitan: Ròse [ˈrɔze]) is one of the major rivers of Europe, rising in Switzerland, passing through Lake Geneva and running through southeastern France. At Arles, near its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, the river divides into two branches, known as the Great Rhône (French: Le Grand Rhône) and the Little Rhône (Le Petit Rhône). The resulting delta constitutes the Camargue region.
Name

The name Rhône continues the name Rhodanus (Greek Ῥοδανός Rhodanos) in Greco-Roman geography. The Gaulish name of the river was *Rodonos or *Rotonos (from a PIE root *ret- "to run, roll" frequently found in river names).
The Greco-Roman as well as the reconstructed Gaulish name is masculine, as is French le Rhône. This form survives in the Italian namesake, Rodano. German has adopted the French name but given it the feminine gender, die Rhone. The original German adoption of the Latin name was also masculine, der Rotten; it survives only in the Upper Valais (dialectal Rottu).
In French, the adjective derived from the river is rhodanien, as in le sillon rhodanien (literally "the furrow of the Rhône"), which is the name of the long, straight Saône and Rhône river valleys, a deep cleft running due south to the Mediterranean and separating the Alps from the Massif Central.
Navigation
Before railroads and highways were developed, the Rhône was an important inland trade and transportation route, connecting the cities of Arles, Avignon, Valence, Vienne and Lyon to the Mediterranean ports of Fos, Marseille and Sète. Travelling down the Rhône by barge would take three weeks. By motorized vessel, the trip now takes only three days. The Rhône is classified as a Class V waterway from the mouth of the Saône to the sea. The Saône, which is also canalized, connects the Rhône ports to the cities of Villefranche-sur-Saône, Mâcon and Chalon-sur-Saône. Smaller vessels (up to CEMT class I) can travel further northwest, north and northeast via the Centre-Loire-Briare and Loing Canals to the Seine, via the Canal de la Marne à la Saône (recently often called the "Canal entre Champagne et Bourgogne") to the Marne, via the Canal des Vosges (formerly called the "Canal de l'Est – Branche Sud") to the Moselle and via the Canal du Rhône au Rhin to the Rhine.
The Rhône is infamous for its strong current when the river carries large quantities of water: current speeds up to 10 kilometres per hour (6 mph) are sometimes reached, particularly in the stretch below the last lock at Valabrègues and in some of the diversion canals. The ten river locks are operated daily from 5:00 a.m. until 9:00 p.m. Night operation can be requested and is usually granted.[1]
Course
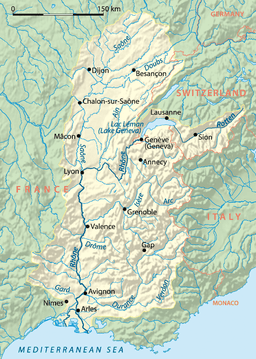
The Rhône rises as an effluent of the Rhône Glacier in the Valais, in the Swiss Alps, at an altitude of approximately 2,208 metres (7,244 ft).[2] From there it flows south through Gletsch and the Goms, the uppermost, valley region of the Valais before Brig. Shortly before reaching Brig, it receives the waters of the Massa from the Aletsch Glacier. It flows onward through the valley which bears its name and runs initially in a westerly direction about thirty kilometers to Leuk, then southwest about fifty kilometers to Martigny .
Down as far as Brig, the Rhône is a torrent; it then becomes a great mountain river running southwest through a glacier valley. Between Brig and Martigny, it collects waters mostly from the valleys of the Pennine Alps to the south, whose rivers originate from the large glaciers of the massifs of Monte Rosa, Dom, and Grand Combin.
At Martigny, where it receives the waters of La Drance on its left bank, the Rhône makes a strong turn towards the north. Heading toward Lake Geneva, the valley narrows, a feature that has long given the Rhône valley strategic importance for the control of the Alpine passes. The Rhône then marks the boundary between the cantons of Valais (left bank) and Vaud (right bank), separating the Valais Chablais and Chablais Vaudois. It enters Lake Geneva near Le Bouveret.
On a portion of its extent Lake Geneva marks the border between France and Switzerland. On the left bank of Lake Geneva the river receives the Morge River. This river marks the border between France (Haute-Savoie) and Switzerland (Valais). The Morge enters Lake Geneva at Saint-Gingolph, a village on both sides of the border. On the right bank of the lake the Rhône receives the Venoge (river) and the Morges River.
Lake Geneva ends in Geneva, where the lake level is maintained by the Seujet dam. The average discharge from Lake Geneva is 251 cubic metres per second (8,900 cu ft/s).[3] In Geneva, the Rhône receives the waters of the Arve from the Mont Blanc. After a course of 290 kilometres (180 mi) the Rhône leaves Switzerland and enters the southern Jura Mountains. It then turns toward the south past the Bourget Lake which it is connected by the Savières channel. At Lyon, which is the biggest city along its course, the Rhône meets its biggest tributary, the Saône. The Saône carries 400 cubic metres per second (14,000 cu ft/s) and the Rhône itself 600 cubic metres per second (21,000 cu ft/s). From the confluence, the Rhône follows the southbound direction of the Saône. Along the Rhône Valley, it is joined on the right (western) bank by the rivers Eyrieux, Ardèche, Cèze, and Gardon coming from the Cévennes mountains; and on the left bank by the rivers Isère, with an average discharge of 350 cubic metres per second (12,000 cu ft/s), Drôme, Ouvèze, and Durance at 188 cubic metres per second (6,600 cu ft/s) from the Alps.
From Lyon, it flows south, between the Alps and the Massif Central. At Arles, the Rhône divides into two major arms forming the Camargue delta, both branches flowing into the Mediterranean Sea, the delta being termed the Rhône Fan. The larger arm is called the "Grand Rhône", the smaller the "Petit Rhône". The average annual discharge at Arles is 1,710 cubic metres per second (60,000 cu ft/s).[3]
History

The Rhône has been an important highway since the times of the Greeks and Romans. It was the main trade route from the Mediterranean to east-central Gaul.[4] As such, it helped convey Greek cultural influences to the western Hallstatt and the later La Tène cultures.[4] Celtic tribes living near the Rhône included the Seduni, Sequani, Segobriges, Allobroges, Segusiavi, Helvetii, Vocontii and Volcae Arecomici.[4]
Navigation was difficult, as the river suffered from fierce currents, shallows, floods in spring and early summer when the ice was melting, and droughts in late summer. Until the 19th century, passengers travelled in coches d'eau (water coaches) drawn by men or horses, or under sail. Most travelled with a painted cross covered with religious symbols as protection against the hazards of the journey.[5]
Trade on the upper river used barques du Rhône, sailing barges, 30 by 3.5 metres (98 by 11 ft), with a 75-tonne (165,000 lb) capacity. As many as 50 to 80 horses were employed to haul trains of five to seven craft upstream. Goods would be transshipped at Arles into 23-metre (75 ft) sailing barges called allèges d'Arles for the final run down to the Mediterranean.
The first experimental steam boat was built at Lyon by Jouffroy d'Abbans in 1783. Regular services were not started until 1829 and they continued until 1952. Steam passenger vessels 80 to 100 metres (260–330 ft) long made up to 20 kilometres per hour (12 mph) and could do the downstream run from Lyon to Arles in a day. Cargo was hauled in bateau-anguilles, boats 157 by 6.35 metres (515.1 by 20.8 ft) with paddle wheels amidships, and bateaux crabes, a huge toothed 'claw' wheel 6.5 metres (21 ft) across to grip the river bed in the shallows to supplement the paddle wheels. In the 20th century, powerful motor barges propelled by diesel engines were introduced, carrying 1,500 tonnes (3,300,000 lb).
In 1933, the Compagnie Nationale du Rhône (CNR) was established to tame the river. Some progress was made in deepening the navigation channel and constructing scouring walls, but World War II brought such work to a halt. In 1942, following the collapse of Vichy France, Italian military forces occupied southeastern France up to the eastern banks of the Rhône, as part of the Italian Fascist regime's expansionist agenda.
In 1948, the government started construction on a series of locked barrages and canal cuts, to improve navigation and generate electricity, with locks raising boats up to 23 metres (75 ft).
Along the Rhône
Cities and towns along the Rhône include:


Switzerland
- Oberwald (Valais)
- Brig (Valais)
- Visp (Valais)
- Leuk (Valais)
- Sierre (Valais)
- Sion (Valais)
- Martigny (Valais)
- St. Maurice (Valais)
- see Lake Geneva for a list of Swiss and French towns around the lake
- Geneva (Geneva)
France
- Lyon, (Rhône (département))
- Vienne (Isère)
- Tournon-sur-Rhône (Ardèche) opposite Tain-l'Hermitage (Drôme)
- Valence (Drôme) opposite Saint-Péray and Guilherand-Granges (Ardèche)
- Montélimar (Drôme) opposite Le Teil and Rochemaure (Ardèche)
- Viviers (Ardèche)
- Bourg-Saint-Andéol (Ardèche)
- Pont-Saint-Esprit (Gard)
- Roquemaure (Gard) opposite Châteauneuf-du-Pape (Vaucluse)
- Avignon (Vaucluse) opposite Villeneuve-lès-Avignon (Gard)
- Beaucaire (Gard) opposite Tarascon (Bouches-du-Rhône)
- Vallabrègues (Gard)
- Arles (Bouches-du-Rhône)
See also
- Berges du Rhône
- Rhône (département)
- Rhône (wine region)
- Witenwasserenstock (triple watershed: Rhône-Rhine-Po)
References and notes
- ↑ NoorderSoft Waterways Database
- ↑ "255 Sustenpass" (Map). Rhône source (online map) (2015 ed.). 1:50 000. National Map 1:50 000 – 78 sheets and 25 composites (in German). Cartography by Swiss Federal Office for Topography, swisstopo. Berne, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Office for Topography, swisstopo. 2013. ISBN 978-3-302-00255-2. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- 1 2 "Le Rhône" (in French). Geneva, Switzerland: La fédération Genevoise des Sociétés de Pêche. March 2001. Retrieved 2015-10-18.
- 1 2 3 Freeman, Philip. John T. Koch, ed. Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia. I. ABC-CLIO. p. 901. ISBN 1-85109-440-7.
- ↑ McKnight, Hugh (September 2005). Cruising French Waterways (4th ed.). Sheridan House. ISBN 978-1-57409-210-3.
Further reading
- Champion, Maurice (1858–1864), Les inondations en France depuis le VIe siècle jusqu'a nos jours (6 Volumes) (in French), Paris: V. Dalmont Scans: Volume 3 (1861) (Bassin du Rhône starts at page 185), Volume 4 (1862).
- Pardé, Maurice (1925), "Le régime du Rhône", Revue de géographie alpine (in French), 13 (13-3): 459–547.
- Pritchard, Sara B. (2011), Confluence: The Nature of Technology and the Remaking of the Rhône, Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-04965-9 A social, environmental, and technological history of the transformation of the river since 1945.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rhône River. |
- InfoRhone Navigation and river conditions
- CNR The Rhône Authority
- Rhône guide Places, ports and moorings on the Grand Rhône.
- Petit Rhône guide Places and moorings on the Petit Rhône.
- The Rhône-Mediterranean page of EauFrance
- Waterways in France



