Revetment
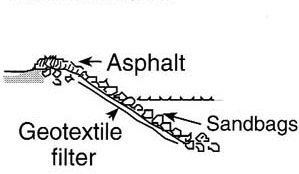
In stream restoration, river engineering or coastal engineering, revetments are sloping structures placed on banks or cliffs in such a way as to absorb the energy of incoming water. In military engineering they are structures, again sloped, formed to secure an area from artillery, bombing, or stored explosives. River or coastal revetments are usually built to preserve the existing uses of the shoreline and to protect the slope, as defense against erosion.
Freshwater revetments

Many revetments are used to line the banks of freshwater rivers, lakes, and man-made reservoirs, especially to prevent damage during periods of floods or heavy seasonal rains (see riprap). Many materials may be used: wooden piles, loose-piled boulders[1] or concrete shapes,[2] or more solid banks.
Revetments as coastal defence
Revetments are used as a low-cost solution for coastal erosion defence in areas where crashing waves may otherwise deplete the coastline. Wooden revetments are made of planks laid against wooden frames so that they disrupt the force of the water. Although once popular, the use of wooden revetments has largely been replaced by modern concrete-based defence structures such as tetrapods.
Tetrapods
In coastal engineering, a tetrapod is a four-legged concrete structure used as armour unit on breakwaters. The tetrapod's shape is designed to dissipate the force of incoming waves by allowing water to flow around rather than against it, and to reduce displacement by allowing a random distribution of tetrapods to mutually interlock.
Fortifications
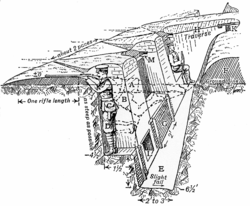
According to the U.S. National Park Service, and referring mostly to their employment in the American Civil War, a revetment is defined as a "retaining wall constructed to support the interior slope of a parapet. Made of logs, wood planks, fence rails, fascines, gabions, hurdles, sods, or stones, the revetment provided additional protection from enemy fire, and, most importantly, kept the interior slope nearly vertical. Stone revetments commonly survive. A few log revetments have been preserved due to high resin pine or cypress and porous sandy soils. After an entrenchment was abandoned, many log or rail revetments were scavenged for other uses, causing the interior slope to slump more quickly. An interior slope will appear more vertical if the parapet eroded with the revetment still in place."[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Lake Ontario Riparian Alliance. "Stone Revetments...Frequently Asked Questions." Accessed 2009-05-25.
- ↑ Concrete shaped revetments
- ↑ U.S. National Park Service. "Military Earthworks Terms". Retrieved 2009-05-25.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Revetment. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Marine revetments. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tetrapods. |
Fortifications
River and Levee Management
- EPA - River Bend Project
- Levee and Revetment Routine Maintenance
- US DOT - Design of Riprap Revetment
