Refrigerator car


A refrigerator car (or "reefer") is a refrigerated boxcar (U.S.), a piece of railroad rolling stock designed to carry perishable freight at specific temperatures. Refrigerator cars differ from simple insulated boxcars and ventilated boxcars (commonly used for transporting fruit), neither of which are fitted with cooling apparatus. Reefers can be ice-cooled, come equipped with any one of a variety of mechanical refrigeration systems, or utilize carbon dioxide (either as dry ice, or in liquid form) as a cooling agent. Milk cars (and other types of "express" reefers) may or may not include a cooling system, but are equipped with high-speed trucks and other modifications that allow them to travel with passenger trains.
History
Background

After the end of the American Civil War, Chicago, Illinois emerged as a major railway center for the distribution of livestock raised on the Great Plains to Eastern markets.[1] Transporting the animals to market required herds to be driven up to 1,200 miles (1,900 km) to railheads in Kansas City, Missouri, where they were loaded into specialized stock cars and transported live ("on-the-hoof") to regional processing centers. Driving cattle across the plains also caused tremendous weight loss, with some animals dying in transit.
Upon arrival at the local processing facility, livestock were either slaughtered by wholesalers and delivered fresh to nearby butcher shops for retail sale, smoked, or packed for shipment in barrels of salt. Costly inefficiencies were inherent in transporting live animals by rail, particularly the fact that about sixty percent of the animal's mass is inedible. The death of animals weakened by the long drive further increased the per-unit shipping cost. Meatt]] sought a way to ship dressed meats from his Chicago packing plant to eastern markets.
Early attempts at refrigerated transport

During the mid-19th century, attempts were made to ship agricultural products by rail. As early as 1842, the Western Railroad of Massachusetts was reported in the June 15 edition of the Boston Traveler to be experimenting with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage.[2] The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the Northern Railroad (New York) (or NRNY, which later became part of the Rutland Railroad). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success since it was only functional in cold weather. That same year, the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice for cooling.
The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stock yards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, proving to be impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.

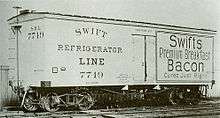
Detroit's William Davis patented a refrigerator car that employed metal racks to suspend the carcasses above a frozen mixture of ice and salt. In 1868, he sold the design to George H. Hammond, a Detroit meat packer, who built a set of cars to transport his products to Boston using ice from the Great Lakes for cooling.[3] The load had the tendency of swinging to one side when the car entered a curve at high speed, and use of the units was discontinued after several derailments. In 1878 Swift hired engineer Andrew Chase to design a ventilated car that was well insulated, and positioned the ice in a compartment at the top of the car, allowing the chilled air to flow naturally downward.[4] The meat was packed tightly at the bottom of the car to keep the center of gravity low and to prevent the cargo from shifting. Chase's design proved to be a practical solution, providing temperature-controlled carriage of dressed meats, This allowed Swift and Company to ship their products across the United States and internationally.
Swift's attempts to sell Chase's design to major railroads were rebuffed, as the companies feared that they would jeopardize their considerable investments in stock cars, animal pens, and feedlots if refrigerated meat transport gained wide acceptance. In response, Swift financed the initial production run on his own, then — when the American roads refused his business — he contracted with the GTR (a railroad that derived little income from transporting live cattle) to haul the cars into Michigan and then eastward through Canada. In 1880 the Peninsular Car Company (subsequently purchased by ACF) delivered the first of these units to Swift, and the Swift Refrigerator Line (SRL) was created. Within a year, the Line's roster had risen to nearly 200 units, and Swift was transporting an average of 3,000 carcasses a week to Boston, Massachusetts. Competing firms such as Armour and Company quickly followed suit. By 1920, the SRL owned and operated 7,000 of the ice-cooled rail cars. The General American Transportation Corporation would assume ownership of the line in 1930.
In the 1870s, the lack of a practical means to refrigerate peaches limited the markets open to Samuel Rumph, a Georgia peach grower. In 1875, he invented a refrigerated railcar and crates that allowed him to grow peaches on a very large scale and ship them to distant markets. He was the first to achieve this. His innovations created Georgia's fame for peaches, a crop now eclipsed economically by blueberries.[5][6]
Edwin Tobias Earl was born on a fruit ranch near Red Bluff, California on May 30, 1858. His father was Joseph Earl and his mother, Adelia Chaffee. His brother was Guy Chaffee Earl. Career. He started his career in the shipping of fruits. By 1886, he was President of the Earl Fruit Company. In 1890, he invented the refrigerator car to transport fruits to the East Coast of the United States. He established the Continental Fruit Express and invested US$2,000,000 in refrigerator cars. In 1901, he sold his refrigerator cars to Armour and Company of Chicago and became a millionaire.
Live cattle and dressed beef deliveries to New York (short tons):
| (Stock Cars) | (Refrigerator Cars) | |
| Year | Live Cattle | Dressed Beef |
| 1882 | 366,487 | 2,633 |
| 1883 | 392,095 | 16,365 |
| 1884 | 328,220 | 34,956 |
| 1885 | 337,820 | 53,344 |
| 1886 | 280,184 | 69,769 |
The subject cars travelled on the Erie, Lackawanna, New York Central, and Pennsylvania railroads.
Source: Railway Review, January 29, 1887, p. 62.
19th Century American Refrigerator Cars:
| Year | Private Lines | Railroads | Total |
| 1880 | 1,000 est. | 310 | 1,310 est. |
| 1885 | 5,010 est. | 990 | 6,000 est. |
| 1890 | 15,000 est. | 8,570 | 23,570 est. |
| 1895 | 21,000 est | 7,040 | 28,040 est. |
| 1900 | 54,000 est. | 14,500 | 68,500 est. |
Source: Poor's Manual of Railroads and ICC and U.S. Census reports.
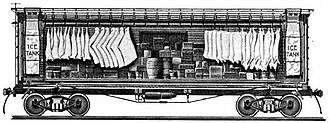
The use of ice to refrigerate and preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome stored ice and snow in caves, dugouts or ice houses lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 19th century, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required re-icing every 250 miles (400 km) to 400 miles (640 km).

By the turn of the 20th century, manufactured ice became more common. The Pacific Fruit Express (PFE), for example, maintained seven natural harvesting facilities, and operated 18 artificial ice plants. Their largest plant (located in Roseville, California) produced 1,200 short tons (1,100 t) of ice daily, and Roseville's docks could accommodate up to 254 cars. At the industry's peak, 1,300,000 short tons (1,200,000 t) of ice was produced for refrigerator car use annually.
Top icing is the practice of placing a 2-inch (51 mm) to 4-inch (100 mm) layer of crushed ice on top of agricultural products that have high respiration rates, need high relative humidity, and benefit from having the cooling agent sit directly atop the load (or within individual boxes). Cars with pre-cooled fresh produce were top iced just before shipment. Top icing added considerable dead weight to the load. Top-icing a 40-foot (12 m) reefer required in excess of 10,000 pounds (4,500 kg) of ice. It had been postulated that as the ice melts, the resulting chilled water would trickle down through the load to continue the cooling process. It was found, however, that top-icing only benefited the uppermost layers of the cargo, and that the water from the melting ice often passed through spaces between the cartons and pallets with little or no cooling effect. It was ultimately determined that top-icing is useful only in preventing an increase in temperature, and was eventually discontinued.
-

Men harvest ice on Michigan's Lake Saint Clair, circa 1905. The ice was cut into blocks and hauled by wagon to a cold storage warehouse, and held until needed
-

Ice blocks (also called "cakes") are manually placed into reefers from a covered icing dock. Each block weighed between 200 pounds (91 kg) to 400 pounds (180 kg). Crushed ice was typically used for meat cars

The typical service cycle for an ice-cooled produce reefer (generally handled as a part of a bice was sporadic) using specially designed field icing cars.
- The cars were delivered to the shipper for loading, and the ice was topped-off.
- Depending on the cargo and destination, the cars may have been fumigated.
- The train would depart for the eastern markets.
- The cars were reiced in transit approximately once a day.
- Upon reaching their destination, the cars were unloaded.
- If in demand, the cars would be returned to their point of origin empty. If not in demand, the cars would be cleaned and possibly used for a dry shipment.
-

This engraving of Tiffany's original "Summer and Winter Car" appeared in the Railroad Gazette just before Joel Tiffany received his refrigerator car patent in July, 1877. Tiffany's design mounted the ice tank in a clerestory atop the car's roof, and relied on a train's motion to circulate cool air throughout the cargo space
-

A rare double-door refrigerator car utilized the "Hanrahan System of Automatic Refrigeration" as built by ACF, circa 1898. The car had a single, centrally located ice bunker which was said to offer better cold air distribution. The two segregated cold rooms were well suited for less-than-carload (LCL) shipments
-

A pre-1911 "shorty" reefer bears an advertisement for Anheuser-Busch's Malt Nutrine tonic. The use of similar "billboard" advertising on freight cars was banned by the Interstate Commerce Commission in 1937, and thereafter cars so decorated could no longer be accepted for interchange between roads
Refrigerator cars required effective insulation to protect their contents from temperature extremes. "Hairfelt" derived from compressed cattle hair, sandwiched into the floor and walls of the car, was inexpensive, yet flawed over its three- to four-year service life it would decay, rotting out the car's wooden partitions and tainting the cargo with a foul odor. The higher cost of other materials such as "Linofelt" (woven from flax fibers) or cork prevented their widespread adoption. Synthetic materials such as fiberglass and polystyrene foam, both introduced after World War II, offered the most cost-effective and practical solution.
The United States Office of Defense Transportation implemented mandatory pooling of class RS produce refrigerator cars from 1941 through 1948. World War II experience found the cars spending 60 percent of their time traveling loaded, 30 percent traveling empty, and 10 percent idle; and indicated the average 14 loads each car carried per year included 5 requiring bunker icing, 1 requiring heating, and 8 using ventilation or top icing.[7] Following experience with assorted car specifications, the United Fresh Fruit and Vegetable Association (UFF&VA) listed what they considered the best features of ice refrigerator cars in 1948:[8]
- Steel cars (vs wood) for better insulation protection and greater rigidity resulting in reduced leakage around doors
- A minimum of 4 inches (10 cm) insulation thickness with all insulation protected from moisture
- Cushioned trucks and draft gear to minimize jarring and bruising of produce
- Standardized interior dimensions to allow improved loading methods with standardized containers
- Adjustable ice bunker bulkheads to allow greater floor space for shippers using top icing alone
- Vertically adjustable grates within the ice bunkers to allow half-stage icing to reduce icing charges where appropriate
- Forced air circulation within the car
- An additional lining to allow side wall flues circulating air around all cargo preventing contact with exterior car walls
- Perforated floor racks providing similar protection and air circulation under the cargo
- Provisions for pre-cooling the cars with a portable unit at the loading platforms.
Mechanical refrigeration
In the latter half of the 20th century, mechanical refrigeration began to replace ice-based systems. Soon after, mechanical refrigeration units replaced the "armies" of personnel required to re-ice the cars. The plug door was introduced experimentally by P.F.E. (Pacific Fruit Express) in April 1947, when one of their R-40-10 series cars, #42626, was equipped with one. P.F.E.'s R-40-26 series reefers, designed in 1949 and built in 1951, were the first production series cars to be so equipped. In addition, the Santa Fe Railroad first used plug doors on their SFRD RR-47 series cars, which were also built in 1951. This type of door provided a larger six foot opening to facilitate car loading and unloading. These tight-fitting doors were better insulated and could maintain an even temperature inside the car. By the mid-1970s, the few remaining ice bunker cars were relegated to "top-ice" service, where crushed ice was applied atop the commodity.
Cryogenic refrigeration
The Topeka, Kansas shops of the Santa Fe Railway built five experimental refrigerator cars employing liquid nitrogen as the cooling agent in 1965. A mist induced by liquified nitrogen was released throughout the car if the temperature rose above a pre-determined level. Each car carried 3,000 pounds (1,400 kg) of refrigerant and could maintain a temperature of minus 20 degrees Fahrenheit (−30 °C). During the 1990s, a few railcar manufacturers experimented with the use of liquid carbon dioxide (CO2) as a cooling agent. The move was in response to rising fuel costs, and was an attempt to eliminate the standard mechanical refrigeration systems that required periodic maintenance. The CO2 system can keep the cargo frozen solid as long as 14 to 16 days.
Several hundred "cryogenic" refrigerator cars were placed in service transporting frozen foodstuffs, though they failed to gain wide acceptance (due, in part, to the rising cost of liquid carbon dioxide). Because cryogenic refrigeration is a proven technology and environmentally friendly, the rising price of fuel and the increased availability of carbon dioxide from Kyoto Protocol-induced capturing techniques may lead to a resurgence in cryogenic railcar usage.
Experimentation
Aluminum and stainless steel
Several experimental cars were built when wartime production restrictions were relaxed in 1946:
- Illinois Central Railroad number 51000 was built in the McComb, Illinois shops with an aluminum superstructure to reduce weight with steel where required for strength and provided the standard dimensions, cushioned draft gear, easy-riding trucks, minimum 4 inches (10 cm) of insulation, adjustable ice bunker bulkheads and half-stage icing racks with forced air circulation through side wall flues and floor racks recommended by UFF&VA.[7]
- Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch number 13000 was built of stainless steel by the Consolidated Steel Corporation of Wilmington, California with convertible ice bunkers, side ventilation ducts, and axle-driven circulation fans. It was thought that stainless steel would better resist the corrosive deterioration resulting from salting the ice. The one-of-a-kind unit entered service as #13000, but was subsequently redesignated as #1300, and later given #4150 in 1955.[9] The car spent most of its life in express service. Cost was cited as the reason no additional units were ordered. The car was dismantled at Clovis, New Mexico in February 1964.
- Pacific Fruit Express rebuilt two steel-sided ventilator refrigerator cars in their Los Angeles shops with aluminum car bodies to test durability of lightweight alloys versus that of steel.[7] It was hoped that weight savings (the units weighed almost 10,000 lb (4,536 kg) less than a like-sized all-steel car) and better corrosion resistance would offset the higher initial cost. Alcoa provided the body for number 44739, and Reynolds Aluminum Company provided number 45698. The cars (outfitted with state-of-the-art fiberglass insulation and axle-driven fans for internal air circulation) traveled throughout the Southern Pacific and Union Pacific systems, where they were displayed to promote PFE's post-World War II modernization. Though both units remained in service over 15 years (#45698 was destroyed in a wreck in May 1962, while #44739 was scrapped in 1966), no additional aluminum reefers were constructed.
- Fruit Growers Express number 38374 was equipped with an experimental aluminum body in the Indiana Harbor, Indiana shops.[7]
"Depression Baby"
During the 1930s, the North American Car Company produced a one-of-a-kind, four-wheeled ice bunker reefer intended to serve the needs of specialized shippers who did not generate sufficient product to fill a full-sized refrigerator car. NADX #10000 was a 22-foot (6.71 m)-long, all-steel car that resembled the forty-and-eights used in Europe during World War I. The prototype weighed 13.5 short tons (12.2 t; 12.1 long tons) and was outfitted with a 1,500 lb (680 kg) ice bunker at each end. The car was leased to Hormel and saw service between Chicago, Illinois and the southern United States. The concept failed to gain acceptance with eastern railroads and no additional units were built.
Dry ice
The Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch (SFRD) briefly experimented with dry ice as a cooling agent in 1931. The compound was readily available and seemed like an ideal replacement for frozen water. Dry ice melts at −109 °F or −78.33 °C (versus 32 °F or 0 °C for conventional ice) and was twice as effective thermodynamically. Overall weight was reduced as the need for brine and water was eliminated. While the higher cost of dry ice was certainly a drawback, logistical issues in loading long lines of cars efficiently prevented it from gaining acceptance over conventional ice. Worst of all, it was found that dry ice can adversely affect the color and flavor of certain foods if placed too closely to them.
Hopper cars
In 1969, the Northern Pacific Railroad ordered a number of modified covered hopper cars from American Car and Foundry for transporting perishable food in bulk. The 55-foot (16.76 m)-long cars were blanketed with a layer of insulation, equipped with roof hatches for loading, and had centerflow openings along the bottom for fast discharge. A mechanical refrigeration unit was installed at each end of the car, where sheet metal ducting forced cool air into the cargo compartments.
The units, rated at 100 short tons (91 t; 89 long tons) capacity (more than twice that of the largest conventional refrigerator car of the day) were economical to load and unload, as no secondary packaging was required. Apples, carrots, onions, and potatoes were transported in this manner with moderate success. Oranges, on the other hand, tended to burst under their own weight, even after wooden baffles were installed to better distribute the load. The Santa Fe Railway leased 100 of the hoppers from ACF, and in April 1972 purchased 100 new units, known as "Conditionaire" cars.[10]
The cars' irregular, orange-colored outer surface (though darker than the standard AT&SF yellow-orange used on reefers) tended to collect dirt easily, and proved difficult to clean. Santa Fe eventually relegated the cars to more typical, non-refrigerated applications.
Refrigerator cars in Japan
The first refrigerated cars in Japan entered service in 1908 for fish transport. Many of these cars were equipped with ice bunkers, however the bunkers were not used generally. Fish were packed in wooden or foam polystyrene boxes with crushed ice.
Fruit and meat transportation in refrigerated rail cars was not common in Japan. For fruits and vegetables, ventilator cars were sufficient due to the short distances involved in transportation. Meat required low temperature storage, transported by ship, since most major Japanese cities are located along the coast.
Refrigerator cars suffered heavy damage in World War II. After the war, the occupation forces confiscated many cars for their own use, utilizing the ice bunkers as originally intended. Supplies were landed primarily at Yokohama, and reefer trains ran from the port to U.S. bases around Japan.
In 1966, JNR developed "resa 10000" and "remufu 10000" type refrigerated cars that could travel at 62 mph (100 km/h) They were used in fish freight express trains. "Tobiuo" (Flying fish) train from Shimonoseki to Tokyo, and "Ginrin" (Silver scale) train from Hakata to Tokyo, were operated.
By the 1960s, refrigerator trucks had begun to displace railcars. Strikes in the 1970s resulted in the loss of reliability and punctuality, important to fish transportation. In 1986, the last refrigerated cars were replaced by reefer containers.
Most Japanese reefers were four-wheeled due to small traffic demands. There were very few bogie wagons in late years. The total number of Japanese reefers numbered approximately 8,100. At their peak, about 5,000 refrigerated cars operated in the late 1960s. Mechanical refrigerators were tested, but did not see widespread use.
There were no privately owned reefers in Japan. This is because fish transportation was protected by national policies and rates were kept low, and there was little profit in refrigerated car ownership.
Preservation
Examples of many styles of refrigerator and ice cars can be found at railroad museums around the world.
The Western Pacific Railroad Museum at Portola, California features a very complete roster of 20th century cars, including wood bodied ice cars, steel bodied ice cars, one of the earliest mechanical refrigerator cars, later mechanical refrigerator cars and a cryogenic reefer, as well as several "insulated" boxcars also used for food transport.
Timeline
- 1842: The Western Railroad of Massachusetts experimented with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage.
- 1851: The first refrigerated boxcar entered service on the Northern Railroad (New York).
- 1857: The first consignment of refrigerated, dressed beef traveled from Chicago to the East Coast in ordinary box cars packed with ice.
- 1866: Horticulturist Parker Earle shipped strawberries in iced boxes by rail from southern Illinois to Chicago on the Illinois Central Railroad.
- 1867: First U.S. refrigerated railroad car patent was issued.[11]
- 1868: William Davis of Detroit, Michigan developed a refrigerator car cooled by a frozen ice-salt mixture, and patented it in the U.S. The patent was subsequently sold to George Hammond, a local meat packer who amassed a fortune in refrigerated shipping.
- 1875: Samuel Rumph invented a railcar specifically to ship peaches, and a mortised-end peach crate., making possible large scale growing and long-distance shipping of peaches[5]
- 1876: German engineer Carl von Linde developed one of the first mechanical refrigeration systems.
- 1878: Gustavus Swift (along with engineer Andrew Chase) developed the first practical ice-cooled railcar. Soon Swift formed the Swift Refrigerator Line (SRL), the world's first.
- 1880: The first patent for a mechanically refrigerated railcar issued in the United States was granted to Charles William Cooper.
- 1884: The Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch (SFRD) was established as a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway to carry perishable commodities.
- 1885: Berries from Norfolk, Virginia were shipped by refrigerator car to New York.
- 1887: Parker Earle joined F.A. Thomas of Chicago in the fruit shipping business. The company owned 60 ice-cooled railcars by 1888, and 600 by 1891.
- 1888: Armour & Co. shipped beef from Chicago to Florida in a car cooled by ethyl chloride-compression machinery. Florida oranges were shipped to New York under refrigeration for the first time.
- 1889: The first cooled shipment of fruit from California was sold on the New York market.
- 1898: Russia's first refrigerator cars entered service. The country's inventory w reached 1,900 by 1908, and 3,000 two years later, and peaked at approximately 5,900 by 1916. The cars were utilized mainly for transporting butter from Siberia to the Baltic Sea, a 12-day journey.
- 1899: Refrigerated fruit traffic within the U.S. reached 90,000 short tons (81,647 t; 80,357 long tons) per year; Transport from California to NY averaged 12 days in 1900.
- 1901: Carl von Linde equipped a Russian train with a mobile, central mechanical refrigeration plant to distribute cooling to cars carrying perishable goods. Similar systems were used in Russia as late as 1975.
- 1905: U.S. traffic in refrigerated fruit reached 430,000 short tons (390,089 t; 383,929 long tons). As refrigerator car designs become standardized, the practice of indicating the "patentee" on the sides was discontinued.
- 1907: The Pacific Fruit Express began operations with more than 6,000 refrigerated cars, transporting fruit and vegetables from Western producers to Eastern consumers. U.S. traffic in refrigerated fruit hit 600,000 short tons (544,311 t; 535,714 long tons).
- 1908: Japan's first refrigerator cars entered service. The cars were for seafood transportation, in the same manner as most other Japanese reefers.
- 1913: The number of thermally insulated railcars (most of which were cooled by ice) in the U.S. topped 100,000.
- 1920: The Fruit Growers Express (or FGE, a former subsidiary of the Armour Refrigerator Line) was formed using 4,280 reefers acquired from Armour & Co.
- 1923: FGE and the Great Northern Railway for the Western Fruit Express (WFE) in order to compete with the Pacific Fruit Express and Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch in the West.
- 1925 to 1930: Mechanically refrigerated trucks enter service and gain public acceptance, particularly for the delivery of milk and ice cream.
- 1926: The FGE expanded its service into the Pacific Northwest and the Midwest through the WFE and the Burlington Refrigerator Express Company (BREX), its other partly owned subsidiary. FGE purchased 2,676 reefers from the Pennsylvania Railroad.
- 1928: The FGE formed the National Car Company as a subsidiary to service the meat transportation market. Customers include Kahns, Oscar Mayer, and Rath.
- 1930: The number of refrigerator cars in the United States reached its maximum of approximately 183,000.
- 1931: The SFRD reconfigured seven reefers to utilize dry ice as a cooling agent.
- 1932: Japanese Government Railways built vehicles specially made for dry ice coolant.
- 1934: The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) regulation #201 came into effect banning billboard advertisements on freight cars.
- 1936: The first all-steel reefers entered service.
- 1946: Two experimental aluminum-body refrigerator cars entered service on the PFE; an experimental reefer with a stainless-steel body was built for the SFRD.
- 1950: The U.S. refrigerator car roster dropped to 127,200.
- 1955: East of Eden popularises refrigerator cars by featuring a major plotline where James Dean's father tries to go into the business and fails when all the produce melts during transit.
- 1957: The last ice bunker refrigerator cars were built.
- 1958: The first mechanical reefers (utilizing diesel-powered refrigeration units) entered revenue service.
- 1959: The flush, "plug" style sliding door was introduced as an option, providing a larger door to ease loading and unloading. The tight-fitting doors were better insulated and allowed the car to be maintained at a more even temperature. Early example is the DT&I XL-1 car by Evans.
- 1966: Japanese National Railways started operation of fish freight express trains by newly built "resa 10000" type refers.
- 1969: ACF constructed several experimental center flow hopper cars incorporating mechanical cooling systems and insulated cargo cells. The units were intended for shipment of bulk perishables.
- 1971: The last ice-cooled reefers were retired.
- 1980: The U.S. refrigerator car roster dropped to 80,000.
- 1986: The last reefers in Japan were replaced by reefer containers.
- 1990s: The first cryogenically cooled reefers entered service.
- 2001: The number of refrigerator cars in the United States bottomed out at approximately 8,000.
- 2005: The number of reefers in the United States climbs to approximately 25,000, due to significant new refrigerator car orders.
- 2006 Railex launches 55-car unit train reefer service between U.S. west coast and New York.
- 2013 Additional unit train reefer services to Florida and Chicago are announced.
Specialized applications
Express service
Standard refrigerated transport is often utilized for goods with less than 14 days of refrigerated "shelf life" — avocados, cut flowers, green leafy vegetables, lettuce, mangoes, meat products, mushrooms, peaches and nectarines, pineapples and papayas, sweet cherries, and tomatoes. "Express" reefers are typically employed in the transport of special perishables: commodities with a refrigerated shelf life of less than seven days, such as human blood, fish, green onions, milk, strawberries, and certain pharmaceuticals.

The earliest express-service refrigerator cars entered service around 1890, shortly after the first express train routes were established in North America. The cars did not come into general use until the early 20th century. Most units designed for express service are larger than their standard counterparts, and are typically constructed more along the lines of baggage cars than freight equipment. Cars must be equipped with speed-rated trucks and brakes, and — if they are to be run ahead of the passenger car, must also incorporate an air line for pneumatic braking, a communication signal air line, and a steam line for train heating. Express units were typically painted in passenger car colors, such as Pullman green.
The first purpose-built express reefer emerged from the Erie Railroad Susquehanna Shops on August 1, 1886. By 1927, some 2,218 express cars traveled America's rails, and three years later that number rose to 3,264. In 1940, private rail lines began to build and operate their own reefers, the Railway Express Agency (REA) being by far the largest. In 1948, the REA roster (which would continue to expand into the 1950s) numbered approximately 1,800 cars, many of which were World War II "troop sleepers" modified for express refrigerated transport. By 1965, due to a decline in refrigerated traffic, many express reefers were leased to railroads for use as bulk mail carriers.
Intermodal
For many years, virtually all of the perishable traffic in the United States was carried by the railroads. While railroads were subject to government regulation regarding shipping rates, trucking companies could set their own rate for hauling agricultural products, giving them a competitive advantage. In March 1979, the ICC exempted rail transportation of fresh fruits and vegetables from all economic regulation. Once the "Agricultural Exemption Clause" was removed from the Interstate Commerce Act, railroads began aggressively pursuing trailer-on-flatcar (TOFC) business (a form of intermodal freight transport) for refrigerated trailers. Taking this one step further, a number of carriers (including the PFE and SFRD) purchased their own refrigerated trailers to compete with interstate trucks.
Tropicana "Juice Train"
In 1970, Tropicana orange juice was shipped in bulk via insulated boxcars in one weekly round-trip from Bradenton, Florida, to Kearny, New Jersey. By the following year, the company was operating two 60-car unit trains a week, each carrying around 1,000,000 US gallons (3,800,000 L; 830,000 imp gal) of juice. On June 7, 1971, the "Great White Juice Train" (the first unit train in the food industry, consisting of 150 100-short-ton (91 t; 89-long-ton) insulated boxcars fabricated in the Alexandria, Virginia, shops of Fruit Growers Express) commenced service over the 1,250 miles (2,010 km) route. An additional 100 cars were soon added, and small mechanical refrigeration units were installed to keep temperatures constant. Tropicana saved $40 million in fuel costs during the first ten years in operation.
Railex and other unit trains
In 2006 Railex LLC launched service in partnership with the Union Pacific Railroad and CSX between Wallula, Washington, and Rotterdam, New York, followed in 2008 by a Delano, California, to NY lane, and Jacksonville, Florida service from the west coast in 2014. Railex runs unit trains of 55 large, "plate F" refrigerated cars.[12] Two additional refrigerated unit-train services were announced in 2013, the Green Express, from Tampa, Florida to Kingsbury, Indiana, operated by CSX and the Tampa Port Authority,[13] and the TransCold Express operated by McKay Transcold, LLC and BNSF, connecting the California Central Valley with the midwest.[14]
AAR classifications
| Class | Description | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RA | Brine-tank ice bunkers | RPB | Mechanical refrigerator with electro-mechanical axle drive |
| RAM | Brine-tank ice bunkers with beef rails | RPL | Mechanical refrigerator with loading devices |
| RAMH | Brine-tank with beef rails and heaters | RPM | Mechanical refrigerator with beef rails |
| RB | No ice bunkers — heavy insulation | RS | Bunker refrigerator — common ice bunker car |
| RBL | No ice bunkers and loading devices | RSB | Bunker refrigerator — air fans and loading devices |
| RBH | No ice bunkers — gas heaters | RSM | Bunker refrigerator with beef rails |
| RBLH | No ice bunkers — loading devices and heaters | RSMH | Bunker refrigerator with beef rails and heaters |
| RCD | Solid carbon-dioxide refrigerator | RSTC | Bunker refrigerator — electric air fans |
| RLO | Special car type — permanently enclosed (covered hopper type) | RSTM | Bunker refrigerator — electric air fans and beef rails |
| RP | Mechanical refrigerator |
- Note: Class B refrigerator cars are those designed for passenger service; insulated boxcars are designated Class L.
See also
References
- Notes
- ↑ Boyle and Estrada
- ↑ White, p. 31
- ↑ White, p. 33
- ↑ White, p. 45
- 1 2
- ↑ Ga. blueberry knocks peach off top of fruit pile, Associated Press, July 21, 2013, published by Yahoo News on-line, retrieved July 21, 2013
- 1 2 3 4 Lambert, Dave; Lambert, Jenny (1994). "The post war refrigerator car -- a brief history: part I". Railroad Model Craftsman. Carstens Publications (March): 86–94.
- ↑ Lambert, Dave; Lambert, Jenny (1994). "The post war refrigerator car -- a brief history: part II". Railroad Model Craftsman. Carstens Publications (April): 86–93.
- ↑ Hendrickson and Scholz, p. 8
- ↑ "Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe covered Hopper Conditionaire car". Kansas Historical Society. 2007–2012. Retrieved 2012-04-01.
- ↑ Improved Refrigerator Car. US Patent 71,423, Nov 26, 1867.
- ↑ http://railex.com/news/railex-opens-jacksonville-florida-services-june-2014/
- ↑ http://www.bizjournals.com/tampabay/blog/morning-edition/2013/08/csxs-green-express-to-link-tampa.html
- ↑ BNSF to serve new TransCold Express refrigerated service offered by McKay, 2013
- ↑ The Great Yellow Fleet, p 126.
- Bibliography
- Boyle, Elizabeth and Rodolfo Estrada. (1994) "Development of the U.S. Meat Industry" — Kansas State University Department of Animal Sciences and Industry.
- Hendrickson, Richard and Richard E. Scholz. (1986). "Reefer car 13000: a postmortem." The Santa Fé Route IV (2) 8.
- Hendrickson, Richard H. (1998). Santa Fe Railway Painting and Lettering Guide for Model Railroaders, Volume 1: Rolling Stock. Highlands Ranch, CO: The Santa Fe Railway Historical and Modeling Society, Inc.
- Pearce, Bill. (2005). "Express Reefer from troop sleeper in N." Model Railroader 72 (12) 62–65.
- Reefer Operations on Model Railroads with an emphasis on the ATSF April 15, 2005 article at The Santa Fe Railway Historical & Modeling Society official website — accessed on November 7, 2005.
- Thompson, Anthony W. et al. (1992). Pacific Fruit Express. Signature Press, Wilton, CA. ISBN 1-930013-03-5.
- White, John H. (1986). The Great Yellow Fleet. Golden West Books, San Marino, CA. ISBN 0-87095-091-6.
- White, John H. Jr. (1993). The American Railroad Freight Car: From the Wood-Car Era to the Coming of Steel. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-4404-5. OCLC 26130632.