Track gauge in North America
| By transport mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tram · Rapid transit Miniature · Scale model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By size (list) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change of gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Break-of-gauge · Dual gauge · Conversion (list) · Bogie exchange · Variable gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By location | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America · South America · Europe · Australia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The vast majority of North American railroads are standard gauge (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in/1,435 mm). Exceptions include some streetcar, subway and rapid transit systems, mining and tunneling operations, and some narrow gauge lines particularly in the west, e.g. the isolated White Pass and Yukon Route system, and the former Newfoundland Railway.
As well as the usual reasons for having one gauge i.e. being able to operate through trains without transfer arrangements, the North American continent-wide system of freight car interchange with rolling stock having the same standard gauge, couplings, and air brakes meant that individual companies could minimise their rolling stock requirements by borrowing from other companies. Peak demand periods varied over the continent, with seasonal requirements e.g. for grain shipments occurring at different times in different areas so that freight cars could be redistributed to cover peaks as required.
Canada
The first railroads in Canada in the 1830s were built to 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) and in 1847 the first 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) gauge line was built. After a Royal Commission, in 1851 the broad gauge, called the Provincial Gauge or Indian gauge, was adopted by the Province of Canada government as the standard gauge. However, in the 1870s, most Canadian railroads (apart from some narrow gauge lines, e.g. on the island of Newfoundland) were changed to standard gauge to facilitate interchange with U.S. railroads. The last broad gauge line closed in 1911.
The Toronto subway uses an overgauge of 4 ft 10 7⁄8 in (1,495 mm).
Guatemala
The 3 ft (914 mm) railroad system of Guatemala no longer operates, see Rail transport in Guatemala.
Mexico
Mexico currently uses standard gauge. See Rail transport in Mexico
Panama
The Panama Railroad was originally 5 ft (1,524 mm) as in much of the Southern United States. This gauge was converted to 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) when the line was rebuilt in 2000. Nowadays only the ship handling trains along the Panama Canal, called mules, still have the 5 ft track.
United States
In 1886, the southern railroads agreed to coordinate changing gauge on all their tracks. After considerable debate and planning, most of the southern rail network was converted from 5 ft (1,524 mm) gauge to 4 ft 9 in (1,448 mm) gauge, then the standard of the Pennsylvania Railroad, over two remarkable days beginning on Monday, May 31, 1886. Over a period of 36 hours, tens of thousands of workers pulled the spikes from the west rail of all the broad gauge lines in the South, moved them 3 in (76 mm) east and spiked them back in place. The new gauge was close enough that standard gauge equipment could run on it without problem. By June 1886, all major railroads in North America were using approximately the same gauge. The final conversion to true standard gauge took place gradually as track was maintained.[1] Now, the only broad-gauge rail systems in the United States are some city transit systems.
See also
- Narrow gauge rail transport
- Narrow gauge railways in Canada
- Narrow gauge railroads in the United States
- Rail gauge in Europe
- Rail gauge in South America
- Rail gauge in Australia
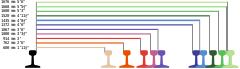
.svg.png)