RGB color space
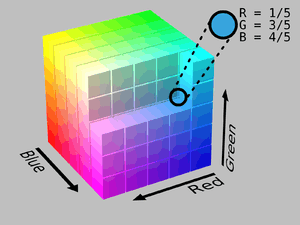
An RGB color space is any additive color space based on the RGB color model.[1] A particular RGB color space is defined by the three chromaticities of the red, green, and blue additive primaries, and can produce any chromaticity that is the triangle defined by those primary colors.[2] The complete specification of an RGB color space also requires a white point chromaticity and a gamma correction curve. As of 2007, sRGB is by far the most commonly used RGB color space.
RGB is an abbreviation for red–green–blue.
Intuition
An RGB color space can be easily understood by thinking of it as "all possible colors" that can be made from three colourants for red, green and blue. Imagine, for example, shining three lights together onto a white wall: one red light, one green light, and one blue light, each with dimmer switches. If only the red light is on, the wall will look red. If only the green light is on, the wall will look green. If the red and green lights are on together, the wall will look yellow. Dim the red light and the wall will become more of a yellow-green. Dim the green light instead, and the wall will become more orange. Bringing up the blue light a bit will cause the orange to become less saturated and more whitish. In all, each setting of the three dimmer switches will produce a different result, either in color or in brightness or both. The set of all possible results is the gamut defined by those particular color lamps. Swap the red lamp for one of a different brand that is slightly more orange, and there will be a slightly different gamut, since the set of all colors that can be produced with the three lights will be changed.
An LCD display can be thought of as a grid of thousands of little red, green, and blue lamps, each with their own dimmer switch. The gamut of the display will depend on the three colors used for the red, green and blue lights. A wide-gamut display will have very saturated, "pure" light colors, and thus be able to display very saturated, deep colors.
Applications
RGB is a convenient color model for computer graphics because the human visual system works in a way that is similar — though not quite identical — to an RGB color space. The most commonly used RGB color spaces are sRGB and Adobe RGB (which has a significantly larger gamut). Adobe has recently developed another color space called Adobe Wide Gamut RGB, which is even larger, in detriment to gamut density.
As of 2007, sRGB is by far the most commonly used RGB color space, particularly in consumer grade digital cameras, HD video cameras, and computer monitors. HDTVs use a similar space, commonly called Rec. 709, sharing the sRGB primaries. The sRGB space is considered adequate for most consumer applications. Having all devices use the same color space is convenient in that an image does not need to be converted from one color space to another before being displayed. However, sRGB's limited gamut leaves out many highly saturated colors that can be produced by printers or in film, and thus is not ideal for some high quality applications. The wider gamut Adobe RGB is being built into more medium-grade digital cameras, and is favored by many professional graphic artists for its larger gamut.
Specifications
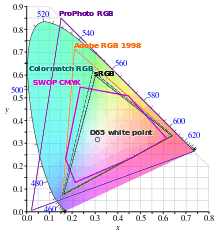
RGB spaces are generally specified by defining three primary colors and a white point. In the table below the three primary colors and white points for various RGB spaces are given. The primary colors are specified in terms of their CIE 1931 color space chromaticity coordinates (x,y).
| Color space | Gamut | White point | Primaries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red | Green | Blue | ||||||
| xR | yR | xG | yG | xB | yB | |||
| ISO RGB | Limited | floating | floating | |||||
| Extended ISO RGB | Unlimited (signed) | floating | floating | |||||
| scRGB | Unlimited (signed) | D65 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| sRGB, HDTV (ITU-R BT.709) | CRT | D65 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Adobe RGB 98 | CRT | D65 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.71 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| PAL/SECAM (1970) (EBU Tech. 3213, ITU-R BT.470 System B, G) |
CRT | D65 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| NTSC (1987) (SMPTE RP 145 "SMPTE C", SMPTE 170M) |
CRT | D65 | 0.63 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.595 | 0.155 | 0.07 |
| Japanese NTSC (1987) | CRT | D93 | 0.63 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.595 | 0.155 | 0.07 |
| Apple RGB | CRT | D65 | 0.625 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.595 | 0.155 | 0.07 |
| NTSC (1953) (FCC 1953, ITU-R BT.470 System M) |
CRT | C | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| DCI-P3 (2010) (SMPTE EG 432-1, RP 431-2) |
Wide | D65 | 0.680 | 0.320 | 0.265 | 0.690 | 0.150 | 0.060 |
| UHDTV (ITU-R BT.2020, BT.2100) | Wide | D65 | 0.708 | 0.292 | 0.170 | 0.797 | 0.131 | 0.046 |
| Adobe Wide Gamut RGB | Wide | D50 | 0.735 | 0.265 | 0.115 | 0.826 | 0.157 | 0.018 |
| ROMM RGB ProPhoto RGB |
Wide | D50 | 0.7347 | 0.2653 | 0.1596 | 0.8404 | 0.0366 | 0.0001 |
| CIE (1931) RGB | Wide | E | 0.7347 | 0.2653 | 0.2738 | 0.7174 | 0.1666 | 0.0089 |
| CIE XYZ (not RGB) | Unlimited | E | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
The CIE 1931 color space standard defines both the CIE RGB space, which is an RGB color space with monochromatic primaries, and the CIE XYZ color space, which works like an RGB color space except that it has non-physical primaries that cannot be said to be red, green, and blue.
See also
References
External links
- Pascale, Danny. "A Review of RGB color spaces...from xyY to R'G'B'" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-01-21.
- Susstrunk, Buckley and Swen. "Standard RGB Color Spaces" (PDF). Retrieved November 18, 2005.
- Lindbloom, Bruce. "RGB Working Space Information". Retrieved November 18, 2005.
- Colantoni, Philippe. "RGB cube transformation in different color spaces".