Psychological warfare
Psychological warfare (PSYWAR), or the basic aspects of modern psychological operations (PSYOP), have been known by many other names or terms, including MISO, Psy Ops, Political Warfare, "Hearts and Minds," and propaganda.[1] The term is used "to denote any action which is practiced mainly by psychological methods with the aim of evoking a planned psychological reaction in other people."[2] Various techniques are used, and are aimed at influencing a target audience's value system, belief system, emotions, motives, reasoning, or behavior. It is used to induce confessions or reinforce attitudes and behaviors favorable to the originator's objectives, and are sometimes combined with black operations or false flag tactics. It is also used to destroy the morale of enemies through tactics that aim to depress troops' psychological states.[3][4] Target audiences can be governments, organizations, groups, and individuals, and is not just limited to soldiers. Civilians of foreign territories can also be targeted by technology and media so as to cause an effect in the government of their country.[5]
In Propaganda: The Formation of Men's Attitudes, Jacques Ellul discusses psychological warfare as a common peace policy practice between nations as a form of indirect aggression in place of military aggression. This type of propaganda drains the public opinion of an opposing regime by stripping away its power on public opinion. This form of aggression is hard to defend against because no international court of justice is capable of protecting against psychological aggression since it cannot be legally adjudicated. The only defense is using the same means of psychological warfare. It is the burden of every government to defend its state against propaganda aggression. "Here the propagandists is [sic] dealing with a foreign adversary whose morale he seeks to destroy by psychological means so that the opponent begins to doubt the validity of his beliefs and actions."[6][7]
History
Early

Since prehistoric times, warlords and chiefs have recognised the importance of inducing psychological terror in opponents and currying favour with supporters. An early practitioner of such tactics was Alexander the Great, who successfully conquered large parts of Europe and the Middle East and held on to his territorial gains by co-opting local elites into the Greek administration and culture. Alexander left some of his men behind in each conquered city to introduce Greek culture and oppress dissident views. His soldiers were paid dowries to marry locals[8] in an effort to encourage assimilation.
Genghis Khan, leader of the Mongolian Empire in the 13th century AD employed this technique. Defeating the will of the enemy before having to attack and reaching a consented settlement was preferable to actually fighting. The Mongol generals demanded submission to the Khan, and threatened the initially captured villages with complete destruction if they refused to surrender. If they had to fight to take the settlement, the Mongol generals fulfilled their threats and massacred the survivors. Tales of the encroaching horde spread to the next villages and created an aura of insecurity that undermined the possibility of future resistance.[9]
The Khan also employed tactics that made his numbers seem greater than they actually were. During night operations he ordered each soldier to light three torches at dusk to give the illusion of an overwhelming army and deceive and intimidate enemy scouts. He also sometimes had objects tied to the tails of his horses, so that riding on open and dry fields raised a cloud of dust that gave the enemy the impression of great numbers. His soldiers used arrows specially notched to whistle as they flew through the air, creating a terrifying noise.[10]
Another tactic favoured by the Mongols was catapulting severed human heads over city walls to frighten the inhabitants and spread disease in the besieged city's closed confines. This was especially used by the later Turko-Mongol chieftain.
The Muslim caliph Omar, in his battles against the Byzantine Empire, sent small reinforcements in the form of a continuous stream, giving the impression that a large force would accumulate eventually if not swiftly dealt with.
Modern
First World War

The start of modern psychological operations in war is generally dated to the First World War. By that point, Western societies were increasingly educated and urbanized, and mass media was available in the form of large circulation newspapers and posters. It was also possible to transmit propaganda to the enemy via the use of airborne leaflets or through explosive delivery systems like modified artillery or mortar rounds.[11]
At the start of the war, the belligerents, especially the British and Germans, began distributing propaganda, both domestically and on the Western front. The British had several advantages that allowed them to succeed in the battle for world opinion; they had one of the world's most reputable news systems, with much experience in international and cross-cultural communication, and they controlled much of the undersea cable system then in operation. These capabilities were easily transitioned to the task of warfare.
The British also had a diplomatic service that kept up good relations with many nations around the world, in contrast to the reputation of the German services.[12] While German attempts to foment revolution in parts of the British Empire, such as Ireland and India, were ineffective, extensive experience in the Middle East allowed the British to successfully induce the Arabs to revolt against the Ottoman Empire.
In August 1914, David Lloyd George appointed Charles Masterman MP, to head a Propaganda Agency at Wellington House. A distinguished body of literary talent was enlisted for the task, with its members including Arthur Conan Doyle, Ford Madox Ford, G. K. Chesterton, Thomas Hardy, Rudyard Kipling and H. G. Wells. Over 1,160 pamphlets were published during the war and distributed to neutral countries, and eventually, to Germany. One of the first significant publications, the Report on Alleged German Outrages of 1915, had a great effect on general opinion across the world. The pamphlet documented atrocities, both actual and alleged, committed by the German army against Belgian civilians. A Dutch illustrator, Louis Raemaekers, provided the highly emotional drawings which appeared in the pamphlet.[13]
In 1917, the bureau was subsumed into the new Department of Information and branched out into telegraph communications, radio, newspapers, magazines and the cinema. In 1918, Viscount Northcliffe was appointed Director of Propaganda in Enemy Countries. The department was split between propaganda against Germany organized by H.G Wells and against the Austro-Hungarian Empire supervised by Wickham Steed and Robert William Seton-Watson; the attempts of the latter focused on the lack of ethnic cohesion in the Empire and stoked the grievances of minorities such as the Croats and Slovenes. It had a significant effect on the final collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Army at the Battle of Vittorio Veneto.[11]
Aerial leaflets were dropped over German trenches containing postcards from prisoners of war detailing their humane conditions, surrender notices and general propaganda against the Kaiser and the German generals. By the end of the war, MI7b had distributed almost 26 million leaflets. The Germans began shooting the leaflet-dropping pilots, prompting the British to develop unmanned leaflet balloons that drifted across no-man's land. At least one in seven of these leaflets were not handed in by the soldiers to their superiors, despite severe penalties for that offence. Even General Hindenburg admitted that "Unsuspectingly, many thousands consumed the poison", and POWs admitted to being disillusioned by the propaganda leaflets that depicted the use of German troops as mere cannon fodder. In 1915, the British began airdropping a regular leaflet newspaper Le Courrier de l'Air for civilians in German-occupied France and Belgium.[14]
At the start of the war, the French government took control of the media to suppress negative coverage. Only in 1916, with the establishment of the Maison de la Presse, did they begin to use similar tactics for the purpose of psychological warfare. One of its sections was the "Service de la Propagande aérienne" (Aerial Propaganda Service), headed by Professor Tonnelat and Jean-Jacques Waltz, an Alsatian artist code-named "Hansi". The French tended to distribute leaflets of images only, although the full publication of US President Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points, which had been heavily edited in the German newspapers, was distributed via airborne leaflets by the French.[15]
The Central Powers were slow to use these techniques; however, at the start of the war the Germans succeeded in inducing the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire to declare 'holy war', or Jihad, against the Western infidels. They also attempted to foment rebellion against the British Empire in places as far afield as Ireland, Afghanistan, and India. The Germans' greatest success was in giving the Russian revolutionary, Lenin, free transit on a sealed train from Switzerland to Finland after the overthrow of the Tsar. This soon paid off when the Bolshevik Revolution took Russia out of the war.[16]
World War II

Adolf Hitler was greatly influenced by the psychological tactics of warfare the British had employed during WWI, and attributed the defeat of Germany to the effects this propaganda had on the soldiers. He became committed to the use of mass propaganda to influence the minds of the German population in the decades to come. Joseph Goebbels was appointed as Propaganda Minister when Hitler came to power in 1933, and he portrayed Hitler as a messianic figure for the redemption of Germany. Hitler also coupled this with the resonating projections of his orations for effect.
Germany's Fall Grün plan of invasion of Czechoslovakia had a large part dealing with psychological warfare aimed both at the Czechoslovak civilians and government as well as, crucially, at Czechoslovak allies.[17] It became successful to the point that Germany gained support of UK and France through appeasement to occupy Czechoslovakia without having to fight an all-out war, sustaining only minimum losses in covert war before the Munich Agreement.
At the start of the Second World War, the British set up the Political Warfare Executive to produce and distribute propaganda. Through the use of powerful transmitters, broadcasts could be made across Europe. Sefton Delmer managed a successful black propaganda campaign through several radio stations which were designed to be popular with German troops while at the same time introducing news material that would weaken their morale under a veneer of authenticity. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill made use of radio broadcasts for propaganda against the Germans.
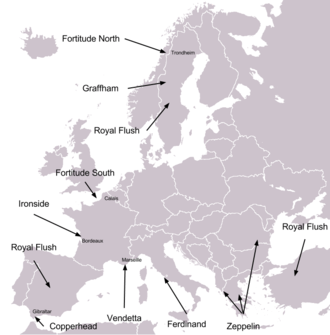
During World War II, the British made extensive use of deception – developing many new techniques and theories. The main protagonists at this time were 'A' Force, set up in 1940 under Dudley Clarke, and the London Controlling Section, chartered in 1942 under the control of John Bevan.[18][19] Clarke pioneered many of the strategies of military deception. His ideas for combining fictional orders of battle, visual deception and double agents helped define Allied deception strategy during the war, for which he has been referred to as "the greatest British deceiver of WW2".[20]
During the lead up to the Allied invasion of Normandy, many new tactics in psychological warfare were devised. The plan for Operation Bodyguard set out a general strategy to mislead German high command as to the exact date and location of the invasion. Planning began in 1943 under the auspices of the London Controlling Section (LCS). A draft strategy, referred to as Plan Jael, was presented to Allied high command at the Tehran Conference. Operation Fortitude was intended to convince the Germans of a greater Allied military strength than existed, through fictional field armies, faked operations to prepare the ground for invasion and leaked information about the Allied order of battle and war plans.
Elaborate naval deceptions (Operations Glimmer, Taxable and Big Drum) were undertaken in the English Channel.[21] Small ships and aircraft simulated invasion fleets lying off Pas de Calais, Cap d'Antifer and the western flank of the real invasion force.[22] At the same time Operation Titanic involved the RAF dropping fake paratroopers to the east and west of the Normandy landings.

The deceptions were implemented with the use of double agents, radio traffic and visual deception. The British "Double Cross" anti-espionage operation had proven very successful from the outset of the war,[23] and the LCS was able to use double agents to send back misleading information about Allied invasion plans.[24] The use of visual deception, including mock tanks and other military hardware had been developed during the North Africa campaign. Mock hardware was created for Bodyguard; in particular, dummy landing craft were stockpiled to give the impression that the invasion would take place near Calais.
The Operation was a strategic success and the Normandy landings caught German defences unaware. Subsequent deception led Hitler into delaying reinforcement from the Calais region for nearly seven weeks.[25]
Vietnam War

The United States ran an extensive program of psychological warfare during the Vietnam War. The Phoenix Program had the dual aim of assassinating NLF personnel and terrorizing any potential sympathizers or passive supporters. Chieu Hoi program of the South Vietnam government promoted NLF defections.
When members of the PRG were assassinated, CIA and Special Forces operatives placed playing cards in the mouth of the deceased as a calling card. During the Phoenix Program, over 19,000 NLF supporters were killed.[26] The United States also used tapes of distorted human sounds and played them during the night making the Vietnamese soldiers think that the dead were back for revenge.
Recent operations

The CIA made extensive use of Contra soldiers to destabilize the Sandinista government in Nicaragua.[27] The CIA used psychological warfare techniques against the Panamanians by delivering unlicensed TV broadcasts. The CIA has extensively used propaganda broadcasts against the Cuban government through TV Marti, based in Miami, Florida. However, the Cuban government has been successful at jamming the signal of TV Marti.
In the Iraq War, the United States used the shock and awe campaign to psychologically maim, and break the will of the Iraqi Army to fight.
Social media has enabled the use of disinformation on a wide scale. Analysts have found evidence of doctored or misleading photographs spread by social media in the Syrian Civil War and 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine, possibly with state involvement.[28]
Methods
Most modern uses of the term psychological warfare, refers to the following military methods:
- Demoralization:
- Distributing pamphlets that encourage desertion or supply instructions on how to surrender
- Shock and awe military strategy
- Projecting repetitive and annoying sounds and music for long periods at high volume towards groups under siege like during Operation Nifty Package
- Propaganda radio stations, such as Lord Haw-Haw in World War II on the "Germany calling" station
- Renaming cities and other places when captured, such as the renaming of Saigon to Ho Chi Minh City after Vietnamese victory in the Vietnam War
- False flag events
- Use of loudspeaker systems to communicate with enemy soldiers
- Terrorism[29]
- The threat of chemical weapons[30]
Most of these techniques were developed during World War II or earlier, and have been used to some degree in every conflict since. Daniel Lerner was in the OSS (the predecessor to the American CIA) and in his book, attempts to analyze how effective the various strategies were. He concludes that there is little evidence that any of them were dramatically successful, except perhaps surrender instructions over loudspeakers when victory was imminent. It should be noted, though, that measuring the success or failure of psychological warfare is very hard, as the conditions are very far from being a controlled experiment.
Lerner also divides psychological warfare operations into three categories:[31]
- White propaganda (Omissions and Emphasis): Truthful and not strongly biased, where the source of information is acknowledged.
- Grey propaganda (Omissions, Emphasis and Racial/Ethnic/Religious Bias): Largely truthful, containing no information that can be proven wrong; the source is not identified.
- Black propaganda (Commissions of falsification): Inherently deceitful, information given in the product is attributed to a source that was not responsible for its creation.
Lerner points out that grey and black operations ultimately have a heavy cost, in that the target population sooner or later recognizes them as propaganda and discredits the source. He writes, "This is one of the few dogmas advanced by Sykewarriors that is likely to endure as an axiom of propaganda: Credibility is a condition of persuasion. Before you can make a man do as you say, you must make him believe what you say."[31]:28 Consistent with this idea, the Allied strategy in World War II was predominantly one of truth (with certain exceptions).
By country
Soviet Union
China
According to U.S. military analysts, attacking the enemy’s mind is an important element of the People's Republic of China's military strategy.[32] This type of warfare is rooted in the Chinese Stratagems outlined by Sun Tzu in The Art of War and Thirty-Six Stratagems. In its dealings with its rivals, China is expected to utilize Marxism to mobilize communist loyalists, as well as flex its economic and military muscle to persuade other nations to act in China's interests. The Chinese government also tries to control the media to keep a tight hold on propaganda efforts for its people.[32]
Germany
In the German Bundeswehr, the Zentrum Operative Information and its subordinate Batallion für Operative Information 950 are responsible for the PSYOP efforts (called Operative Information in German). Both the center and the battalion are subordinate to the new Streitkräftebasis (Joint Services Support Command, SKB) and together consist of about 1,200 soldiers specialising in modern communication and media technologies. One project of the German PSYOP forces is the radio station Stimme der Freiheit (Sada-e Azadi, Voice of Freedom),[33] heard by thousands of Afghans. Another is the publication of various newspapers and magazines in Kosovo and Afghanistan, where German soldiers serve with NATO.
United Kingdom
The British were one of the first major military powers to use psychological warfare in the First and Second World Wars. In current the British Armed Forces, PSYOPS are handled by the tri-service 15 Psychological Operations Group. (See also MI5 and Secret Intelligence Service). The Psychological Operations Group comprises over 150 personnel, approximately 75 from the regular Armed Services and 75 from the Reserves. The Group supports deployed commanders in the provision of psychological operations in operational and tactical environments.[34][35]
The Group was established immediately after the 1991 Gulf War,[36] has since grown significantly in size to meet operational requirements,[37] and from 2015 it will be one of the sub-units of the 77th Brigade, formerly called the Security Assistance Group.[38] Stephen Jolly, the MOD's Director of Defence Communications and former Chair of the UK's National Security Communications Committee (2013–15), is thought to be the most senior serving psyops officer within British Defence.
In June 2015, NSA files published by Glenn Greenwald revealed details of the JTRIG group at British intelligence agency GCHQ covertly manipulating online communities.[39] This is in line with JTRIG's goal: to "destroy, deny, degrade [and] disrupt" enemies by "discrediting" them, planting misinformation and shutting down their communications.[40]
United States

The term psychological warfare is believed to have migrated from Germany to the United States in 1941.[41] During World War II, the United States Joint Chiefs of Staff defined psychological warfare broadly, stating "Psychological warfare employs any weapon to influence the mind of the enemy. The weapons are psychological only in the effect they produce and not because of the weapons themselves."[42] The U.S. Department of Defense currently defines psychological warfare as:
"The planned use of propaganda and other psychological actions having the primary purpose of influencing the opinions, emotions, attitudes, and behavior of hostile foreign groups in such a way as to support the achievement of national objectives."[43]
This definition indicates that a critical element of the U.S. psychological operations capabilities includes propaganda and by extension counterpropaganda. Joint Publication 3-53 establishes specific policy to use public affairs mediums to counterpropaganda from foreign origins.[44]
The purpose of United States psychological operations is to induce or reinforce attitudes and behaviors favorable to US objectives. The Special Activities Division (SAD) is a division of the Central Intelligence Agency's National Clandestine Service, responsible for Covert Action and "Special Activities". These special activities include covert political influence (which includes psychological operations) and paramilitary operations.[45] SAD's political influence group is the only US unit allowed to conduct these operations covertly and is considered the primary unit in this area.[45]
Dedicated psychological operations units exist in the United States Army. The United States Navy also plans and executes limited PSYOP missions. United States PSYOP units and soldiers of all branches of the military are prohibited by law from targeting U.S. citizens with PSYOP within the borders of the United States (Executive Order S-1233, DOD Directive S-3321.1, and National Security Decision Directive 130). While United States Army PSYOP units may offer non-PSYOP support to domestic military missions, they can only target foreign audiences.
A U.S. Army field manual released in January 2013 states that "Inform and Influence Activities" are critical for describing, directing, and leading military operations. Several Army Division leadership staff are assigned to “planning, integration and synchronization of designated information-related capabilities."[46]
See also
- Charles Douglas Jackson
- Demonizing the enemy
- Demoralization (warfare)
- Electromagnetic Weapon
- Information warfare
- Lawfare
- Media manipulation
- Military psychology
- Mind games
- Minor sabotage
- Political Warfare
- Propaganda: The Formation of Men's Attitudes
- Psychological manipulation
- Special Operations
- Taliban propaganda
- Unconventional Warfare
NATO
US specific:
- Information Operations Roadmap
- Military journalism
- NLF and PAVN battle tactics
- Psychological operations (United States)
- Special Activities Division
- Zarqawi PSYOP program
World War II:
USSR
Related:
References
- ↑ "Forces.gc.ca". Journal.forces.gc.ca. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
- ↑ Szunyogh, Béla (1955). Psychological warfare; an introduction to ideological propaganda and the techniques of psychological warfare. United States: William-Frederick Press. p. 13. Retrieved 2015-02-11.
- ↑ Chekinov, S. C.; Bogdanov, S. A. The Nature and Content of a New-Generation War (PDF). United States: Military Thought. p. 16. ISSN 0869-5636. Retrieved 2015-02-11.
- ↑ Doob, Leonard W. "The Strategies Of Psychological Warfare." Public Opinion Quarterly 13.4 (1949): 635-644. SocINDEX with Full Text. Web. 20 Feb. 2015.
- ↑ Wall, Tyler (September 2010). U.S Psychological Warfare and Civilian Targeting. United States: Vanderbilt University. p. 289. Retrieved 2015-02-11.
- ↑ Ellul, Jacques (1973). Propaganda: The Formation of Men’s Attitudes, p. xiii.Trans. Konrad Kellen & Jean Lerner. Vintage Books, New York. ISBN 978-0-394-71874-3.
- ↑ The Psychology of Terrorism: Clinical aspects and responses - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2014-08-10.
- ↑ Lance B. Curke Ph.D., The Wisdom of Alexander the Great: Enduring Leadership Lessons From the Man Who Created an Empire (2004) p. 66
- ↑ David Nicolle, The Mongol Warlords: Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan, Hulegu, Tamerlane (2004) p. 21
- ↑ George H. Quester (2003). Offense and Defense in the International System. Transaction Publishers. p. 43. Retrieved 2016-03-19.
- 1 2 "ALLIED PSYOP OF WWI". Retrieved 2012-12-17.
- ↑ Linebarger, Paul Myron Anthony (2006). Psychological Warfare. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ↑ "The Battle for the Mind: German and British Propaganda in the First World War".
- ↑ Taylor, Philip M. (1999). British Propaganda in the Twentieth Century: Selling Democracy. Edinburgh University Press. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ↑ "ALLIED PSYOP OF WWI". Retrieved 2012-12-17.
- ↑ "GERMAN WWI PSYOP". Retrieved 2012-12-17.
- ↑ Hruška, Emil (2013), Boj o pohraničí: Sudetoněmecký Freikorps v roce 1938 (1st ed.), Prague: Nakladatelství epocha, Pražská vydavatelská společnost, p. 9
- ↑ Latimer (2004), pg. 148–149
- ↑ Cruickshank (2004)
- ↑ Rankin, Nicholas (1 October 2008). Churchill's Wizards: The British Genius for Deception, 1914–1945. Faber and Faber. p. 178. ISBN 0-571-22195-5.
- ↑ Barbier, Mary (30 Oct 2007). D-Day Deception: Operation Fortitude and the Normandy Invasion. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 70. ISBN 0275994791.
- ↑ Barbier, Mary (30 Oct 2007). D-Day Deception: Operation Fortitude and the Normandy Invasion. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 108. ISBN 0275994791.
- ↑ Masterman, John C (1972) [1945]. The Double-Cross System in the War of 1939 to 1945. Australian National University Press. ISBN 978-0-7081-0459-0.
- ↑ Ambrose, Stephen E. (1981). "Eisenhower, the Intelligence Community, and the D-Day Invasion". The Wisconsin Magazine of History. Vol. 64 no. 4. Wisconsin Historical Society. p. 269. ISSN 0043-6534.
- ↑ Latimer, John (2001). Deception in War. New York: Overlook Press. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-58567-381-0.
- ↑ Janq Designs. "Special operation - Phoenix". Specialoperations.com. Archived from the original on May 12, 2011. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
- ↑ "Is the U.S. Organizing Salvador-Style Death Squads in Iraq?". Democracy Now!. 2005-01-10. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- ↑ Rawlsey, Adam (1 November 2014). "Be Very Skeptical—A Lot of Your Open-Source Intel Is Fake". Medium. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ Boaz, Gaynor (April 2004). "Terrorism as a strategy of psychological warfare". Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma. Taylor and Francis. 9 (1–2): 33–4. doi:10.1300/J146v09n01_03.(subscription required)
- ↑ Romano Jr., James A.; King, James M. (2002). "Chemical warfare and chemical terrorism: psychological and performance outcomes". Military Psychology. American Psychological Association via PsycNET. 14 (2): 85–92. doi:10.1207/S15327876MP1402_2.(subscription required)
- 1 2 Lerner, Daniel (1971) [1949]. Psychological warfare against Nazi Germany: the Sykewar Campaign, D-Day to VE-Day. Boston, Mass: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-12045-3. Originally printed by George W. Stewart of New York. Alternative ISBN 0-262-62019-7
- 1 2 "Chinese Military - Psychological Warfare". ufl.edu. Archived from the original on 15 April 2011.
- ↑ "Sada-e-azadi.net". Sada-e-azadi.net. Archived from the original on May 12, 2011. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
- ↑ "15 (UK) Psychological Operations Group". Ministry of Defence. Archived from the original on 2006-06-20. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ↑ "Psychological Ops Group". Royal Navy. Archived from the original on 2010-07-02. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- ↑ Jolly, Stephen (October 2000). Minshall, David, ed. "Wearing the Stag's Head Badge: British Combat Propaganda since 1945". Falling Leaf. The Psywar Society (170): 86–89. ISSN 0956-2400.
- ↑ "15 (United Kingdom) Psychological Operations Group: Annual Report" (PDF). 15 (UK) PSYOPS Group. Retrieved 29 May 2011.
- ↑ Ewan MacAskill (31 January 2015). "British army creates team of Facebook warriors". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ Greenwald, Glenn and Andrew Fishman. Controversial GCHQ Unit Engaged in Domestic Law Enforcement, Online Propaganda, Psychology Research. The Intercept. 2015-06-22.
- ↑ "Snowden Docs: British Spies Used Sex and 'Dirty Tricks'". NBC News. 7 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ↑ WALL, TYLER. "U.S. Psychological Warfare And Civilian Targeting." Peace Review 22.3 (2010): 288-294. SocINDEX with Full Text. Web. 20 Feb. 2015.
- ↑ From "Overall Strategic Plan for the United States' Psychological Warfare, " 1 March 1943, JCS Records, Strategic Issues, Reel 11. Quoted in Robert H. Keyserlingk (July 1990). Austria in World War II. McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 131. ISBN 0-7735-0800-7.
- ↑ Phil Taylor (1987). "Glossary of Relevant Terms & Acronyms Propaganda and Psychological Warfare Studies University of Leeds UK". University of Leeds UK. Archived from the original on 2013-06-22. Retrieved 2008-04-19.
- ↑ Garrison, WC (1999). "Information Operations and Counter-Propaganda: Making a Weapon of Public Affairs" (PDF). Strategy Research Project, U.S. Army War College. p. 12. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- 1 2 Executive Secrets: Covert Action and the Presidency, William J. Daugherty, University of Kentucky Press, 2004.
- ↑ "Pentagon gearing up to fight the PR war" Washington Post, February 6, 2013
Bibliography
- Fred Cohen. Frauds, Spies, and Lies - and How to Defeat Them. ISBN 1-878109-36-7 (2006). ASP Press.
- Fred Cohen. World War 3 ... Information Warfare Basics. ISBN 1-878109-40-5 (2006). ASP Press.
- Gagliano Giuseppe. Guerra psicologia.Disinformazione e movimenti sociali. Introduzione del Gen. Carlo Jean e di Alessandro Politi Editrice Aracne, Roma, 2012.
- Gagliano Giuseppe. Guerra psicologia.Saggio sulle moderne tecniche militari,di guerra cognitiva e disinformazione. Introduzione del Gen. Carlo Jean, Editrice Fuoco, Roma 2012.
- Paul M. A. Linebarger. Psychological Warfare: International Propaganda and Communications. ISBN 0-405-04755-X (1948). Revised second edition, Duell, Sloan and Pearce (1954).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Psychological warfare. |
| Look up psychological warfare in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Movie: Psywar: The Real Battlefield is the Mind by Metanoia films
- Paul Myron Anthony Linebarger. Psychological Warfare at Project Gutenberg
- The history of psychological warfare
- IWS Psychological Operations (PsyOps) / Influence Operations
- "Pentagon psychological warfare operation", USA Today, December 15, 2005
- "U.S. Adapts Cold-War Idea to Fight Terrorists", New York Times, March 18, 2008
- US Army PSYOPS Info - Detailed information about the US Army Psychological Operation Soldiers
- IWS — The Information Warfare Site
- U.S. — PSYOP producing mid-eastern kids comic book
- The Institute of Heraldry — Psychological Operations
- Psychological warfare
