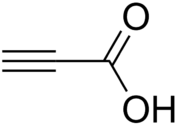
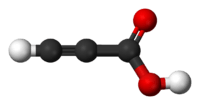
Propiolic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-ynoic acid | |
| Other names
Propiolic acid (no longer recommended[1]) Acetylene carboxylic acid Propargylic acid Acetylene mono-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 471-25-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:33199 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1213530 |
| ChemSpider | 9706 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.763 |
| EC Number | 207-437-8 |
| KEGG | C00804 |
| MeSH | C011537 |
| PubChem | 10110 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 70.05 g/mol |
| Density | 1.1325 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 9 °C (48 °F; 282 K) |
| Boiling point | 144 °C (291 °F; 417 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Propiolic acid is the organic compound with the formula HC2CO2H. It is the simplest acetylenic carboxylic acid. It is a colourless liquid that crystallises to give silky crystals. Near its boiling point, it decomposes. It is soluble in water and possesses an odor like that of acetic acid.[2]
Preparation
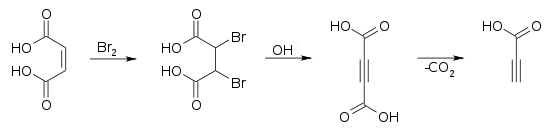
It is prepared commercially by oxidizing propargyl alcohol at a lead electrode.[3] It can also be prepared by decarboxylation of acetylenedicarboxylic acid.
Reactions and applications
Exposure to sunlight converts it into trimesic acid (benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid). It undergoes bromination to give dibromoacrylic acid. With hydrogen chloride it forms chloroacrylic acid. Its ethyl ester condenses with hydrazine to form pyrazolone.
It forms a characteristic explosive solid upon treatment to its aqueous solution with ammoniacal silver nitrate. An amorphous explosive precipitate forms with ammoniacal cuprous chloride.
See also
References
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 748. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ ed, Susan Budavari, (1990). The Merck index an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals (11. ed., 2. print. ed.). Rahway, NJ: Merck. pp. 7833, 1911. ISBN 9780911910285.
- ↑ Wilhelm Riemenschneider "Carboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_235.
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Propiolic Acid". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Propiolic Acid". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.