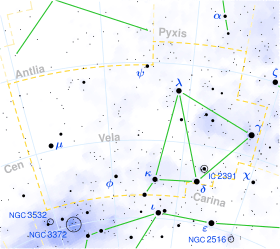
Phi Velorum
| |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Vela |
| Right ascension | 09h 56m 51.742s[1] |
| Declination | −54° 34′ 04.04″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.53[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B5 Ib[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.62[2] |
| B−V color index | −0.08[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 13.9[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −13.08 ± 0.10[1] mas/yr Dec.: 3.55 ± 0.10[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.05 ± 0.11[1] mas |
| Distance | 1,590 ± 90 ly (490 ± 30 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −5.4[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 10.1[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 31[5] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 28,200[5] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.55[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 14,600[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 17[7] km/s |
| Age | 22.6[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
- "Tseen Ke" redirects here. Tseen Ke can also refer to Lambda Velorum.
Phi Velorum (φ Vel, φ Velorum) is a star in the constellation Vela. It is a blue-white B-type supergiant with an apparent magnitude of +3.53. It is approximately 1,590 light years from Earth.
Nomenclature
φ Velorum (latinised to Phi Velorum, abbreviated to φ Vel) is the Bayer designation for this star. It is also listed as HR 3940 in the Bright Star Catalogue and HD 86440 in the Henry Draper Catalogue. It has the traditional name Tseen Ke, from Chinese 天紀 (Mandarin tiānjì) "star chart". (lit. "Record of Heaven").
Properties
φ Velorum has a temperature of 14,600 K. Combined with a radius of 31 R☉, it has a luminosity of 28,200 L☉. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and left the main sequence to become a supergiant. It has a current mass of about 10 M☉.
Companion
φ Velorum has an optical companion 39" away. It is a 12th magnitude K0 giant star.[9][10]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752
 . Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Vizier catalog entry
. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Vizier catalog entry - 1 2 3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ Houk, N.; Cowley, A. P. (1975). "University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations -90_ to -53_ƒ0". University of Michigan Catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Volume I. Declinations -90_ to -53_ƒ0. Bibcode:1975MSS...C01....0H.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065.
- 1 2 3 Lefever, K.; Puls, J.; Aerts, C. (2007). "Statistical properties of a sample of periodically variable B-type supergiants. Evidence for opacity-driven gravity-mode oscillations". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 463 (3): 1093. arXiv:astro-ph/0611484
 . Bibcode:2007A&A...463.1093L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066038.
. Bibcode:2007A&A...463.1093L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066038. - 1 2 Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410: 190. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x.
- 1 2 3 Fraser, M.; Dufton, P. L.; Hunter, I.; Ryans, R. S. I. (2010). "Atmospheric parameters and rotational velocities for a sample of Galactic B-type supergiants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 404: 1306. arXiv:1001.3337
 . Bibcode:2010MNRAS.404.1306F. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16392.x.
. Bibcode:2010MNRAS.404.1306F. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16392.x. - ↑ Allen, Richard Hinck (1899). Star Names & Their Meanings. Kessinger Publishing. p. 74. ISBN 9780766140288.
- ↑ Lindroos, K. P. (1985). "A study of visual double stars with early type primaries. IV Astrophysical data". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series (ISSN 0365-0138). 60: 183. Bibcode:1985A&AS...60..183L.
- ↑ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal. 122 (6): 3466. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M. doi:10.1086/323920.