Park Street Church

The Park Street Church (built in 1809) in downtown Boston, Massachusetts is an active Conservative Congregational church with 2,000 in Sunday attendance and around 1,000 members [1] at the corner of Tremont Street and Park Street. The church is currently pastored by Gordon P. Hugenberger.
History
Park Street Church is a historic stop on the Freedom Trail. The founding of the church is predated to 1804 when the "Religious Improvement Society" began weekly meetings with lectures and prayer.[2] The society organized the charter of the church on February 27, 1809 by twenty-six local people, mostly former members of the Old South Meeting House, who wanted to plant a church with orthodox Trinitarian theology.
The cornerstone of the church was laid on May 1 and construction was completed by the end of the year, under the guidance of Peter Banner (architect), Benajah Young (chief mason) and Solomon Willard (woodcarver). Banner took inspiration from several early pattern books, and his design is reminiscent of a London church by Christopher Wren. Park Street church's steeple rises to 217 feet (66 m), and remains a landmark visible from several Boston neighborhoods.[3] The church was the tallest building in the United States from 1810 to 1846.
.jpg)
The church is located adjacent to the historic Granary Burying Ground. It had its first worship service on January 10, 1810. The church became known as "Brimstone Corner", in part because of the fervent missionary character of its preaching,[4] and in part because of the storage of gunpowder during the War of 1812.[5]
Park Street Church has a strong tradition of missions, evangelical doctrine, and application of Scripture to social issues as well as a notable list of Firsts. Edward Dorr Griffin (1770–1837) served as the first pastor of the Park Street Church and preached a famous series of Sunday evening sermons attacking the New Divinity.[6] In 1816 Park Street Church joined with Old South Church to form the City Mission Society, a social service society to serve Boston's urban poor.
In 1826 Edward Beecher, the brother of Harriet Beecher Stowe and son of Lyman Beecher, a notable abolitionist, became pastor of the church. On July 4, 1829, William Lloyd Garrison delivered his Address to the Colonization Society at Park Street, making his first major public statement against slavery. From 1829–1831 Lowell Mason, a notable Christian composer, served as choirmaster and organist. The church hosted the debut of My Country, 'Tis of Thee, also known as America, by Samuel Francis Smith on July 4, 1831.[7] Park Street also played a role in founding the First "Homeland" or American Mission to the then Sandwich Islands (now Hawaii), where that church still stands; the Handel and Haydn Society started there. Benjamin E. Bates, an industrialist who founded Bates College in Maine in 1855, was a Sunday school teacher and active attendant of Park Street in the mid-19th century. In 1857–58 evangelist, Charles Finney led a revival at Park Street which led the pastor, Andrew Leete Stone, to experience a spiritual awakening.
Gleason Archer, a prominent inerrantist theologian was the assistant pastor of Park Street from 1945 to 1948, and his father, Suffolk University founder Gleason Archer, Sr., served as president of the Park Street Men's Club in the 1920s. In 1949 Billy Graham's first transcontinental mid-century crusade began at Park Street. Harold J. Ockenga, notable theologian and co-architect of the (Neo-)Evangelical movement was the senior pastor from 1936 to 1969, and during this time co-founded Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary with Billy Graham, co-founded Fuller Theological Seminary, the National Association of Evangelicals, War Relief (which later became World Relief), and the Christian publication Christianity Today.
In 1974, the church built a Church Ministries Building at 1 Park Street beside the main edifice. Designed in a modernist architectural style by Stahl/Bennett Associates with a concrete structure, window-walls and purplish brick facing, the building is described by the Boston Preservation Alliance as follows: "The Church Ministries Building Addition to Park Street Church breaks dramatically with its surroundings in style, while relating coherently to it in materials. The building rises with large panes of glass stretching across its narrow facade and handsome red brick covering the rest of the building. The ground floor is glass and looks out to the Granary Burial Ground beyond the building to the rear.".[8]
In the 1990s, the church purchased the 2 and 3 Park Street buildings from Houghton-Mifflin.[9]
Today

The church still holds to its Statement of Faith adopted by the church in 1877 and readopted in 2003.[10] After 200 years, the church is still engaged in current social issues. For example, Park Street Church helped launch a private high school in Hyde Park, Boston Trinity Academy, in 2002, to help address the educational needs of inner-city Boston (more than 70% of its students are on scholarship and more than 50% are minorities); it hosts many English as a Second Language classes during the week; it has and supports ministries for the homeless, such as Boston Rescue Mission and Park Street's Starlight Ministry and Thursday Evening Outreach; it partners with crisis pregnancy centers Daybreak Pregnancy Resource Center and A Woman's Concern; it provides English classes for international students and immigrants. There are many affinity groups including ministries for young adults, college students, international students and scholars, children and teens, as well as introductory classes on Christianity and various adult education classes. There is also a ministry called Alive in Christ, an affiliate of Hope for Wholeness.
Park Street is an international congregation, with members from more than 60 countries. The church attracts many regular worshippers from among the undergraduates, graduate students, and faculty at Boston-area universities. Park Street believes strongly in education integrated with faith, so it is associated with Park Street Kids, Park Street School, and Boston Trinity Academy, as well as partnering with Campus Crusade for Christ and InterVarsity Christian Fellowship for undergraduate and graduate ministries, and a long-time partnership with Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary. Park Street recently sponsored a $200,000 contest for social change.[11]
Boston Mayor Menino[12] announced February 27, 2009 as Park Street Day in honor of its bicentennial.
Senior ministers (1811–present)
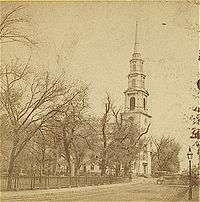
- Edward D. Griffin 1811–1815
- Sereno E. Dwight 1817–1826
- Edward Beecher 1826–1830
- Joel H. Linsley 1832–1835
- Silas Aiken 1837–1848
- Andrew Leete Stone 1849–1866[13]
- William H.H. Murray 1868–1874
- John L. Withrow 1876–1887; 1898–1907
- David Gregg 1887–1890
- Isaac J. Lansing 1893–1897
- Arcturus Z. Conrad 1905–1937
- Harold J. Ockenga 1936–1969
- Paul E. Toms 1969–1989
- David C. Fisher 1989–1995
- Pablo Polischuk (Interim) 1995–1997
- Gordon P. Hugenberger 1997–present
References
- ↑ http://hirr.hartsem.edu/cgi-bin/mega/db.pl?db=default&uid=default&view_records=1&ID=*&sb=1
- ↑ "Boston, Massachusetts. Park Street Church. Records, 1804–1976.". Congregational Library. 2008. Retrieved 2012-12-30.
- ↑ The preservation of Park Street Church, p. 12
- ↑ Roff, Sandra. "The Beecher Tradition: Edward Beecher." http://newman.baruch.cuny.edu/digital/2001/beecher/edward.htm
- ↑ "Park Street Church: Our Beginnings" http://www.parkstreet.org/our_beginnings
- ↑ Old, Hughes Oliphant. The Reading and Preaching of the Scriptures in the Worship of the Christian Church: Volume 6, The Modern Age. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 2007: 164.
- ↑ Howe, Daniel Walker, What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815–1848. ISBN 978-0-19-507894-7, p. 641.
- ↑ "Park Street Church Ministries Building Addition," Downtown Boston's Modern Buildings, google.com/maps
- ↑ The Boston Globe, December 1, 1992. Jerry Ackerman. "Park St. Church eyes 2 buildings"
- ↑ Statement of Faith
- ↑ "Park Street Church". "Social Change Competition". "Park Street Church". Retrieved 2010-03-11.
- ↑ "Park Street Church Celebrates Its Bicentennial". 2009-03-01. Retrieved 2009-04-20.
- ↑ "Boston Pulpit". Gleasons Pictorial. Boston, Mass. 5. 1853.
Further reading
- The semi-centennial celebration of the Park Street Church and Society: held on the Lords̓ Day, February 27, 1859 : with the festival on the following day. H. Hoyt, 1861
- Committee for the Preservation of Park Street Church, Boston. The preservation of Park Street Church, Boston. Ellis, 1903.
- Arcturus Z. Conrad. Commemorative exercises at the one hundredth anniversary of the organization of Park Street Church, February 26–March 3, 1909. Published by the Park Street Centennial Committee, 1909.
- Rosell, Garth M. Boston's Historic Park Street Church, commissioned by Park Street Church for the bicentennial. Kregel Publications, 2009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Park Street Church. |
Images
 Edward Griffin, minister 1811–1815
Edward Griffin, minister 1811–1815 Overview of Common, with Park St. Church (left), across from the Masonic Temple on Tremont St., 1850
Overview of Common, with Park St. Church (left), across from the Masonic Temple on Tremont St., 1850 19th century
19th century Park St. Church, 19th century
Park St. Church, 19th century Hamilton Place, with Park St. Church in distance, c. 1885
Hamilton Place, with Park St. Church in distance, c. 1885 c. 1890
c. 1890 Subway construction, 1896
Subway construction, 1896 Arturus Conrad, minister 1903–1937
Arturus Conrad, minister 1903–1937 Deacons, 1909
Deacons, 1909 Tremont St. and Park St. Church, 1915
Tremont St. and Park St. Church, 1915 Park Street Church lot at Mount Auburn Cemetery, 2008 photo
Park Street Church lot at Mount Auburn Cemetery, 2008 photo
| Preceded by Massachusetts State House |
Locations along Boston's Freedom Trail Park Street Church |
Succeeded by Granary Burying Ground |
| Records | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Old North Church |
Tallest Building in Boston 1810–1867 66 m |
Succeeded by Church of the Covenant |
| Preceded by Christ Church (Philadelphia) |
Tallest building in the United States 1810–1846 |
Succeeded by Trinity Church, Manhattan |
| Tallest building in the United States outside of New York City 1810–1856 |
Succeeded by Tenth Presbyterian Church | |
Coordinates: 42°21′25″N 71°03′44″W / 42.356911°N 71.062151°W