Parvalbumin
| parvalbumin | |
|---|---|
 PARVALBUMIN [1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | PVALB |
| Entrez | 5816 |
| HUGO | 9704 |
| OMIM | 168890 |
| RefSeq | NM_002854 |
| UniProt | P20472 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 22 q12-q13.1 |

Parvalbumin is a calcium-binding albumin protein with low molecular weight (typically 9-11 kDa).
It has three EF hand motifs and is structurally related to calmodulin and troponin C. Parvalbumin is localised in fast-contracting muscles, where its levels are highest, as well as in the brain and some endocrine tissues.
Parvalbumin is a small, stable protein containing EF-hand type calcium binding sites. It is involved in calcium signaling. Typically, this protein is broken into three domains, domains AB, CD and EF, each individually containing a helix-loop-helix motif.[3] The AB domain houses a two amino-acid deletion in the loop region, whereas domains CD and EF contain the N-terminal and C-terminal, respectively.[3]
Calcium binding proteins like parvalbumin play a role in many physiological processes, namely cell-cycle regulation, second messenger production, muscle contraction, organization of microtubules and phototransduction.[1] Alterations in the function of parvalbumin-expressing neurons have been implicated in various areas of clinical interest such as Alzheimer's disease,[4] age-related cognitive defects and some forms of cancer.[3]
Location and function
 Pvalb is expressed in the reticular nucleus of the thalamus in the postnatal day 56 mouse. Allen Brain Atlases |
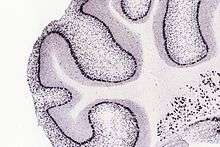 In the cerebellum of adult mice Pvalb is expressed in Purkinje cells and molecular layer interneurons. Allen Brain Atlases |
Parvalbumin (PV) is present in GABAergic interneurons in the nervous system, especially the reticular thalamus,[5] and expressed predominantly by chandelier and basket cells in the cortex. In the cerebellum, PV is expressed in Purkinje cells and molecular layer interneurons.[6] In the hippocampus, PV+ interneurons are subdivided into basket, axo-axonic, bistratified, and oriens-lacunosum moleculare (O-LM) cells, each subtype targeting distinct domains of pyramidal cells.[7]
PV interneurons' connections are mostly perisomatic (around the cell body of neurons). Most of the PV interneurons are fast-spiking. They are also thought to give rise to gamma waves recorded in EEG.
PV-expressing interneurons represent approximately 25% of GABAergic cells in the primate DLPFC.[8][9] Other calcium-binding protein markers are calretinin (most abundant subtype in DLPFC, about 50%) and calbindin. Interneurons are also divided into subgroups by the expression of neuropeptides such as somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, cholecystokinin.
Role in pathology
Decreased PV and GAD67 expression was found in PV+ GABAergic interneurons in schizophrenia.[10][11] PV has been identified as an allergen causing fish allergy.[12]
References
- 1 2 Cates MS, Berry MB, Ho EL, Li Q, Potter JD, Phillips GN (October 1999). "Metal-ion affinity and specificity in EF-hand proteins: coordination geometry and domain plasticity in parvalbumin". Structure. 7 (10): 1269–78. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)80060-X. PMID 10545326.
- ↑ Smargiassi, M. T.; Daghfous, G.; Leroy, B.; Legreneur, P.; Toubeau, G.; Bels, V.; Wattiez, R. (2012). Permyakov, Eugene A, ed. "Chemical Basis of Prey Recognition in Thamnophiine Snakes: The Unexpected New Roles of Parvalbumins". PLoS ONE. 7 (6): e39560. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039560. PMC 3384659
 . PMID 22761824.
. PMID 22761824. - 1 2 3 Cates MS, Teodoro ML, Phillips GN (March 2002). "Molecular mechanisms of calcium and magnesium binding to parvalbumin". Biophys. J. 82 (3): 1133–46. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75472-6. PMC 1301919
 . PMID 11867433.
. PMID 11867433. - ↑ Verret L, Mann EO, Hang GB, Barth AM, Cobos I, Ho K, Devidze N, Masliah E, Kreitzer AC, Mody I, Mucke L, Palop JJ (2012). "Inhibitory interneuron deficit links altered network activity and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer model". Cell. 149 (3): 708–21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.046. PMC 3375906
 . PMID 22541439.
. PMID 22541439. - ↑ Cowan, Ronald L.; Wilson, Charles J.; Emson, Piers C.; Heizmann, Claus W. (8 December 1990). "Parvalbumin-containing gabaergic interneurons in the rat neostriatum". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 302 (2): 197–205. doi:10.1002/cne.903020202.
- ↑ Schwaller B, Meyer M, Schiffmann S (2002). "'New' functions for 'old' proteins: the role of the calcium-binding proteins calbindin D-28k, calretinin and parvalbumin, in cerebellar physiology. Studies with knockout mice". Cerebellum. 1 (4): 241–58. doi:10.1080/147342202320883551. PMID 12879963.
- ↑ Klausberger T, Marton LF, O'Neill J, Huck JH, Dalezios Y, Fuentealba P, Suen WY, Papp E, Kaneko T, Watanabe M, Csicsvari J, Somogyi P (2005). "Complementary roles of cholecystokinin- and parvalbumin-expressing GABAergic neurons in hippocampal network oscillations". J. Neurosci. 25 (42): 9782–93. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3269-05.2005. PMID 16237182.free full text
- ↑ Condé F, Lund JS, Jacobowitz DM, Baimbridge KG, Lewis DA (1994). "Local circuit neurons immunoreactive for calretinin, calbindin D-28k or parvalbumin in monkey prefrontal cortex: distribution and morphology". J. Comp. Neurol. 341 (1): 95–116. doi:10.1002/cne.903410109. PMID 8006226.
- ↑ Gabbott PL, Bacon SJ (1996). "Local circuit neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (areas 24a,b,c, 25 and 32) in the monkey: II. Quantitative areal and laminar distributions". J. Comp. Neurol. 364 (4): 609–36. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960122)364:4<609::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID 8821450.
- ↑ Hashimoto T, Volk DW, Eggan SM, Mirnics K, Pierri JN, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2003). "Gene expression deficits in a subclass of GABA neurons in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia". J. Neurosci. 23 (15): 6315–26. PMID 12867516.
- ↑ Nakazawa, K; Zsiros, V; Jiang, Z; Nakao, K; Kolata, S; Zhang, S; Belforte, JE (2011). "GABAergic interneuron origin of schizophrenia pathophysiology.". Neuropharmacology. 62 (3): 1574–83. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.022. PMC 3090452
 . PMID 21277876.
. PMID 21277876. - ↑ Swoboda I, Bugajska-Schretter A, Verdino P, Keller W, Sperr WR, Valent P, Valenta R, Spitzauer S (2002). "Recombinant carp parvalbumin, the major cross-reactive fish allergen: a tool for diagnosis and therapy of fish allergy". J. Immunol. 168 (9): 4576–84. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.168.9.4576. PMID 11971005.
External links
- Parvalbumins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Baig, I.; Bertini, I.; Del Bianco, C.; Gupta, Y. K.; Lee, Y. M.; Luchinat, C.; Quattrone, A. (2004). "Paramagnetism-Based Refinement Strategy for the Solution Structure of Human α-Parvalbumin†". Biochemistry. 43 (18): 5562–5573. doi:10.1021/bi035879k. PMID 15122922.