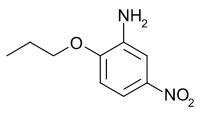
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
| 553-79-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL322314 |
| ChemSpider | 10647 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.228 |
| PubChem | 11118 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 196.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 48 °C (118 °F; 321 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline, also known as P-4000 and Ultrasüss, is one of the strongest sweet-tasting substances known, about 4,000 times the intensity of sucrose (hence its alternate name, P-4000). It is an orange solid that is only slightly soluble in water. It is stable in boiling water and dilute acids. 5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline was once used as an artificial sweetener but has been banned in the United States because of its possible toxicity.
In the US, food containing any added or detectable level of 5-nitro-2-propoxyaniline is deemed to be adulterated in violation of the act based upon an order published in the Federal Register of January 19, 1950 (15 FR 321).[2]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 6727.
- ↑ FDA Code of Regulations
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/12/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.