Carding (fraud)

Carding is a term describing the trafficking of credit card, bank account and other personal information online as well as related fraud services.[1] Activities also encompass procurement of details,[2] and money laundering techniques.[3] Modern carding sites have been described as full-service commercial entities.[4]
Acquisition
There are a great many of methods to acquire credit card and associated financial and personal data. The earliest known carding methods have also included 'trashing' for financial data, raiding mail boxes and working with insiders.[5][6] Some bank card numbers can be semi-automatically generated based on known sequences via a 'BIN attack'.[7] Carders might attempt a 'distributed guessing attack' to discover valid numbers by submitting numbers across a high number of ecommence sites simultaneously.[8]
Today, various methodologies include skimmers at ATMs, hacking an ecommerce or payment processing site or even intercepting card data within a point of sale network.[9] Randomly calling hotel room phones asking guests to 'confirm' credit card details is example of a social engineering attack vector.[10]
Resale
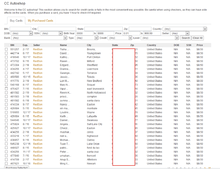
Stolen data may be bundled as a 'Base' or 'First-hand base' if the seller participated in the theft themselves. Resellers may buy 'packs' of dumps from multiple sources. Ultimately, the data may be sold on darknet markets and other carding sites and forum 'dump shops'[11] specialising in these types of illegal goods.[12][13]
On the more sophisticated of such sites, individual 'dumps' may be purchased by zip code and country so as to avoid alerting banks about their misuse.[14] Automatic checker services perform validation en masse in order to quickly check if a card has yet to be blocked. Sellers will advertise their dump's 'valid rate', based on estimates or checker data. Cards with a greater than 90% valid rate command higher prices. 'Cobs' or changes of billing are highly valued, where sufficient information is captured to allow redirection of the registered card's billing and shipping addresses to one under the carder's control.[15]
Full identity information may be sold as 'Fullz' inclusive of social security number, data of birth and address to perform more lucrative identity theft.[16]
Fraudulent vendors are referred to as 'rippers', vendors who take buyer's money then never deliver. This is increasingly mitigated via forum and store based feedback systems as well as through strict site invitation and referral policies.[17]
Whist some carding forums will exist only on the dark web, today most exist on the internet, and many will use the Cloudflare network protection service.[18][19][20]
Estimated per card prices, in US$, for stolen payment card data 2015[21]
| Payment Card Number With CVV2 | United States | United Kingdom | Canada | Australia | European Union |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software-generated | $5–8 | $20–$25 | $20–$25 | $21–$25 | $25–$30 |
| With Bank ID Number | $15 | $25 | $25 | $25 | $30 |
| With Date of Birth | $15 | $30 | $30 | $30 | $35 |
| With Fullzinfo | $30 | $35 | $40 | $40 | $45 |
Money laundering
The 2004 investigation into the ShadowCrew forum also led to investigations of the online payment service E-gold that had been launched in 1996, one of the preferred money transfer systems of carders at the time. In December 2005 its owner Douglas Jackson's house and businesses were raided as a part of 'Operation Goldwire'. Jackson discovered that the service had become a bank and transfer system to the criminal underworld. Pressured to disclose ongoing records disclosed to law enforcement, many arrests were made through to 2007. However, in April 2007 Jackson himself was indicted for money laundering, conspiracy and operating an unlicensed money transmitting business. This led to the service freezing the assets of users in 'high risk' countries and coming under more traditional financial regulation.[22]
Since 2006, Liberty Reserve had become a popular service for cybercriminals. When it was seized in May 2013 by the US government, this caused a major disruption to the cybercrime ecosystem.[23]
Today, some carders prefer to make payment between themselves with bitcoin,[24][25] as well as traditional wire services such as Western Union, MoneyGram or the Russian WebMoney service.[26][27]
Funds from stolen cards themselves may be cashed out via buying pre-paid cards, gift cards or through reshipping goods though mules then reselling through online marketplaces like eBay.[28][29] Increased law enforcement scrutiny over reshipping services has led to the rise dedicated criminal operations for reshipping stolen goods.[30][31]
Related services
Many forums also provide related computer crime services such as phishing kits, malware and spam lists.[32] They may also act as a distribution point for the latest fraud tutorials either for free or commercially.[33] ICQ was at one point the instant messenger of choice due to its anonymity as well as MSN clients modified to use PGP.[34] Carding related sites may be hosted on botnet based fast flux web hosting for resilience against law enforcement action.[35]
Other account types like PayPal,[36] Uber,[37] Netflix and loyalty card points may be sold alongside card details.[38] Logins to many sites may also be sold such a site backdoor access apparently for major institutions such as banks, universities and even industrial control systems.[21]
Tax refund fraud is an increasingly popular method of using identify theft to acquire prepaid cards ready for immediate cash out.[3][39] Popular coupons may be counterfeited and sold also.[40]
Personal information and even medical records are sometimes available.[21] Theft and gift card fraud may operated entirely independently of online carding operations.[41]
History
1980s–1999
Since the 1980s[42] in the days of the dial-up BBSes, the term carding has been used to describe the practices surrounding credit card fraud. Methods such as 'trashing', raiding mail boxes and working with insiders at stores were cited as effective ways of acquiring card details. Use of drops at places like abandoned houses and apartments or with persuadable neighbors near such a location were suggested. Social engineering of mail order sales representatives are suggested in order to provide passable information for card not present transactions.[6] Characters such as 'The Video Vindicator' would write extensive guides on 'Carding Across America', burglary, fax fraud, supporting phreaking,[43] and advanced techniques for maximizing profits.[44] During the 1980s the majority of hacker arrests were attributable to carding-related activities due to the relative maturity of financial laws compared to emerging computer regulations.[42]
Started in 1989, by 1990 Operation Sundevil was launched by the United States Secret Service to crack down on use of BBS groups involved in credit card fraud and other illegal computer activities, the most highly publicised action by the US federal government against hackers at the time.[45] The severity of the crack down was so much that the Electronic Freedom Foundation was formed in response to the violation of civil liberties.[46]
In the mid-1990s with the rise of AOL dial-up accounts, the AOHell software became a popular tool for phishing and stealing information such as credit card details from new Internet users.[47] Such abuse was exacerbated because prior to 1995 AOL did not validate subscription credit card numbers on account creation.[48] Abuse was so common AOL added "no one working at AOL will ask for your password or billing information" to all instant messenger communications. Only by 1997 when warez and phishing were pushed off the service did these types of attacks begin to decline.[48]
December 1999 featured an unusual case of extortion when Maxim, a Russian 19-year-old, stole the 25,000 users' card details from CD Universe and demanded $100,000 for its destruction. When the ransom was not paid, the information was leaked on the Internet.[49]
One of the first books written about carding, 100% Internet Credit Card Fraud Protected, featured content produced by 'Hawk' of carding group 'Universal Carders'. It described the spring 1999 hack and credit card theft on CyberCash, the stratification of carder proficiencies (script kiddie through to professionals) common purchases for each type and basic phishing schemes to acquire credit card data.[50]
By 1999, United States offline and online credit card fraud annual losses were estimated at between $500,000 and $2 million.[50]
2000–2006
From the early 2000s, sites like 'The Counterfeit Library', also functioning as a diploma mill, grew to prominence, with many of its members going on to join larger cybercrime websites in later years until it closure around September 2004.[34]
In 2001 Russian speaking hackers founded CarderPlanet in Odessa which would go on to be one of the most notorious forums of its kind.[51]
In the summer of 2003, separate US secret service and FBI investigations led to the arrest the top administrator Albert Gonzalez of the large ShadowCrew carding forums, turned informant as a part of 'Operation Firewall'. By March 2004, the administrator of 'CarderPlanet' disappeared with Gonzalez taking over. In October 2004 dozens of ShadowCrew members were busted across the US and Canada. Carder's speculate that one of the USSS infiltrators might have been detected by a fellow site member causing the operation to be expedited.[34] Ultimately, the closure of ShadowCrew and CarderPlanet did not reduce the degree of fraud and led to the proliferation of smaller sites.[52][53]
ShadowCrew admin Brett Shannon Johnson managed to avoid being arrested at this time, but was picked up in 2005 on separate charges then turned informant. Continuing to commit tax fraud as an informant, 'Operation Anglerphish' embedded him as admins on both ScandinavianCarding and CardersMarket. When his continued carding activities were exposed as a part of a separate investigation in 2006, he briefly went on the run before being caught for good in August of that year.[54]
In June 2005 the credit card processing company CardSystems was hacked in what was at the time the largest personal information breach in history with many of the stolen information making its way to carding sites.[15] Later in 2007 the TJX Companies breach perpetuated by Albert Gonzalez (who was still an informant at the time)[55] would only come to the public's attention after stolen cards detected being misused to buy large amounts of gift cards.[56] Gonzalez's 2008, intrusion into Heartland Payment Systems to steal card data was characterized as the largest ever criminal breach of card data.[57]
Also in June 2005, UK-based carders were found to be collaborating with Russian mafia and arrested as a result of a National Hi-Tech Crime Unit investigation, looking into Eastern European crime syndicates.[34][58] Some time in 2005, J. Keith Mularski from the National Cyber-Forensics & Training Alliance headed up a sting into popular English language site DarkMarket.ws. One of the few survivors of 'Operation Firewall', Mularski was able to infiltrate the site via taking over the handle 'Master Splynter', an Eastern European spammer named Pavel Kaminski. In late 2006 the site was hacked by Max Butler, who detected user 'Master Splynter' had logged in from the NCFTA's offices, but the warning was dismissed as inter-forum rivalry. In 2007 details of the operation was revealed to German national police, that the NCFTA had successfully penetrated the forum's inner 'family'. By October 4, 2007 Mularski announced he was shutting the site due to unwanted attention from a fellow administrator, ironically framed as 'too much attention' from law enforcement.[59] For several years following site closure multiple arrests were made internationally.[60]
From 2004 through to 2006, CardersMarket assimilated various rival forums through marketing, hacking databases.[61] Arrested in 2007, in 2010 the site's owner Max Butler was sentenced to 13 years in prison.[62]
2007–present
In more recent years, Russian language forums have gained dominance over English language ones, with the former considerably more adept at identifying security researchers and counterintelligence activities[63] and strict invitation systems.[2] Russia's lack of extradition treaty with the United States has made the country somewhat of a safe haven of cyber criminals, with the Russian foreign ministry going as far as to recommend citizens not travel abroad to countries with such treaties.[64] Investigative journalist Brian Krebs has extensively reported on Russian carders as an ongoing game of cat and mouse.[65]
Since 2007 to present, Operation Open Market, an operation run by the HIS and the USSS has targeted the primarily Russian language Carder.su organisation, believed to be operating out of Las Vegas.[66] In 2011, alleged site owner Roman Seleznev was apprehended in the Maldives by US law enforcement[67][68] and in 2012, identity thief David Ray Camez was arrested and charged in an unprecedented use of RICO legislation.[69][70]
In 2011, former Bulgarian ShadowCrew member Aleksi Kolarov (also known as 'APK') was finally arrested and held Paraguay before being extradited to the United States in 2013 to face charges.[71]
In June 2012, the FBI seized carding and hacking forums UGNazi.com and Carders.org in a sting as a part of a 2-year investigation dubbed Operation Card Shop[1] after setting up a honeypot forum at carderprofit.cc.[72]
In August 2013, hacker and carding forum HackBB was taken down as part of the raid on Freedom Hosting.[73]
In January 2014, fakeplastic.net was closed following an investigation by the US postal service and FBI, after collating previously seized information from TorMail, ShadowCrew and Liberty Reserve. This led to multiple arrests and prosecutions as well as the site's closure.[74][75][76]
A 2014 report from Group-IB suggested that Russian cybercriminals could be making as much as $680 million a year based on their market research.[77]
In December 2014 the Tor based Tor Carding Forum closed following a site hack, with its administrator 'Verto' directing users to migrate to the Evolution darknet market's[78] forums[79] which would go on to be the largest darknet market exit scam ever seen.[80][81]
'Alpha02', who was notorious for his carding guides, went on to found the AlphaBay darknet market,[82] the first to ever deal in stolen Uber accounts.[83] The site is working on rebuilding the damage to the reputation of markets founded by carders precipitated by the Evolution scam.[84] Meanwhile, most Russian carders selling details do not trust the darknet markets due to the high level of law enforcement attention, however buyers are more open.[85]
See also
References
- 1 2 J. Schwartz, Mathew (27 June 2012). "FBI Busts Massive International Carding Ring". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- 1 2 DeepDotWeb (18 March 2015). "Evolution Market Background: Carding Forums, Ponzi Schemes & LE". Retrieved 27 August 2015.
- 1 2 Krebs, Brian (4 August 2014). "'White Label' Money Laundering Services". Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ van Hardeveld, Gert Jan (26 October 2015). "Stolen TalkTalk customer details: time bombs that may tick a while before being triggered". Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (19 December 2013). "Target Admits Massive Credit Card Breach; 40 Million Affected". Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- 1 2 Wizzard, Black. "The Art of Carding". textfiles.com. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ "Credit Card Bin Attack Fraud". Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- ↑ Reporters, Telegraph (2 December 2016). "Hacked in just six seconds: How criminals only need moments to guess card number and security code". Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ Ilascu, Ionut (11 August 2014). "Russian Point-of-Sale Hacker Pleads Not Guilty in US Court". Retrieved 14 September 2015.
- ↑ Weisbaum, Herb. "Summer travel alert: Scammer target hotel guests". Retrieved 20 September 2015.
- ↑ Shah, Khushbu (9 April 2015). "Meet the Man Crusading Against Restaurant Credit Card Hackers". Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (4 June 2014). "Peek Inside a Professional Carding Shop". Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ DeepDotWeb (20 May 2015). "AlphaBay Market Launched a Fully-Automated Stolen Credit Card Shop". Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ↑ Montemayor, Stephen (2 August 2015). "Out-of-state criminals bring cloned credit card schemes to Twin Cities". Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- 1 2 Zeller JR, Tom (21 June 2005). "Black Market in Stolen Credit Card Data Thrives on Internet". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ Ducklin, Paul (5 November 2012). "Credit card fraud - want to join the party?". Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ Vijayan, Jaikumar (6 May 2015). "The identity underworld: How criminals sell your data on the Dark Web". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "Carders love CloudFlare". Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ Yadron, Danny (29 September 2014). "CloudFlare Pushes More Encrypted Web". Retrieved 10 August 2015.
- ↑ Kovacs, Eduard (17 March 2014). "Underground Payment Card Store Rescator Hacked and Defaced". Retrieved 10 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 "The Hidden Data Economy" (PDF). Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (9 June 2009). "Bullion and Bandits: The Improbable Rise and Fall of E-Gold". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ Halpern, Jake (May 2015). "Bank of the Underworld". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Kiell (11 December 2014). "A Carder's First Experience". Retrieved 18 August 2015.
- ↑ Kujawa, Adam (24 January 2014). "FBI Takes Down Poorly Secured Carders". Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ PULKKINEN, LEVI (16 January 2015). "Piles of cash, bunches of bling and a public defender?". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (14 July 2014). "Feds Charge Carding Kingpin in Retail Hacks". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (3 November 2015). "How Carders Can Use eBay as a Virtual ATM". Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- ↑ Westin, Ken (21 December 2013). "Stolen Target Credit Cards and the Black Market: How the Digital Underground Works". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (12 October 2011). "Shady Reshipping Centers Exposed, Part I". Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (4 August 2014). "'White Label' Money Laundering Services". Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ Leinwand Leger, Donna (19 October 2014). "How stolen credit cards are fenced on the Dark Web". Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ Jackson Higgins, Kelly (15 December 2014). "Price Tag Rises For Stolen Identities Sold In The Underground". Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Allen, Hoffmann (5 January 2015). "Before DarkNetMarkets Were Mainstream". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Peters, Sara (1 December 2016). "Avalanche Botnet Comes Tumbling Down In Largest-Ever Sinkholing Operation". Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (October 5, 2011). "How Much is That Phished PayPal Account?". Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ↑ Hackett, Robert (30 March 2015). "Stolen Uber user logins are for sale on the dark web: only $1 each". Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ↑ Paganini, Pierluigi (15 May 2015). "Hacking communities in the Deep Web". Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (15 August 2015). "IRS: 330K Taxpayers Hit by 'Get Transcript' Scam". Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ↑ Cox, Joseph (14 January 2016). "Dark Web Vendor Sentenced for Dealing Counterfeit Coupons". Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "'Operation Plastic Paradise' nets 18 arrests in $2 million gift card scheme". WFTV. 14 December 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- 1 2 "Credit Cards for fun and profit!". textfiles.com.
- ↑ "Hacking Calling Cards".
- ↑ "Textfile Writing Groups: The Video Vindicator". textfiles.com. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ Sterling, Bruce (1994). "Part Three: Law and Order". The Hacker Crackdown: Law And Disorder On The Electronic Frontier. New York: Bantam Books. ISBN 0-553-56370-X. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- ↑ Charles, Dan (1990-07-21). "Crackdown on hackers 'may violate civil rights'". New Scientist. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- ↑ LANGBERG, MIKE (8 September 1995). "AOL ACTS TO THWART HACKERS". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Phishing: General Information". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ MARKOFF, JOHN (10 January 2000). "Thief Reveals Credit Card Data When Web Extortion Plot Fails". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- 1 2 Vesper (2000). 100% Internet Credit Card Fraud Protected. ISBN 1552125343. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Farivar, Cyrus (12 December 2013). "Ukrainian fraudster and CarderPlanet "Don" finally sentenced to 18 years". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (1 February 2007). "Crime Boards Come Crashing Down". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (1 July 2013). "9 Years After Shadowcrew, Feds Get Their Hands on Fugitive Cybercrook". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (6 June 2007). "Secret Service Operative Moonlights as Identity Thief". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Hacker Charged With Heartland, Hannaford Breaches - wired.com - August 17, 2009
- ↑ Hines, Matt (21 March 2007). "Stolen TJX data used in Florida crime spree".
- ↑ King, Rachael (6 July 2009). "Lessons from the Data Breach at Heartland". Retrieved 8 June 2014.
- ↑ "Phishing pair jailed for ID fraud". 29 June 2005. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Poulsen, Ken (13 October 2008). "Cybercrime Supersite 'DarkMarket' Was FBI Sting, Documents Confirm". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ Davies, Caroline (14 January 2010). "Welcome to DarkMarket – global one-stop shop for cybercrime and banking fraud". Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ↑ Acohido, Byron (11 October 2006). "Cybercrime flourishes in online hacker forums". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Poulsen, Kevin (12 February 2010). "Record 13-Year Sentence for Hacker Max Vision". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Howard, Rick. Cyber Fraud: Tactics, Techniques and Procedures. p. 117. ISBN 978-1420091274.
- ↑ Poulsen, Kevin (4 September 2013). "Russia gives travel advice to its hackers: don't leave the motherland". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Clements, Sam (8 August 2013). "Cyber Criminals Hate Brian Krebs So Much They're Sending Heroin and SWAT Teams to His Home". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "Federal Authorities Arrest 19 Persons in Operation "Open Market"". 16 March 2012. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (8 July 2014). "Feds Charge Carding Kingpin in Retail Hacks". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Chiacu, Doina (8 July 2014). "Moscow accuses United States of 'kidnapping' Russian hacker". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "US cyber-thief gets 20-year jail term". 19 May 2014. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ J. Schwartz, Mathew (12 December 2013). "Cybercrime Milestone: Guilty Verdict In RICO Case". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Zetter, Kim (1 July 2013). "9 Years After Shadowcrew, Feds Get Their Hands on Fugitive Cybercrook". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (26 June 2012). "'Carderprofit' Forum Sting Nets 26 Arrests". Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ↑ Neal, Meghan (5 August 2013). "To Bust a Giant Porn Ring, Did the FBI Crack the Dark Web?". Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ Kovacs, Eduard (25 January 2014). "Operators of Credit Card Counterfeiting Service Fakeplastic.net Charged". Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ↑ "Mastermind of Online Counterfeit Card Retail Shop Pleads Guilty". FBI. 25 September 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (14 January 2015). "Feds Infiltrate, Bust Counterfeit Card Shop". Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ↑ E Dunn, John (16 October 2014). "Russian cybercriminals made $680 million from stolen credit cards". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Wired Staff (1 January 2015). "The Most Dangerous People on the Internet Right Now". Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ↑ Farivar, Cyrus (19 December 2014). "After Silk Road takedowns, Dark Web drug sites still thriving". Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ↑ Krebs, Brian (2015-03-18). "Dark Web's 'Evolution Market' Vanishes". Krebs on Security. Retrieved 2015-03-18.
- ↑ DeepDotWeb (10 May 2014). "Evolution Marketplace Staff Speak: We are growing fast!". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Cox, Joseph (23 April 2015). "The Kalashnikov Carding Club". Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "Stolen Uber Customer Accounts Are for Sale on the Dark Web for $1". Motherboard.
- ↑ G, Joshua (20 April 2015). "Interview With AlphaBay Market Admin". Retrieved 18 August 2015.
- ↑ G, Joshua (11 April 2015). "Darknetmarkets And Their Reputation in The Russian Community". Retrieved 27 August 2015.
Further reading
- Kingpin: The true story of Max Butler, the master hacker who ran a billion dollar cyber crime network[1]
- DarkMarket: How Hackers Became the New Mafia[2]
External links
- ↑ Poulsen, Kevin (2011). Kingpin: The true story of Max Butler, the master hacker who ran a billion dollar cyber crime network. ISBN 0733628389. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ Glenny, Misha (2 October 2012). DarkMarket: How Hackers Became the New Mafia. ISBN 9780307476449. Retrieved 16 August 2015.