Notholaenic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
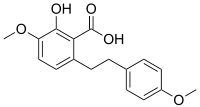
| IUPAC name
2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-6-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]benzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 72578-97-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.069.726 |
| PubChem | 3085829 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H18O5 | |
| Molar mass | 302.33 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 149 to 150 °C (300 to 302 °F; 422 to 423 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Notholaenic acid is a dihydrostilbenoid found in the farina of some ferns of the genus Notholaena.[1] It has been shown to have anti-HSV-1 (Herpes simplex virus 1) activity at high concentrations in vitro.[2] It was artificially synthesized, starting from 3-benzyloxy-5-methoxybenzyl alcohol, in 1985.[3]
References
- ↑ Wollenweber, Eckhard; Favre-Bonvin, Jean (1979). "Novel dihydrostilbene from fronds of Notholaena dealbata and Notholaena limitanea". Phytochemistry. 18 (7): 1243–1244. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(79)80153-3.
- ↑ Rinehart, Kenneth L.; Tom G. Holt, Nancy L. Fregeau, Paul A. Keifer, George Robert Wilson, Thomas J. Perun Jr., Ryuichi Sakai, Anthony G. Thompson, Justin G. Stroh, Lois S. Shield, David S. Seigler, Li H. Li, David G. Martin, Cornelis J. P. Grimmelikhuijzen, Gerd Gäde (July–Aug 1990). "Bioactive Compounds from Aquatic and Terrestrial Sources". Journal of Natural Products. 53: 771–792. doi:10.1021/np50070a001. Retrieved 29 April 2012. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ El-Feraly, Farouk S.; Cheatham, Steve F.; McChesney, James D. (1985). "Total Synthesis of Notholaenic Acid". Journal of Natural Products. 48 (2): 293–298. doi:10.1021/np50038a015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.