Flushing and North Side Railroad

The Flushing and North Side Railroad is a former railroad on Long Island built by Conrad Poppenhusen as a replacement for the former New York and Flushing Railroad. The railroad was established in 1868, was merged with the Central Railroad of Long Island in 1874 to form the Flushing, North Shore and Central Railroad, and was finally acquired by the Long Island Rail Road in 1876. Today the main line is known as the Port Washington Branch of the Long Island Rail Road.
Precedent: New York and Flushing Railroad
Before the Flushing and North Side, most of the line was originally built by the Flushing Railroad, in 1854 from Hunters Point in Long Island City to Flushing, before the LIRR opened its line to Long Island City.[1] Chartered on March 3, 1852, it was the first railroad on Long Island not to be part of the Long Island Rail Road. The company was taken over by Oliver Charlick and reorganized in 1859 as the New York and Flushing Railroad,[2] and established a subsidiary known as the "North Shore Railroad" to extend the line from Flushing to Great Neck in 1866 (see below). Originally intending to run further east to Roslyn, Oyster Bay, and even Huntington, the NY&F's plans were thwarted by the LIRR who reached those destination first, as well as poor service that the company became known for. Due to the NY&F's reputation, the residents of Flushing convinced the LIRR to incorporate the Flushing and Woodside Railroad on February 24, 1864 to build a competing branch to Flushing.[3][4]
North Shore Branch (Long Island)
Despite service complaints, New York and Flushing established a subsidiary called the North Shore Railroad of Long Island in 1866 which extended the line from Flushing to Great Neck[5] Unfortunately, the NY&F realized that they could not survive the competition, and sold their line (and their lease on the North Shore Railroad of Long Island.[6]) to the LIRR in 1867. The LIRR benefitted by preventing the South Side Railroad from using the New York and Flushing access to the LIRR's Long Island City terminal, and by keeping the North Side Railroad from extending east to Huntington in competition with the LIRR.[7] The LIRR also stopped construction on the incomplete Flushing and Woodside.[8][9]
Flushing and North Side

Flushing citizens, feeling they had been tricked into building the Flushing and Woodside in order to scare the Flushing and North Side into selling out to the LIRR, convinced wealthy residents of College Point and Whitestone, including Conrad Poppenhusen, to incorporate the Flushing and North Side Railroad in 1868. This company had the right to build a line from Long Island City to Flushing and beyond to Roslyn, with a branch from Flushing to Whitestone. The group gained control of the unfinished Flushing and Woodside Railroad, and opened its line to Flushing, paralleling the LIRR from Long Island City to Woodside, in 1868[10] and to College Point and Whitestone in 1869.[11] This new line attracted most of the traffic from the older New York and Flushing, and the LIRR wanted to get rid of its Flushing branch. In 1869, the New York State Legislature authorized the Flushing and North Side to buy the New York and Flushing east of the LIRR crossing at Winfield Junction[12] connections were built by the Flushing and North Side at Woodside/Winfield and Flushing to connect its lines. The New York and Flushing continued to own the line west of Winfield, and soon became the South Side Railroad's access to Long Island City. The segment between what was to become the former Laurel Hill Station and Winfield Station, was abandoned for passenger service in 1875, and completely abandoned in 1880. Part of the right-of-way ran through what is today the Mount Zion Jewish Cemetery in Maspeth.[13] The Flushing and Woodside was merged into the Flushing and North Side in 1871, and its line was abandoned in favor of the ex-New York and Flushing line.[9][14]
Woodside Branch
Dissatisfied with NY&F's service, Residents of Flushing and Newtown convinced the LIRR to build the Flushing and Woodside Railroad, on February 24, 1864 as a competing branch to Flushing,[15] which ran from Woodside Station toward Great Neck Junction. When the NY&F collapsed after construction of the Great Neck Extension, the LIRR acquired the railroad and left this branch unfinished. After Poppenhausen created the Flushing and North Side Railroad, he also acquired the Flushing and Woodside, but was able to complete construction of the line, which became the Woodside Branch of the Flushing and North Side. The line only contained one other station at Junction Boulevard and 35th Avenue called Grinnell Station. East of Grinnell Station and the Flushing River, there was a junction leading either toward the main line of the F&NS railroad or the Whitestone Branch.
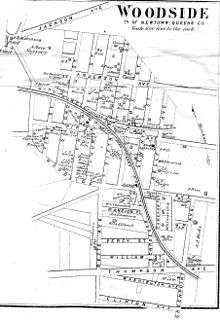
Whitestone Branch
The Whitestone Branch was originally built in 1869 by an affiliate of the F&NS called the Whitestone and Westchester Railroad. It was intended to cross the East River to Westchester County, but never had the chance to do so. The line had a spur to a freight dock on Flushing Bay which crossed the Woodside Branch and the connecting line between the Woodside and Whitestone Branches. After the Flushing Bay Freight spur, the line itself also crossed the Woodside Branch, and then merged with the Woodside-Whitestone connector before crossing the Flushing River. From there it contained four stations, one at Bridge Street, College Point, and two in Whitestone, one at 14th Avenue and the other at 155th Street, which has been called "Whitestone Landing Station," and "Beechhurst Yacht Club Station." Malba Station wasn't built until decades after the line was acquired by the LIRR.
Proposed expansion
Since both the New York and Flushing Railroad and Flushing and North Side Railroad had plans to expand service east of Great Neck, subsidiaries of the railroad were created for this purpose. In the case of the F&NS, two proposed railroads included the North Shore and Port Washington Railroad and the Roslyn and Huntington Railroad. Neither of these proposal were carried out and were eliminated during the merger with the Central Railroad of Long Island in 1874 (see below), although the LIRR did try to extend the line to Roslyn until 1882 due to the difficulty of construction around the Manhasset Valley.
Mergers
By 1874, all branches of the Flushing and North Side Railroad, including the Main Line to Great Neck were incorporated into the Flushing, North Shore and Central Railroad, which included the Central Railroad of Long Island. Two years later, it would become part of the Long Island Rail Road. Despite the failed attempt to extend the line from Great Neck to Roslyn in 1882, wealthy Port Washington residents persuaded the LIRR to bring the terminus to their hometown in 1895. This required the construction of the Manhasset Viaduct over Manhasset Bay, which was completed on June 23, 1898. The Woodside and Whitestone Branches were abandoned.
Station listing
Main Line
| Station/ location |
Station link |
Miles (kilometers) to Penn Station |
Current Connections/notes | History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woodside 58th Street (formerly Betts Avenue/Fifth Street) & 39th Avenue (formerly Riker Avenue), Woodside |
[16] | 5.1 (8.2) | Subway: (7 <7>) Bus (New York City Bus): Q18, Q32, Q53 |
Opened November 15, 1869 on north side of tracks west of 58th Street; closed 1914 and demolished 1916 (replaced with current structure during grade crossing elimination) |
| Winfield Woodside |
Opened July 1854 on southeast corner of 50th Avenue and 69th Street; moved to the junction in August 1876 to also serve the Main Line; closed 1929 | |||
| Elmhurst Elmhurst |
Opened 1855 as Newtown; name changed to Elmhurst June 1897; closed 1985 | |||
| Corona Corona |
Service began June 26, 1854; station opened April 2, 1855 on west side of National Avenue as Fashion Race Course; renamed West Flushing when 108th Street was abandoned, and Corona in June 1872; closed 1963 | |||
| West Flushing Corona |
Opened September 1854 on north side of line and east side of 108th Street; later abandoned and name assigned to later Corona station | |||
| Whitestone Junction | For the Whitestone Branch. Located east of the current Mets-Willets Point station | |||
| Great Neck Junction | For the Woodside Branch, Creedmoor Branch, and short-lived Flushing Branch. Located on the east bank of the Flushing River | |||
| Flushing Main Street Main Street and 41st Avenue, Flushing |
9.5 (15.3) | Subway: (7 <7>) Bus (New York City Bus): Q12, Q17, Q20, Q25, Q26, Q28, Q34, Q44, Q48, Q58 Bus (Nassau Inter-County Express): n20, n20L, n21 |
Service began June 26, 1854 | |
| Murray Hill 150th Street and 41st Avenue, Flushing |
10.3 (16.6) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q15 | Not built until either 1889 or 1890 by the LIRR. | |
| Broadway 162nd Street and Northern Boulevard, Flushing |
11.1 (17.9) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q12, Q13, Q28 | Service began October 27, 1866, as East Flushing station until 1872. Sometimes called Flushing - Broadway station. Elevated between 1912 and 1913. | |
| Auburndale 192nd Street and Station Road, Auburndale |
11.7 (18.8) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q12, Q13, Q28, Q76 | Not built until 1901 by the LIRR. | |
| Bayside 213th Street and 41st Avenue, Bayside |
12.6 (20.3) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q13, Q31 | ||
| Douglaston 235th Street and 41st Avenue, Douglaston |
13.9 (22.4) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q12, QM3 Bus (Nassau Inter-County Express): n20G |
Originally Little Neck Station between 1866 and June 1870. | |
| Little Neck Little Neck Parkway and 39th Road, Little Neck |
14.5 (23.3) | Bus (New York City Bus): Q12, Q36 Bus (Nassau Inter-County Express): n20G |
||
| Great Neck Middle Neck Road and Station Plaza at Great Neck Road, Great Neck Plaza |
15.7 (25.3) | Bus (Nassau Inter-County Express): n20G, n20H, n21, n25, n57, n58 | Service began on October 27, 1866, and served as the terminus of the line until 1898. | |
| All stations beyond this point were built by the Long Island Rail Road as the Port Washington Branch which was completed on June 23, 1898 | ||||
Original New York & Flushing section
| Station/ location |
Station link |
Miles (kilometers) to Penn Station |
Connections/notes | History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunter's Point Hunter's Point, Long Island City |
1854. Later became Long Island City (LIRR station) | |||
| Penny Bridge Long Island City |
Opened in 1854. Acquired by the South Side Railroad of Long Island, before becoming an LIRR station. Decommissioned in 1998. | |||
| Junction with South Side Railroad of Long Island(now LIRR Montauk Branch) at Laurel Hill. Segment abandoned in 1880. LIRR installed small station from 1890-1900. | ||||
| Maspeth Maspeth |
1855 to 1858. Revived along Montauk Branch from 1895 and 1924. | |||
| Winfield Junction Woodside |
Junction between LIRR and NY&F Main Lines. The former NY&F between Laurel Hill and Winfield was abandoned in 1880. | |||
| Continues as F&NS Main Line to Great Neck. | ||||
Woodside Branch
| Station/ location |
Station link |
Miles (kilometers) to Penn Station |
Connections/notes | History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woodside 61st Street and Roosevelt Avenue, Woodside |
5.1 (8.2) | Subway: (7 <7>) Bus (New York City Bus): Q18, Q32, Q53 |
Western terminus of Woodside Branch | |
| Grinnell | 1874-1877. Only station on the entire Woodside Branch. Was located at Junction Boulevard and 35th Avenue. | |||
| Junction with Central Railroad of Long Island. | ||||
| Junction with Flushing Bay Freight Spur. | ||||
| Eastern terminus at Junction with Whitestone Branch. | ||||
| The entire line was abandoned | ||||
Whitestone Branch
| Station/ location |
Station link |
Miles (kilometers) to Penn Station |
Connections/notes | History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whitestone Junction | Begin at Port Washington Branch near Corona Yard east of the current Mets-Willets Point station. | |||
| Junction with Flushing Bay Freight Spur. | ||||
| Connection to Woodside Branch. | ||||
| Flushing–Bridge Street | Named in order to distignuish itself from Flushing-Main Street Station. 1870-1932. | |||
| College Point | 1869-1932. | |||
| Malba | Only station on the line to have been built by the Long Island Railroad; 1909-1932. | |||
| Whitestone–14th Avenue | Whitestone Line (NY&NST Trolley) | 1869-1932. | ||
| Whitestone Landing (at 155th Street). | Also known as "Beechhurst Yacht Club Station". 1886-1932. | |||
| The entire line was abandoned on February 15, 1932. | ||||
References
- ↑ "PRR Chronology, 1854" (PDF). (95.9 KiB), June 2004 Edition
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1859 (March 2005 Edition)
- ↑ "PRR Chronology, 1864" (PDF). (109 KiB), June 2004 Edition
- ↑ Flushing and Woodside Railroad (Arrt's Arrchives)
- ↑ "PRR Chronology, 1866" (PDF). (89.2 KiB), June 2004 Edition
- ↑ "PRR Chronology, 1866" (PDF). (89.2 KiB), June 2004 Edition
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1867 (June 2004 edition)
- ↑ Ron Ziel and George H. Foster, Steel Rails to the Sunrise, ©1965
- 1 2 Peter Ross, A History of Long Island From its Earliest Settlement to the Present Time, History of the Long Island Railroad, 1903
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1868 (June 2004 Edition)
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1867 (June 2004 edition)
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1869 (June 2004 Edition)
- ↑ 1924 Long Island Railroad Corporate Blueprint (Arrt's Arrchives)
- ↑ PRR Chronology 1871 (January 2005 Edition)
- ↑ "PRR Chronology, 1864" (PDF). (109 KiB), June 2004 Edition
- ↑ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AWoodside-1908-map.jpg
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
External links
- MTA Long Island Rail Road
- Bob Andersen's Unofficial LIRR History Website:
- NYCSubway.org: Port Washington Branch
- Forgotten New York:
- Whitestone Branch Part One, Part Two, Part Three, Part Four, and Part Five (Arrt's Arrchives)
- The Third Rail; LIRR History Part 1(Page 10)
