North–South divide (England)

In England, the term North–South divide refers to the cultural and economic differences between
Southern England (the South-East, Greater London, the South-West and parts of the East) and
Northern England (the North-East, Yorkshire and the Humber) and North West England including Merseyside, Greater Manchester.
The status of the Midlands is often disputed; geographically, most areas of the Midlands are more Southern than Northern. This ambiguity also applies to parts of East Anglia. A grouping of Central England based on UK EU parliamentary constituency boundaries combines the Midlands and East Anglia.
In political terms, the South, and particularly the South-East (outside Greater London) and East Anglia, is largely centre-right, and supportive of the Conservative Party, while Northern England (particularly the towns and cities) is generally more supportive of the Labour Party.
An article in The Economist (15–21 September 2012) argued that the gap between the north and south in life expectancy, political inclinations and economics trends was growing to the extent that they were almost separate countries.[1]
Existence
The North–South divide is not an exact line, but one that can involve many stereotypes, presumptions and other impressions of the surrounding region relative to other regions. The existence of the North–South divide is fiercely contested. Some sources claim that not only does it exist, but that it is expanding. For example, a 'Cambridge Econometrics' report of March 2006 found that economic growth above the UK average was occurring only in the South and South East England, whilst North East England showed the slowest growth.[2][3] The same data has been interpreted otherwise to indicate only a very small difference.[4] Indeed, results are highly dependent on the categories chosen for evaluation. As a generalisation, the following tend to indicate that there is some sort of north-south divide:
- Health conditions, which are generally seen as being worse in the north,[5][6] though spending on health care is higher.[7]
- House prices, which are higher in the south, particularly the south-east.[8]
- Earnings, which are higher in the south and east.[9]
- Government expenditure, which is higher relative to tax revenues in the North,[10] but higher in key areas such as infrastructure investment in the South.[11]
- Political influence.[12]
However, when factors such as the cost of living[13] or urban poverty are included,[14][15] the divisions are sometimes less clear.
Furthermore, many middle class and affluent areas are located near Leeds and Manchester. A report into wealth by Barclays Bank also highlighted the anomaly that the second-wealthiest parliamentary constituency after Kensington and Chelsea is Sheffield Hallam. Yorkshire and Cheshire, geographically part of The North, include prosperous towns and suburbs such as Harrogate, Ilkley and Alwoodley in Yorkshire and Alderley Edge, Wilmslow and Chester in Cheshire. On the other hand, geographically southern areas such as the Isle of Thanet in Kent have struggled with the same industrial decline as parts of the north. Cornwall, many London boroughs such as Hackney and Haringey and southern towns like Luton are other anomalies to the North-South divide with poor health and education.
This has led some commentators to suggest that other divisions, such as class[16] or ethnicity might be more important.[17]
The Economist claims that one of the main causes of the divide was the migration of young professionals from the north to work in London, whereas it is much less common for young professionals from the south to move to a northern city.[1]
Identities and differences
Culture
There is also a perceived cultural divide between the north and the south. The It's Grim Up North BBC television series and subsequent book attempted to tease out some of these divisions.[18] Those in the north complained of having fewer cultural opportunities, the book also provided a view of southern life as faceless and bland.[18]
When the commercial broadcaster Granada Television began transmission in 1956, it was primarily based in Manchester. Granada's strapline before both networked and regional programming was originally "From The North, Granada Presents...". A large arrow pointing Upward (North) was part of this caption. Granada Television's 1960s updated arrow (a G with an upwards arrow) was prominent on local idents and production endcaps until Granada's identity was divided between the ITV Granada and Granada Productions (later ITV Studios) brands as part of the creation of ITV plc in 2004.
Counterbalancing the image of the rich South/poor North divide are television programmes like Cold Feet, which feature Yuppie-esque, rich or upper-class Northerners, a deviation from the stereotypical North. Meanwhile, Only Fools and Horses is based around working-class life in Peckham.
During regional television and radio broadcasts, mainly South-Eastern Standard English accents are heard and there are very few regional or typically 'Northern accents'. Northern accents are often regarded as humorous, celebrities like comedians Peter Kay and Johnny Vegas both have prominent Northern accents. However this is starting to change, with national stations such as BBC Radio 1Xtra employing northern DJs such as DJ Q, from Huddersfield with a distinctive Northern accent, taking into account the current trend of Black music emerging from the north, such as Bassline House.
Some statistics suggest that the consumption of fast food appears to be higher in 'The North', with the UK's fourteen 'fattest cities' to the north or west of the dividing lines detailed above.[19]
Politics
The journalist Kelvin MacKenzie has suggested that the south of England needs a political party to campaign for its interests, including "home rule" for the region.[20] City AM editor Allister Heath had made a similar suggestion in April 2012, and opined that increased powers for the London region might be obtained when the constitutional status of Scotland is debated.[21]
Language and dialect
Although younger generations may be less likely to use speech that is specific to a particular town, there is still a clear difference between north and south; young Northerners are more resistant to sounding as if they are Southern than sounding as if they are from a different Northern town.[22]
The division is sometimes used for comedy, but has its serious side as well. The London media are sometimes claimed to look down upon those with northern English accents. For example, Ken Livingstone (a Londoner) suggested that the press's unsympathetic treatment of John Prescott was partly because he is one to "speak like ordinary people".[23]
Some linguistic research has concluded that many people in the North of England have a dislike of the /ɑː/ vowel in BATH words. AF Gupta wrote, "Many of the northerners were noticeably hostile to /ɡrɑːs/, describing it as 'comical', 'snobbish', 'pompous' or even 'for morons'."[24] On the subject, KM Petyt wrote that several respondents "positively said that they did not prefer the long-vowel form or that they really detested it or even that it was incorrect"[25] Mark Newbrook has assigned this phenomenon the name "conscious rejection", and has cited the BATH vowel as "the main instance of conscious rejection of RP" in his research in the West Wirral.[26]
Religion
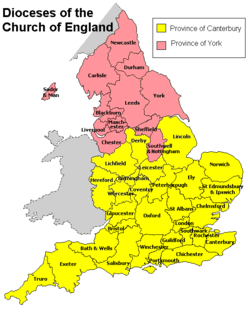
Within the Church of England, a North–South divide appeared in England with the Province of York and the Province of Canterbury. This drew rough lines for a North–South divide. The North was also a stronghold of religious Nonconformism during its industrial heyday.
Explanation
Industrial decline is most usually given as an explanation for the North-South divide.[27] During the Industrial Revolution, many northern cities underwent a process of intense industrialisation, as raw materials such as coal and iron ore could be found in these areas.[28] This led to comparatively high wealth; Shaw, Greater Manchester reportedly had the highest concentration of millionaires in the country at the time.[29] It also led to over reliance on a few key industries and, as heavy industry began to leave the UK for developing countries under the 'New international division of Labour',[30] these areas declined rapidly. Events like the UK miners' strike (1984–85) polarised public opinion and led to an increase in the divide.
The Midlands
Many Midlands towns and cities appear, at least historically, to have more in common with their northern counterparts than with those in the south. This is mainly because they have a history of concentrated industrialisation and post-industrial economic depression (especially in the West Midlands metropolitan county and Stoke-on-Trent), plus the dry ironic humour which is borne out of this, rather than the nonindustrialised 'service centre' and 'county' towns and cities of southern England, which are perceived to be singularly dominated by London (where the purpose of those towns was essentially to service the capital). The film Once Upon a Time in the Midlands (2004), starring Ricky Tomlinson, was made very-much in the character of the straight-talking and dry humoured northern comedies.
However, during the 1930s while the North (along with Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland) suffered badly from the Great Depression,[31] the Midlands shared the fortunes of the South as these two areas of the country both prospered, with a booming Midlands motor car industry matching the Southern growth in manufacture of electrical goods.[32] This not only placed the Midlands socially on the same side as the South during a crucial defining period in Northern working class cultural identity, but also has had still-visible matching effects on the landscape of both Midlands and South - a property boom in the middle years of the decade[31] resulted in the proliferation of the 1930s-style semi-detached houses in Midland areas such as Birmingham's south suburbs to match a similar manifestation in areas of the South such as West London.[31]
As in the North, many Midlands towns and cities have experienced redevelopment, including a second Birmingham Bullring complex which replaced a postwar development, including a branch of the upmarket Selfridges department store, and The Mailbox redevelopment which houses a branch of Harvey Nichols. Solihull metropolitan borough is one of the most affluent in the country.[33]
On the social side of the divide, most people from the Midlands usually refer to themselves as being a "Midlander" rather than a "Northerner" or a "Southerner" and very rarely partake on either side of the social rivalry or stereotyping. One exception to this is a certain resentment held by the people of Birmingham towards London due to what they see as excessive centralisation in the capital of England's cultural and political activity, which they commonly attribute to snobbery against provincial areas in general on the part of London authorities.
Closing the gap
Many Northern post-industrial cities and towns are now experiencing renaissance. Examples include Manchester, Kingston upon Hull,[34] Leeds, Liverpool, Newcastle upon Tyne, Sheffield and the Midlands cities of Birmingham, Derby and Nottingham. The Bank of England retain their only offices outside London in Leeds, which also hosts BT and Royal Mail's secondary communication centres for the UK. A strong gaming industry in Leeds has produced global titles such as Grand Theft Auto and L.A. Noire. Some of the world's service industries and banks are also relocating to northern cities, examples include the opening of Bank of New York, Google and RBS offices in Manchester. One can also note the present decentralisation of many BBC departments from London to Salford Quays in Greater Manchester.
Typically Southern upmarket department stores and shops have located new stores in the north; these include Harvey Nichols (opening first in Leeds, then Manchester, followed by Birmingham) and Selfridges in the Trafford Centre in 1998, Manchester in 2002 and Birmingham in 2003. Exclusive shopping destinations such as Leeds' Victoria Quarter have led to the city being dubbed 'The Knightsbridge of the North'.[35] Bradford based supermarket Morrisons, which mainly operated in the North of England acquired 479 stores when it bought Safeway in 2004, the majority of these new supermarkets were in the South of England.[36] Other Northern founded Supermarkets such as Asda, Co-op Food and Marks & Spencer are also popular in the South of England.
Writer and journalist Stuart Maconie argues that "there is no south of England... There's a bottom half of England... but there isn't a south in the same way that there's a north".[37] He goes on to state that "there's no conception of the south comparable to the north. Good or bad, 'the north' means something to all English people wherever they hail from... [to southerns] it means desolation, arctic temperatures, mushy peas, a cultural wasteland with limited shopping opportunities and populated by aggressive trolls. To northerners it means home, truth, beauty, valour, romance, warm and characterful people, real beer and decent chip shops. And in this we are undoubtedly biased, of course". This suggests that all people in England have biased views regarding the North-South divide.[38] Maconie says regarding on where the North starts that "Crewe is surely the gateway to the North", suggesting that Crewe is the most southern part of the North of England.[39]
See also
- North–South divide
- North–South divide in the United Kingdom
- North Britain and South Britain
- North–South divide (Wales)
- Lloegyr
- River Trent
- Stereotypes
References
- 1 2 The north of England: the great divide, The Economist, 15–21 September 2012, volume 404, number 8802
- ↑ "The North-South Divide Widened in the Last Economic Cycle" (PDF). Cambridge Econometrics. 27 March 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-07-25. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ "Is there a north-south divide in social class inequalities in health in Great Britain? Cross sectional study using data from the 2001 census". Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Bland, J Martin (3 July 2004). "North-south divide in social inequalities in Great Britain". British Medical Journal. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Carvel, John (11 November 2005). "Wide life expectancy gap between rich and poor". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Meikle, James (6 July 2005). "Cancer atlas reveals north-south divide". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ "Public sector finances: views from the inside". June 2010. Archived from the original on 22 June 2011.
- ↑ "UK House Prices". BBC News. 8 May 2006. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Carvel, John (10 November 2005). "North-south, east-west wealth divides in survey". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Doughty, Steve (12 October 2007). "The REAL north-south divide How South East bankrolling Britain". London: The Daily Mail.
- ↑ "Press Release: nearly half of UK transport investment spent in London & South East". London: Press Release, Yes to High Speed Rail. 12 July 2011.
- ↑ Elliott, Larry (5 July 2004). "The United Kingdom of London". The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Wainwright, Martin (8 December 2005). "North just as prosperous as the south, survey finds". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Seager, Ashley (28 October 2005). "London revealed as Britain's worst employment blackspot". The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Asthana, Anushka (27 June 2004). "Rise of the new north has its price". London: The Observer. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Ahmed, Kamal (10 November 2002). "Britain's class divide starts even before nursery school". London: The Observer. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ "Making a difference: Tackling poverty - a progress report" (PDF). Department for Work and Pensions. March 2006. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- 1 2 Holder, Judith (2005-09-01). It's (Not) Grim Up North. London: BBC Books. ISBN 0-563-52281-X.
- ↑ "Bradford named UK's fattest city". London: The Guardian. 1 February 2006. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Kelvin MacKenzie (2 December 2012). "Kelvin MacKenzie: overtaxed South needs its own party". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ Allister Heath (5 April 2012). "Boris is right to want to transform London into a city-state". City AM. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ By 'eck! Bratford-speak is dyin' out
- ↑ White, Michael (2006-05-30). "Prescott's survival hopes recede as MPs speak out". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ↑ Baths and Becks, AF Gupta in English Today, page 25, Cambridge University Press, 2005
- ↑ KM Petyt, Dialect and Accent in Industrial West Yorkshire, page 286, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 1985
- ↑ West Wirral: norms, self-reports and usage, page 101, Urban Voices, edited by Paul Foulkes & Gerard Docherty, Arnold, London, 1999
- ↑ Lupton, Ruth; Power, Anne (July 2004). "The Growth and Decline of Cities and Regions" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Population growth in Victorian Manchester: "Work, Health, Housing and Working People in the City of Manchester". Manchester UK. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ "Shaw and Royton area plan" (PDF). Oldham Metropolitan Borough. January 2004. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- ↑ von Mises, Ludwig (1938). "The Disintegration of the International Division of Labour". Ludwig von Mises Institute. Retrieved 2006-07-16.
- 1 2 3 What's Left? by Nick Cohen, Harper Perrenial 2007, pp220-221
- ↑ Constantine, Stephen (1983) Social Conditions in Britain 1918-1939 ISBN 0-416-36010-6
- ↑ National Statistics Neighbourhood Profile Summary showing indicators of prosperity
- ↑ "Welcome to Hull Citybuild". Hull Citybuild. Hull Citybuild. 2007. Archived from the original on 2007-06-07. Retrieved 2007-10-26.
- ↑ "City is 'Knightsbridge of North'". BBC News Online. BBC. 24 May 2005. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- ↑ "Morrisons seals Safeway takeover". BBC NEWS. 8 March 2004. Retrieved 25 January 2012.
- ↑ Maconie (2007), p. 1.
- ↑ Maconie (2007), p. 2.
- ↑ Maconie (2007), p. 35.
Bibliography
- Jewell, Helen M. (1994). The North-South Divide: the origins of Northern consciousness In England. Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 0-7190-3803-0.
- Maconie, Stuart (2007). Pies and Prejudice: In Search of the North. Reading: Ebury Press/ Ebury Publishing. ISBN 978-0-09-191023-5.