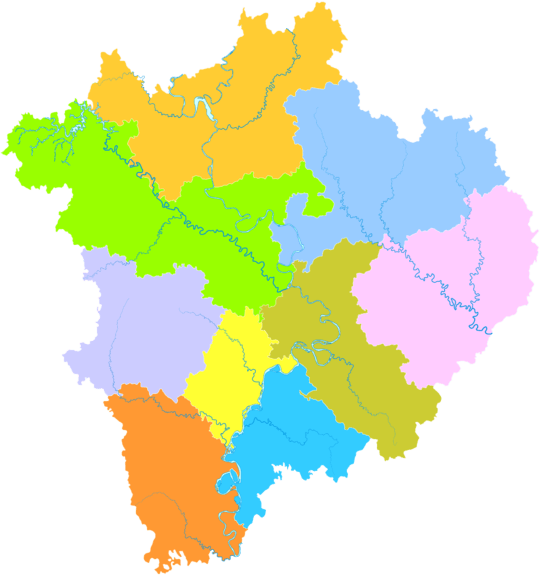
Nanchong
| Nanchong 南充市 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
.png) | |
| Nickname(s): The fruit City | |
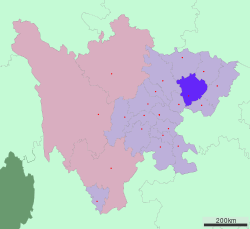 Location of Nanchong City jurisdiction in Sichuan | |
| Coordinates: 30°48′00″N 106°5′00″E / 30.80000°N 106.08333°ECoordinates: 30°48′00″N 106°5′00″E / 30.80000°N 106.08333°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Sichuan |
| Officiated | 1993 |
| Government | |
| • Party Secretary | Liu Hongjian |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 12,479.96 km2 (4,818.54 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,527.8 km2 (976.0 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,527.8 km2 (976.0 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 340 m (1,120 ft) |
| Population (2010 census)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 6,278,614 |
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,858,875 |
| • Metro | 1,858,875 |
| • Metro density | 740/km2 (1,900/sq mi) |
| [2] | |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | 637000 |
| Area code(s) | 0817 |
| Licence plate prefixes | 川R |
| Website |
nanchong |
Nanchong (Chinese: 南充; pinyin: Nánchōng; Wade–Giles: Nan-ch'ung; Sichuanese: lan2cong1; ) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of 12,479.96 square kilometres (4,818.54 sq mi),[3] and at the 2010 census was home to 6,278,614 people whom 1,858,875 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 3 urban districts. It is the second most populated city of Sichuan Province, only after Chengdu. The administrative center is Shunqing District.
History
Nanchong was in the territory of the state of Ba before it was conquered by the Qin dynasty in 314 BC. The Qin set up a government at Langzhong City. Anhan City was established in Shunqinq district at the beginning of the Han Dynasty.
In 202 BC, Emperor Gaozu of Han instituted the Anhan (simplified Chinese: 安汉; traditional Chinese: 安漢) County in this place. Anhan literally means "to establish or stabilize Han". In 8 AD, the name was changed to Anxin (安新) when Wang Mang seized the throne of the Han Dynasty, but it reverted to Anhan in 25 AD. It was again changed to Guozhou (果州, "fruit city") in 621 AD (Tang dynasty), and then to Nanchong in 742 AD. The nickname of Nanchong is Guocheng (果城), derived from Guozhou.
Subdivisions
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2004 est.) | Area (km²) | Density (/km²) |
| Shunqing District | 顺庆区 | Shùnqìng Qū | 620,000 | 545 | 1,138 |
| Gaoping District | 高坪区 | Gāopíng Qū | 570,000 | 812 | 702 |
| Jialing District | 嘉陵区 | Jiālíng Qū | 680,000 | 1,170 | 581 |
| Langzhong City | 阆中市 | Lángzhōng Shì | 860,000 | 1,877 | 458 |
| Nanbu County | 南部县 | Nánbù Xiàn | 1,240,000 | 2,305 | 538 |
| Yingshan County | 营山县 | Yíngshān Xiàn | 900,000 | 1,633 | 551 |
| Peng'an County | 蓬安县 | Péng'ān Xiàn | 680,000 | 1,334 | 510 |
| Yilong County | 仪陇县 | Yílǒng Xiàn | 1,060,000 | 1,695 | 625 |
| Xichong County | 西充县 | Xīchōng Xiàn | 640,000 | 1,108 | 578 |
Geography
Nanchong is located in the north-east of Sichuan Province. To the east of Nanchong is Dazhou, to the west are Mianyang and Suining and to the north is Guangyuan.
The vast majority of this area is hilly. The woodland coverage is 25%.
The Jialing River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, crosses the prefecture from north to south, and there are another thirty rivers in the prefecture with a drainage basin of more than 30 square kilometres (12 sq mi).
Climate
As with the rest of the Sichuan Basin, Nanchong has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa) with high humidity year-round; winters are short and mild while summers long, hot, and humid. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 6.4 °C (43.5 °F) in January to 27.5 °C (81.5 °F) in August; the annual mean is 17.33 °C (63.2 °F). Frost is uncommon and the frost-free period lasts 290−320 days.[4] Over 70% of the 987 mm (38.9 in) of annual precipitation occurs from May to September. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from around 9% in December to 47% in August, the city receives only 1,135 hours of bright sunshine annually. Spring (March–April) tends to be sunnier and warmer in the day than autumn (October–November).
| Climate data for Nanchong (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.4 (59.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
31.6 (88.9) |
35.2 (95.4) |
37.2 (99) |
36.8 (98.2) |
38.9 (102) |
41.2 (106.2) |
40.1 (104.2) |
32.0 (89.6) |
27.6 (81.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
41.2 (106.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.2 (48.6) |
11.7 (53.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
22.3 (72.1) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.9 (84) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.5 (79.7) |
21.1 (70) |
16.0 (60.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.4 (43.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
12.5 (54.5) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
27.2 (81) |
27.5 (81.5) |
22.6 (72.7) |
17.7 (63.9) |
12.9 (55.2) |
8.0 (46.4) |
17.3 (63.15) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.3 (39.7) |
6.1 (43) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.5 (70.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.9 (67.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.6 (51.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
14.5 (58.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −2.8 (27) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
1.2 (34.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
9.5 (49.1) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.9 (64.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
3.5 (38.3) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 16.2 (0.638) |
16.9 (0.665) |
30.3 (1.193) |
75.1 (2.957) |
118.4 (4.661) |
147.2 (5.795) |
188.3 (7.413) |
125.9 (4.957) |
135.5 (5.335) |
78.1 (3.075) |
37.3 (1.469) |
18.0 (0.709) |
987.2 (38.867) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 8.9 | 8.6 | 10.7 | 12.5 | 13.5 | 13.6 | 12.8 | 10.1 | 14.6 | 14.0 | 10.6 | 8.3 | 138.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85 | 81 | 77 | 76 | 75 | 79 | 80 | 76 | 82 | 84 | 84 | 86 | 80.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 31.7 | 43.6 | 81.7 | 118.4 | 130.7 | 122.6 | 168.6 | 193.8 | 96.5 | 67.5 | 53.3 | 26.9 | 1,135.3 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 10 | 14 | 22 | 31 | 31 | 29 | 39 | 47 | 26 | 19 | 17 | 9 | 26 |
| Source #1: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Demographics
The Han people are the largest ethnic group in this area, contributing to 99.88% of its total population, another 48 ethnic groups can be found in the city. Langzhong has a large Hui Muslim community.
As in other cities of China, the population of Nanchong can be divided into two parts, upper urban population and lower rural population; the registered urban population is about 1.2 million.
Shunqing District, located downtown, is the most dense area in Nanchong. At the center of Shunqing District, and the proverbial heart of the city, is Five Star Garden (simplified Chinese: 五星花园); a large roundabout with five exits leading to various other sections of the city.
Economy
Agriculture
Agriculture is the pillar of Nanchong’s economy, with 80% of Nanchong’s population located in rural areas and committed to traditional agricultural activities. Nanchong’s manufacturing industry also relies on raw materials which are provided by agriculture. Nanchong’s main agricultural product is food. A large quantity of rice, orange, silk worms, and pork are produced to support related manufacturers.[5]
Manufacturing
Nanchong’s main manufacturing outputs are petroleum products, automobiles and parts, mechanical equipment, textiles, and building materials. [6]
Natural resources
There is a large quantity of rock oil and natural gas found in Nanchong, and it has the largest slate mine in the west of China. The dams on Jialing River and its branches have a large potential to increase electric power generation. But the largest resource of Nanchong is human : Nanchong is one of the main providers of Chinese cheap migrant workers.[7]
Transport
Transportation in Nanchong is quite convenient compared with other cities in Sichuan province because of its extensive express railway network, shipping, and air service.
Nanchong is a transport hub of the northeast Sichuan Province, it is crossed by the strategic China National Highway 318, built by the Chinese government in the 1930s, and China National Highway 212 and several newly built expressways, Cheng-Nan, and Nan-Guang expressway which link the city to Chengdu, and another prefecture-level city Guang'an. The expressway to Chongqing is under construction.
The Dazhou–Chengdu Railway through Nanchong links Chengdu and Dazhou. The Chongqing–Lanzhou Railway, when in 2015, will link Lanzhou (Gansu) and Chongqing, and turn Nanchong into a railway hub in northeast Sichuan province. The Nanchong railway station provides passenger and cargo services to several regional and national economic centres such as Shanghai, Beijing, Chongqing, Wuhan, Chengdu and Shenzhen.
Old Nanchong airport was built in the 1950s and closed in 2003. The new Nanchong Airport which has capacity to land bigger planes, provides regular air services to Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Kunming, Xi'an and Sanya.
Nanchong is suggested as a tradition shipping hub in ancient times, ships from Gansu could reach Chongqing along the Jialing river, but the river is not suitable for modern shipping.
Higher education
There are five academic institutions in Nanchong which provide higher education.
- Southwest Petroleum University (www.swpu.edu.cn)
- China West Normal University
- North Sichuan Medical College (www.nsmc.edu.cn)
- Nanchong Professional Technic College (www.nczy.com)
- Hope College of Southwest Jiaotong University(www.swjtuhc.cn)
Notable persons
- Chen Shou, historian in the Western Jin Dynasty,the author of San guo zhi (the record of Three Kingdoms)
- Luo Ruiqing, General of the Chinese Army, former minister of Public Security of People's Republic of China
- Zhang Lan, former Vice-President of People's Republic of China
- Zhang Side, a soldier of the People's Liberation Army of the People's Republic of China. He was posthumously honored by Chairman Mao and became an icon of self-sacrifice and noble character.
- Zhu De, one of the leaders of the Chinese Communist Party, Chinese communists government and People's Liberation Army
References
- ↑ (Chinese) Profile of Nanchong, official website of Nanchong Civil Affairs Bureau, visited on May 17, 2008.
- ↑ http://www.citypopulation.de/php/china-sichuan-admin.php
- ↑ (Chinese) Profile of Nanchong.
- ↑ Weather China
- ↑ http://www.ncagri.gov.cn/bmzc_s.asp
- ↑ http://www.nanchong.gov.cn/article.php?id=769
- ↑ http://www.nanchong.gov.cn