N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine
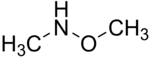 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Methoxymethanamine | |
| Other names
Methoxymethylamine; Methylmethoxyamine; HNMeOMe | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1117-97-1 6638-79-5 (HCl) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 13596 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.960 |
| PubChem | 14232 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 61.08 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 112 to 115 °C (234 to 239 °F; 385 to 388 K) (HCl) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine is used in amide coupling reactions to form Weinreb amides for use in the Weinreb ketone synthesis.[1]
It was identified as a microbial degradation product of the herbicide linuron formed in the presence of extracts of Bacillus sphaericus ATCC 12123 by characterization of its dinitrophenyl derivative.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ G. Engelhardt; P. R. Wallnofer; R. Plapp (1972). "Identification of N, O-Dimethylhydroxylamine as a Microbial Degradation Product of the Herbicide, Linuron" (PDF). Applied Microbiology. 23 (3): 664–666. PMC 380407
 . PMID 5021977.
. PMID 5021977.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.